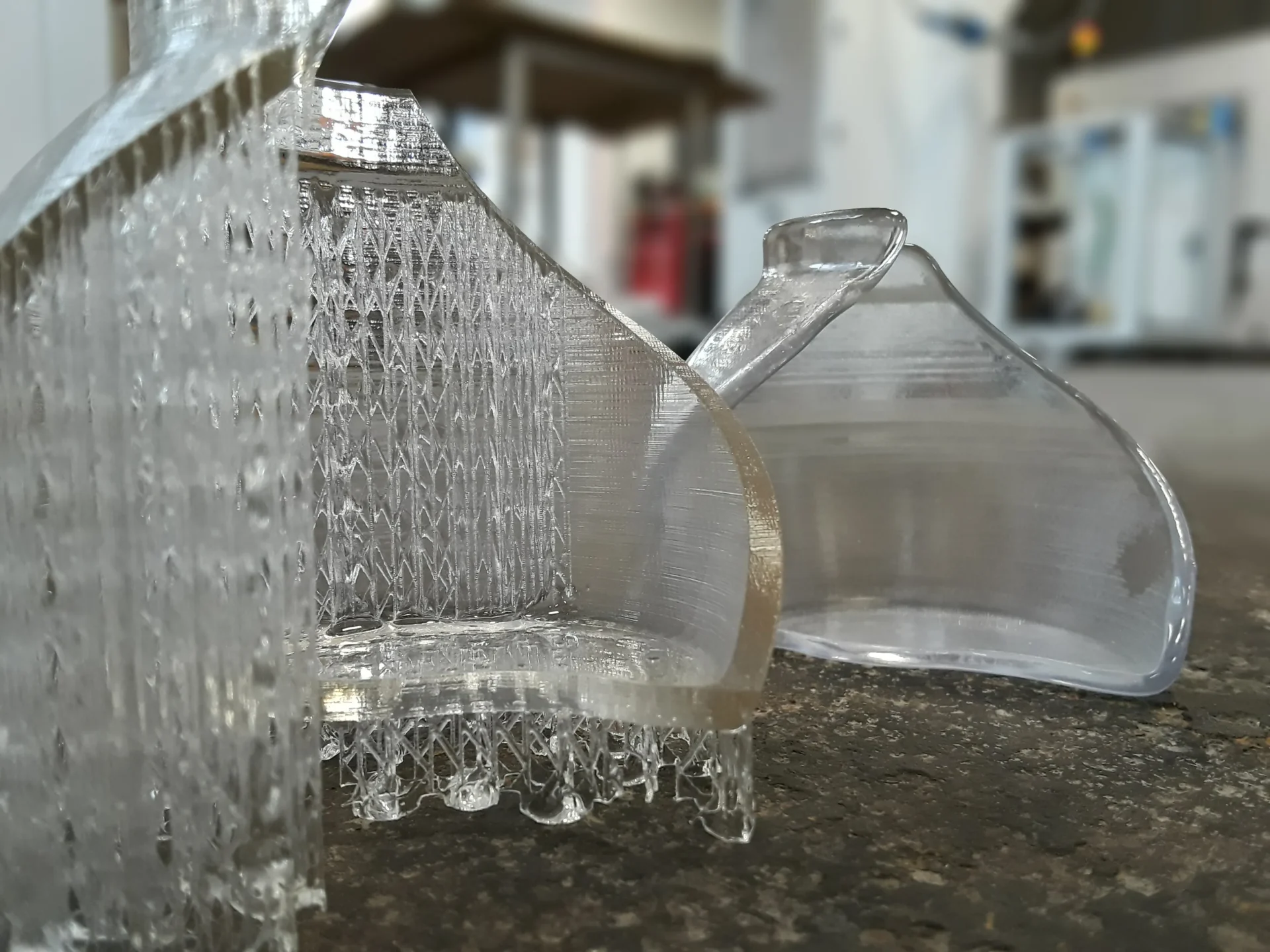
In the realm of 3D printing, Stereolithography (SLA) is a highly precise and versatile technology. Selecting the appropriate an SLA 3d printing materials is crucial as it directly affects the quality, durability, and functionality of printed objects.
Understanding SLA 3D Printing
What is SLA 3D Printing?
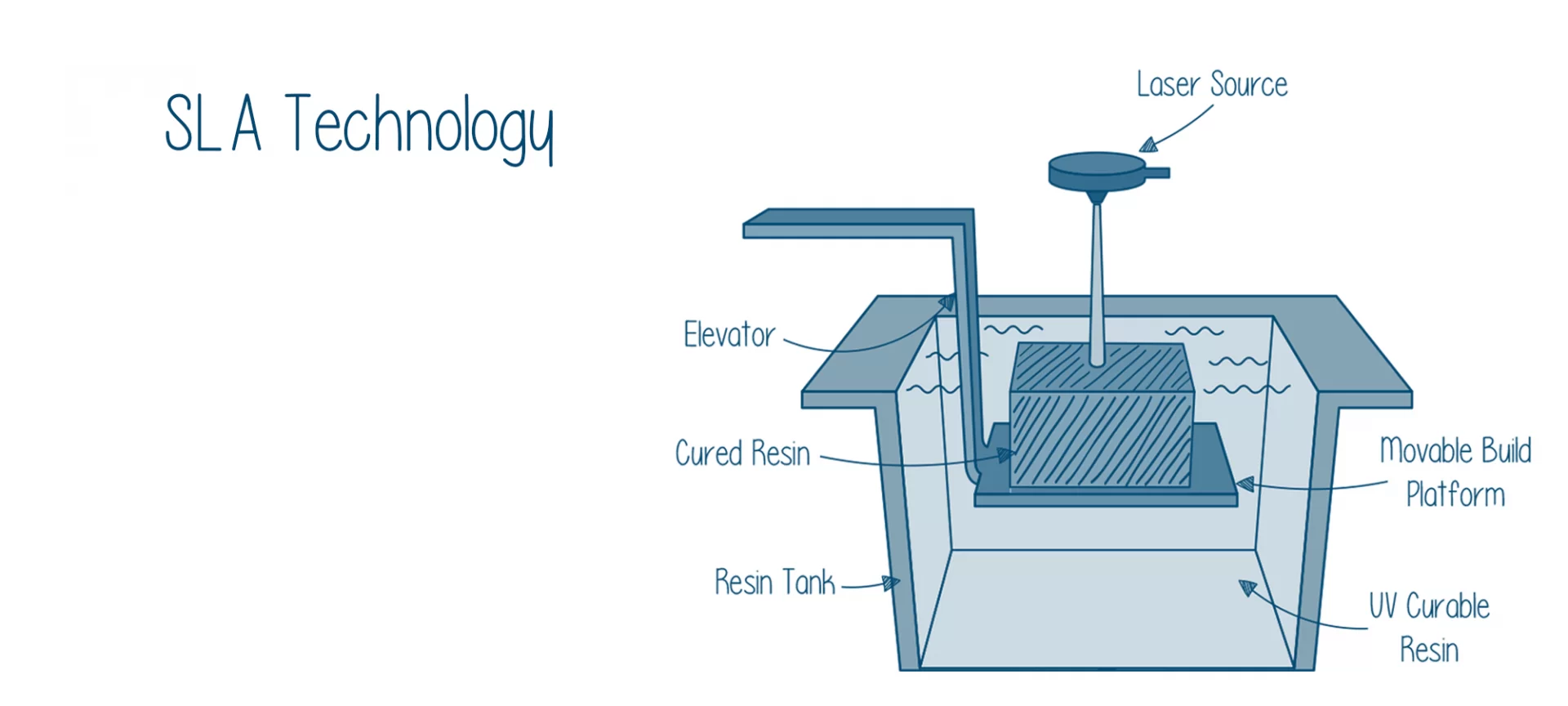
SLA 3D printing relies on photopolymer resins that solidify when exposed to laser or ultraviolet (UV) light. The process involves creating a 3D model in CAD software or downloading one, then the SLA printer selectively cures the resin layer by layer. After printing, the model typically requires washing in isopropyl alcohol (IPA) to remove excess resin and post-curing under UV light. SLA printing offers high resolution, with layer heights as thin as 25 microns, enabling detailed prints with smooth surfaces.
Advantages of SLA Printing
SLA printing provides several benefits. It produces high-resolution prints with fine details and smooth finishes, making it suitable for applications demanding precision. The printed objects usually have better surface quality compared to other 3D printing methods like Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) or Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). SLA printers support a variety of resins, offering options from flexible to high-strength materials. It also excels in printing complex geometries.
Disadvantages of SLA Printing
However, SLA printing has limitations. The material variety is relatively limited compared to FDM, and the resins are often more expensive. Post-processing is necessary, including curing and washing, which can be time-consuming. The equipment and materials for SLA printing are costly, although the quality of the final prints may justify the investment. Additionally, SLA resins are usually toxic and require careful handling with proper ventilation, gloves, and protective gear.

| Pros | Cons |
| High-resolution, fine details | Expensive printers and materials |
| Smooth surface finish | Post-processing (washing, curing) required |
| Ideal for intricate designs | Limited material selection compared to FDM |
| Excellent for prototyping | Resin handling and safety concerns |
SLA vs. Other 3D Printing Technologies
It is important to compare SLA with other popular 3D printing methods. SLA offers very high print quality with fine details, while FDM has moderate quality with visible layer lines and SLS is good for functional parts. SLA uses resins, FDM uses filaments, and SLS uses powder-based materials. SLA prints have a smooth and shiny surface finish, FDM is rougher and may require sanding, and SLS is also rougher and often needs post-processing. SLA has a moderate speed depending on resolution, FDM is fast for basic prints, and SLS is slow. SLA has a higher upfront cost for equipment, FDM is more affordable, and SLS is expensive for both equipment and materials.
| Aspect | SLA | FDM | SLS |
| Print Quality | Very high, fine details | Moderate, visible layer lines | High, good for functional parts |
| Materials | Resins | Filaments | Powder-based materials |
| Surface Finish | Smooth and shiny | Rougher, often requiring sanding | Rougher, can require post-processing |
| Speed | Moderate, depends on resolution | Fast, especially for basic prints | Slow, requires more processing time |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost for equipment | Lower cost, more affordable materials | Expensive equipment and materials |
Types of Materials Used in SLA 3D Printing
Selecting the right material for SLA 3D printing is essential for achieving optimal results. SLA printers use liquid photopolymer resins that cure when exposed to UV light. These resins can be categorized into standard resins, engineering resins, and specialty resins.
Overview of SLA Resin Types
Standard resins are commonly used for general-purpose printing and are affordable. They are suitable for prototypes and models that do not require high durability. Engineering resins are designed for functional applications demanding strength, heat resistance, and durability, and are usually more expensive. Specialty resins are for specific applications such as casting, dental, or flexible prints, offering unique properties but are costly and less commonly used.
Categories of SLA Materials
Standard Resins

Standard resins are the preferred choice for general-purpose prints. They provide good accuracy and surface finish but lack the strength and heat resistance of engineering resins. Monochrome resin is often used for prototyping and visual models, while transparent resin is ideal for creating clear or translucent parts.
Advantages: Affordable, easy to use, and offer good surface finish.
Disadvantages: Limited durability and tend to be brittle.
Engineering Resins

Engineering resins are engineered for functional applications. Tough resin is suitable for parts requiring strength and durability, high-temperature resin can withstand high heat, and durable resin is resistant to wear.
Advantages: Strong, heat-resistant, and some have flexibility.
Disadvantages: Higher cost and require more complex post-processing.
Specialty Resins

Specialty resins are tailored for specific applications. Castable resin is used in jewelry making and dental casting, flexible resin mimics rubber properties, biocompatible resin is suitable for medical and dental applications, and ceramic resin is used for artistic and functional ceramics.
Advantages: Unique properties, precision, and flexibility (for some types).
Disadvantages: High cost, limited availability, and niche applications.
Choosing the Right SLA Material for Your Project
When choosing an SLA resin, consider the project’s specific needs. For functional parts under stress or high temperatures, engineering resins are recommended. For parts requiring flexibility, flexible resin is the best option. If on a budget and producing many models, standard resins are cost-effective. Also, consider post-processing requirements.
| Resin Type | Best For | Key Features | Example Uses |
| Standard Resin | Prototypes, models, visual designs | Affordable, smooth surface finish | Prototyping, concept models |
| Tough Resin | Functional parts, impact-resistant prototypes | Strong, durable, impact-resistant | Functional prototypes, mechanical parts |
| High-Temperature Resin | Heat-resistant parts | Can withstand high temperatures | Automotive parts, aerospace components |
| Flexible Resin | Parts that require flexibility | Rubber-like texture, bendable | Soft-touch parts, gaskets, elastomeric parts |
| Castable Resin | Jewelry casting, dental molds | Burns away cleanly, high detail | Jewelry, dental models |
| Biocompatible Resin | Medical, dental applications | FDA-approved, safe for the body | Dental implants, surgical guides |
Factors to Consider When Choosing SLA Printing Materials
Purpose of the Printed Object
The intended use of the printed object determines the material choice. For prototypes for design testing or presentation, standard resins are sufficient. For functional parts under stress, engineering resins are ideal. For artistic or decorative models, standard or clear resins are suitable depending on the visual requirements.
Mechanical Properties
Consider the mechanical properties such as tensile strength, impact resistance, flexibility, and wear resistance when printing parts that will experience mechanical stress. Choose a resin that can meet these requirements.
Print Quality
Think about the print quality needed, including resolution, surface finish, and transparency. Ensure the resin can achieve the desired level of detail and finish.
Environmental Considerations
If the printed part will be exposed to heat, chemicals, or UV light, choose a resin that can withstand these conditions. Consider heat resistance, UV stability, and chemical resistance.
Cost and Availability
Balance the budget with the performance of the material. Standard resins are usually more affordable, while specialty resins can be expensive. Also, check the availability of the resin.
| Factor | What to Consider |
| Purpose of Print | Is it a prototype, functional part, or decorative model? |
| Mechanical Properties | Does it need to be strong, flexible, impact-resistant, or heat-resistant? |
| Print Quality | How fine and detailed does the print need to be? What kind of surface finish is needed? |
| Environmental Considerations | Will the print be exposed to UV light, heat, or chemicals? |
| Cost and Availability | Does the cost align with your budget? Is the resin easily available? |
5. Post-Processing and Material-Specific Considerations
Cleaning and Curing
After printing, cleaning and curing are essential steps. Cleaning removes excess resin, which can be done by rinsing with IPA or using an ultrasonic cleaner, followed by drying. Curing solidifies the resin and enhances its properties, usually done under UV light. Different resins may require different curing times.
Safety Considerations
Handle SLA resins safely by wearing gloves, working in a well-ventilated area, and using protective eyewear. Dispose of waste resin and used IPA properly according to local regulations.
Common Issues and Solutions
- Resin Failure or Cracking: Ensure proper curing time and UV exposure.
- Adhesion Issues: Check platform adhesion and use brim or raft if necessary.
- Warping or Bending: Use supports and ensure even UV exposure.
- Surface Imperfections: Sand or polish the surface.
Material-Specific Post-Processing Tips
| Resin Type | Post-Processing Considerations |
| Standard Resins | Minimal post-processing; focus on cleaning and curing. |
| Tough Resin | May require longer curing times to achieve full strength. |
| High-Temperature Resin | Needs longer post-curing to handle heat resistance properly. |
| Flexible Resin | Ensure proper drying to avoid warping during curing. |
| Castable Resin | After curing, burn out cleanly for casting. |
| Biocompatible Resin | Follow strict guidelines for safe handling and sterilization. |
| Ceramic Resin | Requires kiln firing after curing to achieve the final ceramic finish. |
Comparing SLA Resins with Other 3D Printing Materials
SLA vs. FDM Materials
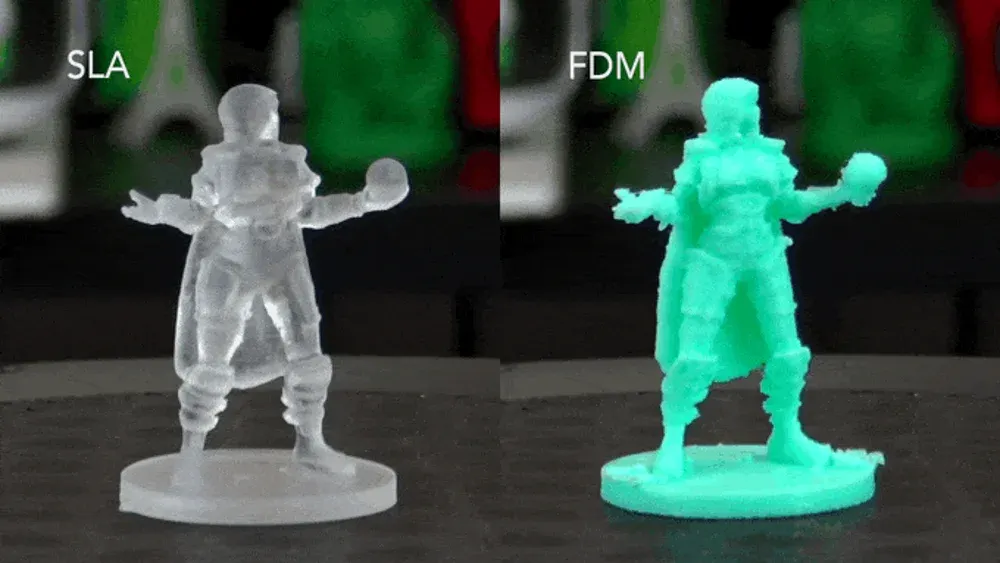

SLA uses liquid photopolymer resins, while FDM uses thermoplastic filaments. SLA offers higher resolution and a wider range of specialized materials, but is more expensive and requires more post-processing. FDM is more affordable and easier to use, suitable for larger objects and basic prototypes.
| Aspect | SLA | FDM |
| Material Types | Resins (standard, engineering, specialty) | Thermoplastics (PLA, ABS, Nylon, TPU) |
| Resolution | Very high (25 microns or less) | Moderate (typically 100–300 microns) |
| Print Speed | Slower due to curing process | Faster, especially for larger prints |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, glossy finish | Rougher, more noticeable layer lines |
| Post-Processing | Requires curing and washing | Minimal post-processing |
| Material Cost | Expensive per volume | Generally lower cost |
SLA vs. SLS Materials
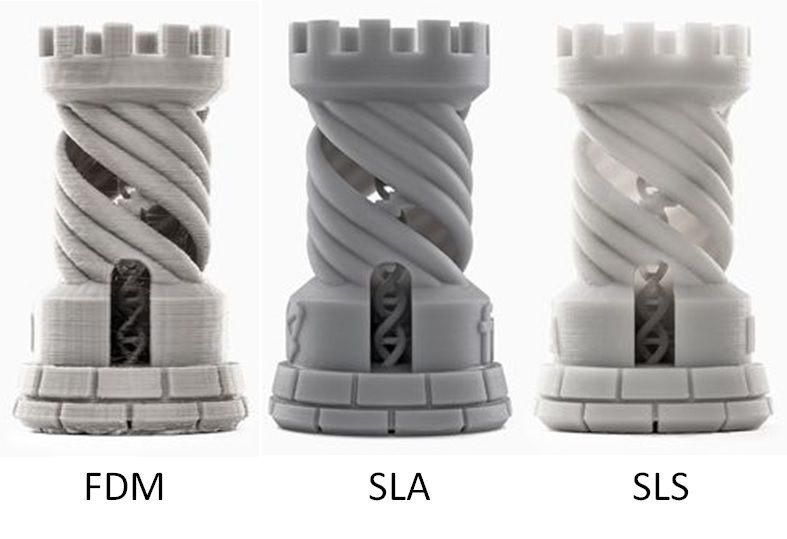

SLS uses powder-based materials and can print stronger and more functional parts without support structures. SLA has higher print quality for detailed models and a wider selection of specialized resins, but requires post-curing and washing.
| Aspect | SLA | SLS |
| Material Types | Resins (standard, engineering, specialty) | Powders (Nylon, metal, ceramics, etc.) |
| Resolution | Very high (25 microns or less) | High (typically 100 microns) |
| Strength | Moderate to high (depending on resin) | Very high (especially for nylon and metals) |
| Support Structures | Requires supports for overhangs | No supports required (powder bed supports part) |
| Post-Processing | Curing, washing, sanding | Powder removal, cleaning, post-curing |
| Cost | Expensive for specialized resins | High equipment and material costs |
SLA vs. DLP Materials
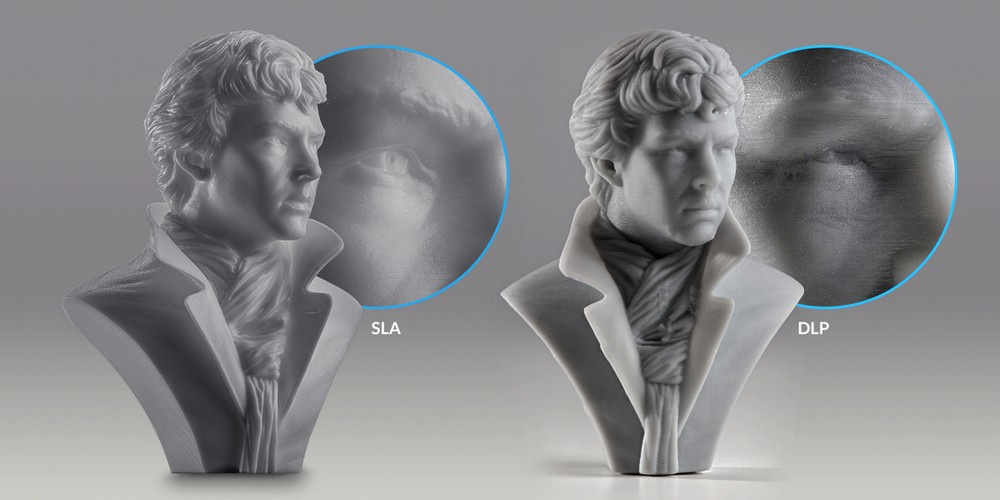

DLP uses a digital projector to cure the resin and can print faster than SLA for large-scale prints. SLA offers higher precision for fine details. The material options are similar for both methods.
| Aspect | SLA | DLP |
| Printing Speed | Slower due to laser curing | Faster (cures entire layer at once) |
| Resolution | Higher precision for fine details | Good resolution but not as high as SLA |
| Material Types | Liquid resins (wide range of types) | Liquid resins (similar to SLA) |
| Surface Finish | Very smooth | Smooth but can be less refined than SLA |
Where to Buy SLA Printing Materials
Trusted Suppliers and Manufacturers
- Formlabs: Offers a wide range of resins for different applications and is known for high-quality products and good customer support.
- Anycubic: Provides affordable resins with good performance, including water-washable resins.
- Elegoo: Offers budget-friendly resins with good quality, such as gray and clear resins.
- Photocentric: Specializes in high-performance and specialized resins like biocompatible and high-temperature resins.
- Siraya Tech: Offers premium performance resins, especially water-washable and flexible resins.
Key Brands in SLA Resins
| Brand | Specialty | Popular Resins |
| Formlabs | High-quality resins, professional-grade | Standard Resin, Tough Resin, Dental Resin, Castable Resin |
| ZONGHENG3D | High-quality resins, Industrial-grade, low cost selection | Standard Resin, Tough Resin, Dental Resin, Clear Resin |
| Anycubic | Affordable, suitable for hobbyists and entry-level users | Standard Resin, ABS-Like Resin, Water-Washable Resin |
| Elegoo | Budget-friendly, popular with hobbyists | Standard Resin, Gray Resin, ABS-Like Resin |
| Photocentric | Specializes in high-performance and specialized resins | Biocompatible Resin, High-Temp Resin, Castable Resin |
| Siraya Tech | Premium resins with focus on ease of use and performance | Water-Washable Resin, Flex Resin, Tough Resin |
Where to Buy SLA Resins Online
- Original Website: The most convenient and direct method is to purchase directly from the brand’s official website, especially when buying in large quantities, where you can inquire about more favorable pricing.
- Amazon: Offers a wide selection of resins from various brands with discounted prices and fast shipping.
- MatterHackers: Stocks a range of SLA resins with detailed specifications and good customer service.
- 3D Printing Canada: Provides a large selection of SLA resins for users in Canada or nearby regions with competitive pricing and fast shipping.
- iGo 3D: Offers an array of SLA resins, including specialized materials, and provides resin compatibility guides.
Tips for Purchasing SLA Materials
- Printer Compatibility: Ensure the resin is compatible with your SLA printer.
- Budget: Consider the cost of the resin based on your needs.
- Resin Properties: Choose the resin according to the required mechanical properties.
- Shipping Costs and Delivery Times: Take note of shipping details when purchasing from international suppliers.
- Reviews and Recommendations: Look for user reviews or ask for recommendations in 3D printing communities.
Conclusion
Key Takeaways
- SLA 3D printing is known for its precision, smooth finishes, and ability to print detailed models using liquid photopolymer resins cured by UV light or lasers.
- There are three main types of SLA resins: standard resins for general-purpose models, engineering resins for functional parts, and specialty resins for specific applications.
- When choosing a resin, consider the purpose of the print, mechanical properties, and post-processing requirements.
- Proper post-processing, including cleaning and curing, is crucial for achieving the desired print quality. It is necessary to handle resins safely and dispose of waste properly.
- SLA has its own advantages and disadvantages compared to other 3D printing technologies like FDM and SLS. The choice depends on the specific requirements of the project.
- There are many reliable suppliers and brands offering SLA resins. When purchasing, consider factors such as printer compatibility, budget, resin properties, shipping costs, and user reviews.
Final Advice
When selecting SLA printing materials, it is essential to balance performance, cost, and application needs. Thoroughly research different resin types to understand how they will impact the prints. With experience, experimenting with various materials can help optimize the printing process and consistently produce high-quality results.
Looking Ahead
As the 3D printing field evolves, new resin materials and technological advancements will continue to emerge. Stay updated with the latest innovations and be willing to explore different materials to find the best fit for projects. This will enable users to take full advantage of the capabilities of SLA 3D printing and expand the possibilities of what can be achieved.



