In the fast-paced global of fashion and personal accessories, staying ahead of the curve is critical for any manufacturer. This is specifically genuine for eyewear manufacturers, in which innovation in design and manufacturing can set a brand apart in a surprisingly competitive market. Enter Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing for eyewear—a era remodeling how eyewear is designed, prototyped, and synthetic.

Imagine being capable of create bespoke eyewear tailored to the precise specs of each client, unexpectedly iterate on designs with minimal waste, and convey the ones creations to marketplace faster than ever before. This is not the destiny; it is occurring now, thanks to SLS 3D printing. But what exactly is SLS 3D printing, and why need to eyewear manufacturers be paying interest?
In this comprehensive manual, we are able to take you from the concept of SLS 3D printing to its software inside the eyewear enterprise. We’ll explore its blessings, delve into real-global case studies, and speak technical issues and future tendencies. Whether you are an eyewear producer seeking to innovate or honestly curious about the technology’s capacity, this article will offer you with treasured insights and actionable facts.
What is SLS 3D Printing?
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing is one of the most advanced and versatile 3D printing technologies available today. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which often involve removing material from a solid block, SLS builds objects layer by layer from a powdered material, using a laser to fuse these particles together. But what exactly does this mean, and why is it so revolutionary?
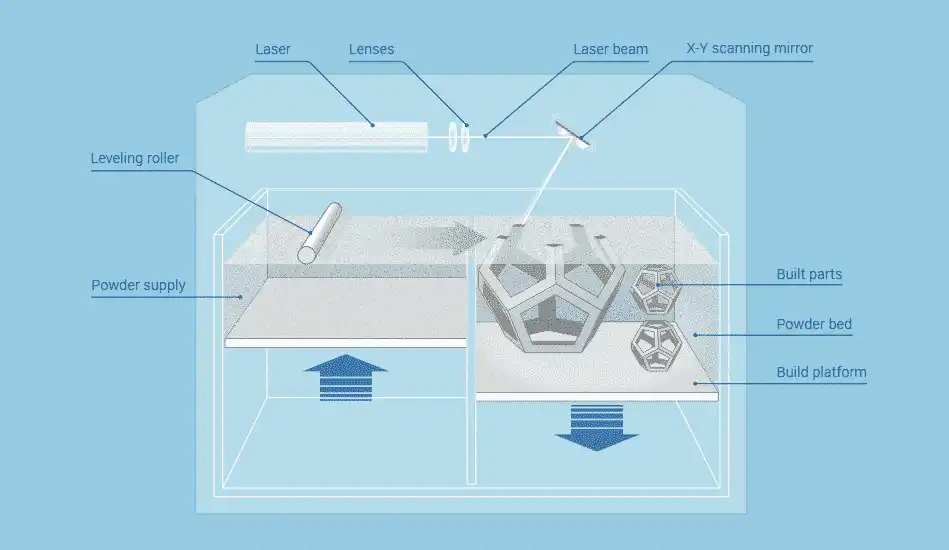
How Does SLS 3D Printing Work?
The process of SLS 3D printing can be broken down into several key steps:
- Design: The journey begins with a digital 3D model, usually created in CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. This model is then converted into a format readable by the 3D printer, typically an STL file.
- Preparation: The STL file is uploaded to the SLS 3D printer’s software, where the model is sliced into thin layers. The printer’s build chamber is filled with powdered material, such as nylon or polyamide.
- Printing: A high-powered laser scans each layer’s cross-section, selectively fusing the powder particles together. The build platform lowers slightly after each layer, and a new layer of powder is spread over the surface.
- Cooling and Cleaning: Once printing is complete, the build chamber needs to cool down before the printed parts can be removed. The excess powder is then brushed off and can often be recycled for future prints.
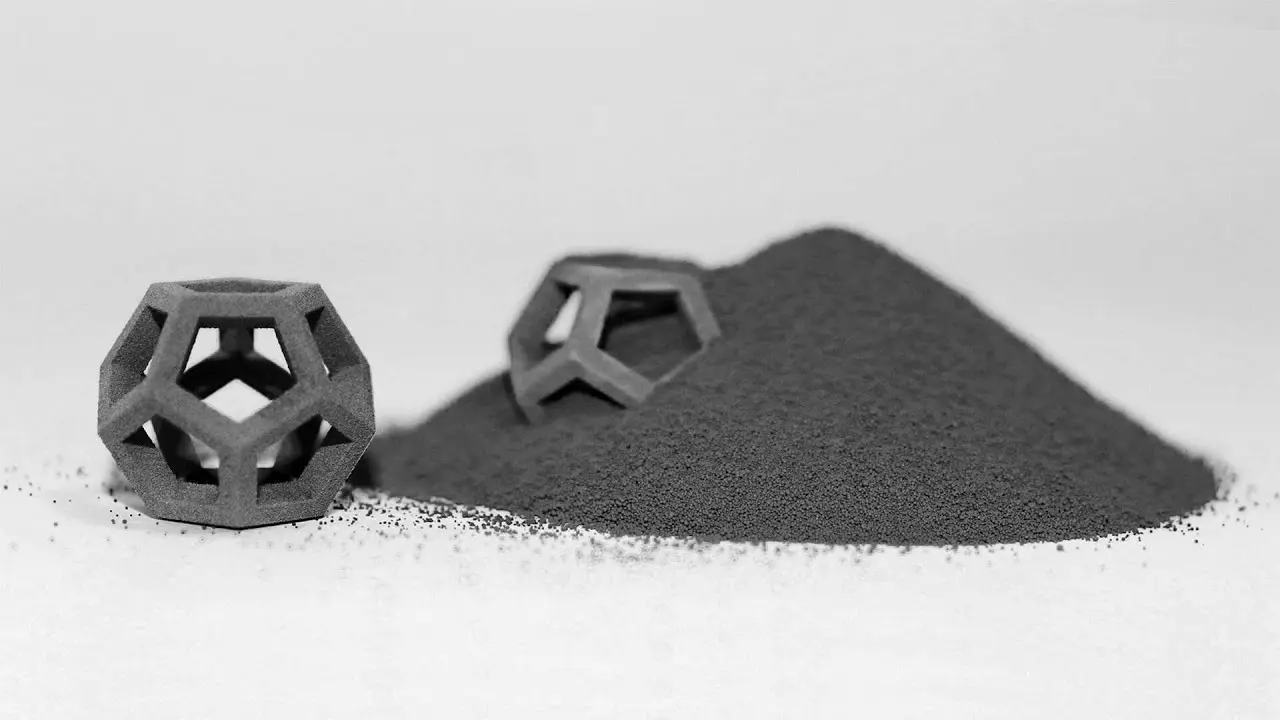
Materials Used in SLS 3D Printing
One of the most significant advantages of SLS 3D printing is its compatibility with a wide range of materials. Here are some commonly used ones:

| Material | Properties | Applications |
| Nylon (PA12) | Strong, flexible, and durable | Prototyping, functional parts |
| Polyamide | Lightweight, strong, and heat-resistant | Automotive, aerospace components |
| TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) | Flexible, rubber-like | Wearables, medical devices |
| Alumide | Nylon filled with aluminum particles | Decorative objects, heat-resistant parts |
Comparison with Other 3D Printing Technologies
To understand the unique benefits of SLS, it’s helpful to compare it with other popular 3D printing methods:
| Feature | SLS | FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) | SLA (Stereolithography) |
| Material | Powder (nylon, polyamide, etc.) | Filament (PLA, ABS, etc.) | Resin |
| Resolution | High | Medium | Very High |
| Strength | High | Medium | Medium |
| Cost | Medium to High | Low to Medium | Medium to High |
| Speed | Fast | Slow to Medium | Fast |
Advantages of SLS 3D Printing
Now that we have a basic understanding of how SLS works, let’s dive into its advantages:
- Design Freedom: SLS allows for the creation of complex geometries that would be impossible or very difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Material Efficiency: Since SLS uses powdered material, any unused powder can often be recycled, reducing waste.
- Strength and Durability: Parts produced with SLS are often more robust and durable compared to other 3D printing methods.
- No Need for Support Structures: Unlike FDM and SLA, SLS doesn’t require support structures, making post-processing simpler and less time-consuming.
Applications of SLS 3D Printing
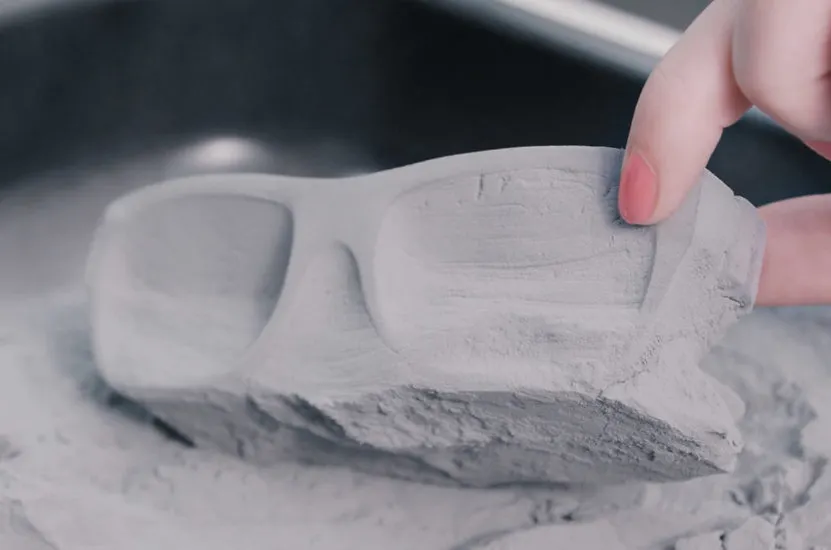

SLS 3D printing is used across various industries, thanks to its versatility and robustness. Some notable applications include:
- Prototyping: Rapidly creating functional prototypes that can be tested and iterated upon.
- End-Use Parts: Manufacturing small to medium-sized batches of final parts, particularly in industries like aerospace and automotive.
- Medical Devices: Producing custom-fit medical implants and prosthetics.
- Consumer Goods: Creating customized products like eyewear, footwear, and more.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing is a effective generation that offers unprecedented design freedom, cloth performance, and part electricity. Its capacity to produce complex geometries with out the want for help systems makes it a super preference for industries starting from aerospace to consumer items. As we continue to discover its packages, specially in eyewear manufacturing, the advantages of SLS end up even greater apparent.
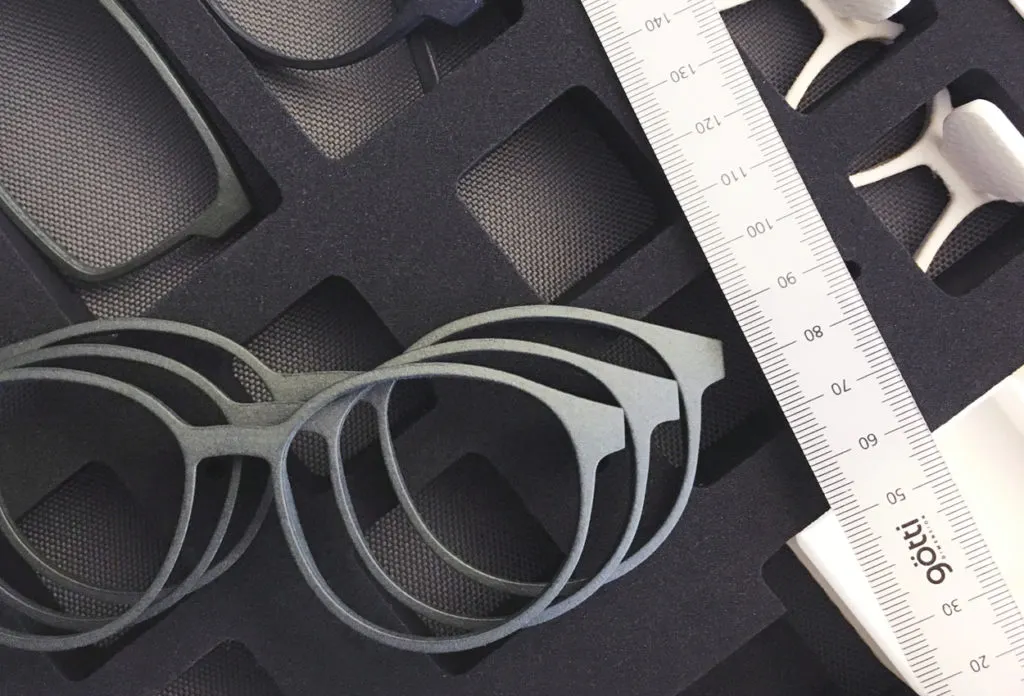
The Eyewear Manufacturing Process
Eyewear has evolved from a in basic terms practical item to a essential style assertion and private accent. As consumer choices shift towards customization and speedy developments, the producing technique have to adapt to meet these demands. Let’s explore the traditional strategies of eyewear manufacturing and the way SLS 3D printing is reshaping this industry.
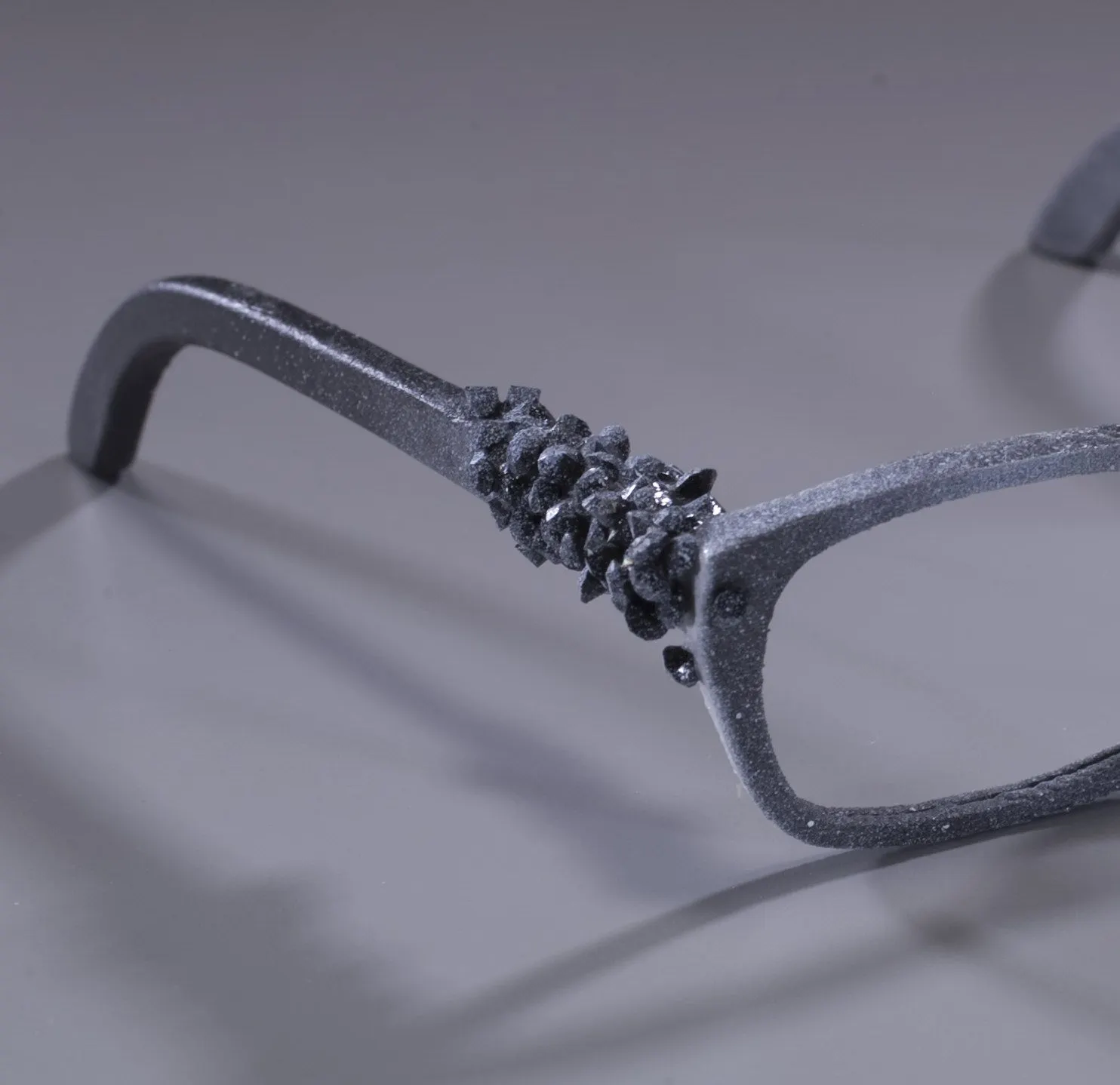

Traditional Eyewear Manufacturing Methods
The conventional manufacturing of eyewear involves several intricate steps, each requiring precision and craftsmanship. Here’s a look at the typical process:
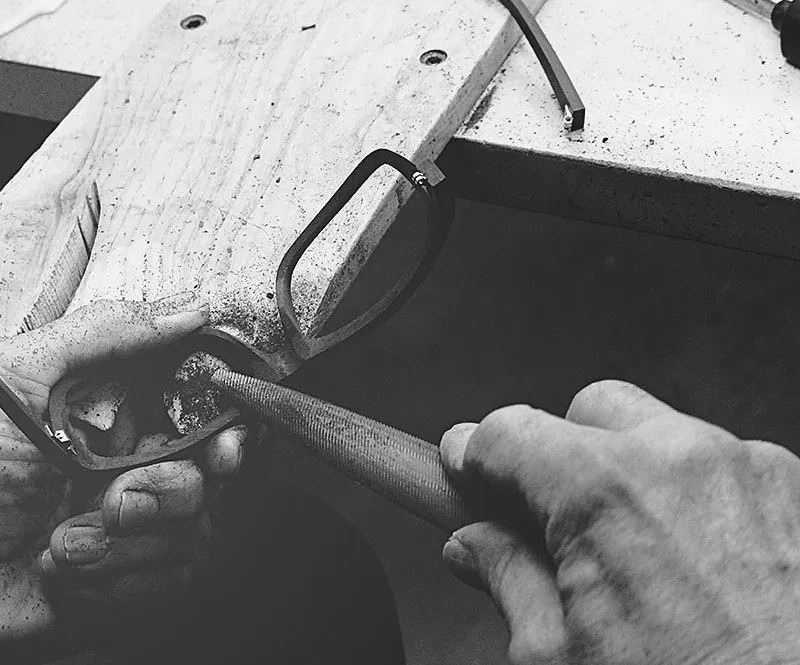

- Design and Prototyping
- Sketching: Designers create initial sketches based on trends and customer feedback.
- CAD Modeling: These sketches are transformed into detailed digital models.
- Prototyping: Physical prototypes are crafted, often by hand, to evaluate fit and aesthetics.
- Material Selection
- Acetate: A popular choice for frames due to its flexibility and color variety.
- Metal: Stainless steel and titanium offer durability and a sleek appearance.
- Injection Molding Plastic: Used for mass production, offering cost efficiency.
- Production
- Cutting and Shaping: Frames are cut from sheets of material or molded.
- Assembly: Components like hinges and nose pads are attached.
- Polishing and Finishing: Frames are polished to enhance appearance and comfort.
- Quality Control
- Each pair undergoes rigorous inspections to ensure alignment, fit, and finish.
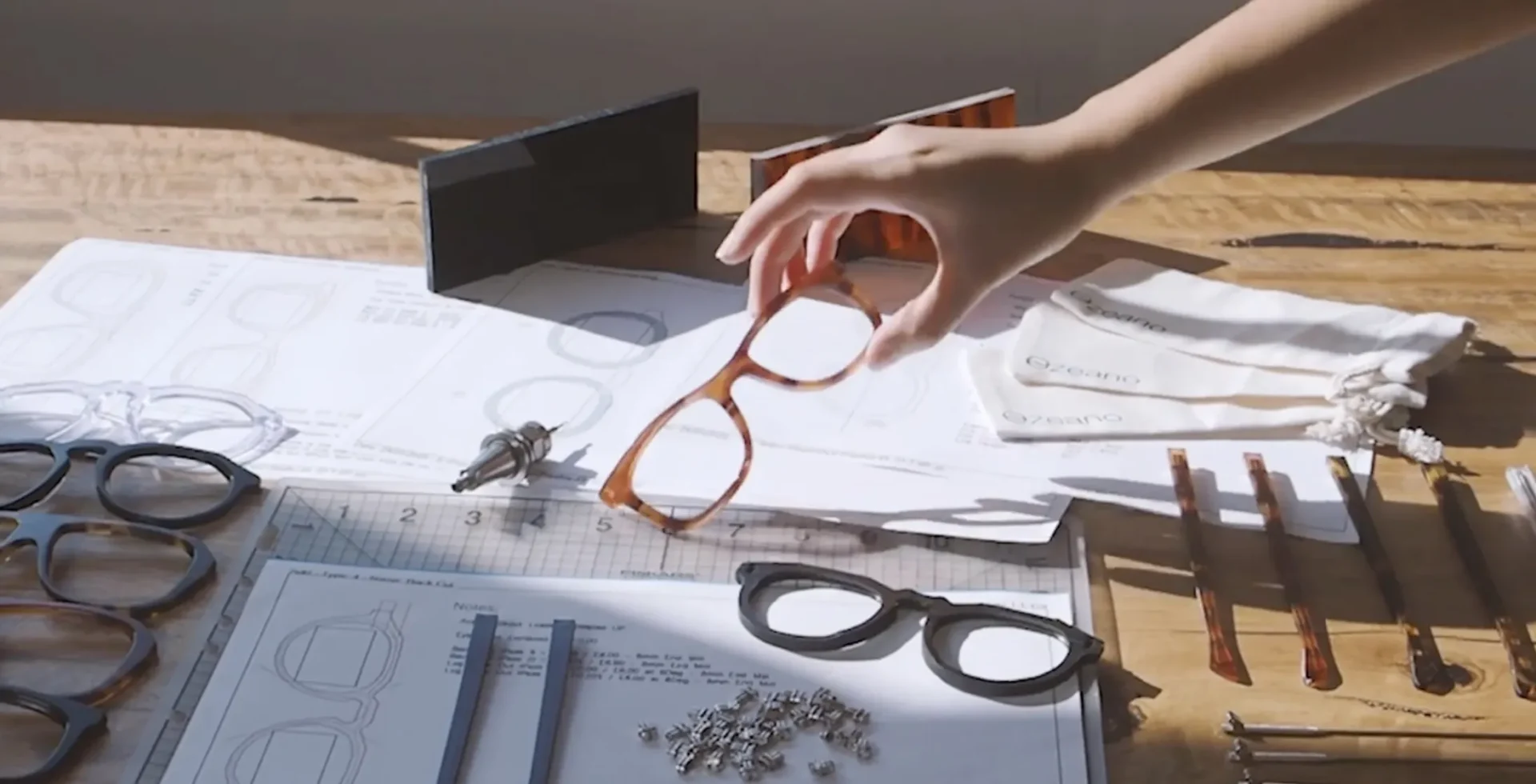

Challenges in Traditional Manufacturing

While effective, traditional methods come with several challenges:
- Time-Consuming: The process from design to production can take several months.
- Limited Customization: Custom designs are often costly and time-prohibitive.
- Material Waste: Cutting frames from sheets often results in significant waste.
- High Inventory Risk: Predicting demand for various styles can lead to overproduction.
SLS 3D Printing: A Game Changer in Eyewear
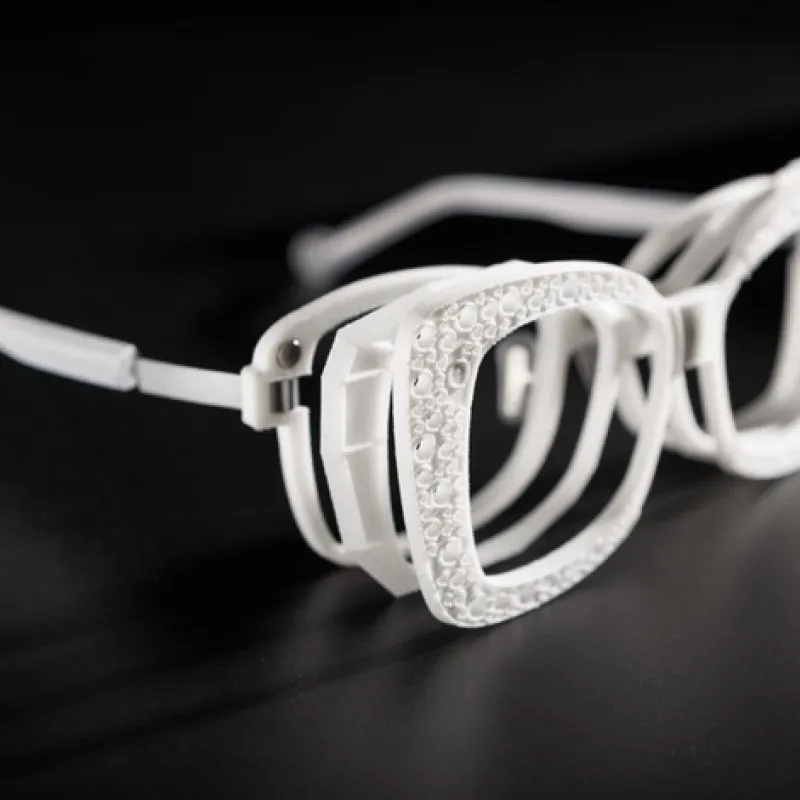

Enter SLS 3D printing—a technology that addresses these challenges head-on. Here’s how SLS is revolutionizing eyewear manufacturing:
- Rapid Prototyping and Production
- Speed: Quickly iterate designs and produce prototypes in days, not weeks.
- On-Demand Manufacturing: Produce eyewear as needed, reducing inventory risks.
- Customization and Personalization
- Bespoke Designs: Easily create custom-fit eyewear tailored to individual preferences.
- Complex Geometries: Design intricate patterns and structures that traditional methods can’t achieve.
- Efficiency and Sustainability
- Material Utilization: Minimize waste by recycling unused powder.
- Eco-Friendly Options: Use sustainable materials to cater to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Cost-Effectiveness
- Reduced Labor Costs: Automate many aspects of production, lowering labor requirements.
- Lower Entry Barriers: Smaller batches become economically viable, allowing niche designers to compete.
Comparing Traditional vs. SLS Methods
| Aspect | Traditional Manufacturing | SLS 3D Printing |
| Design Turnaround | Weeks to Months | Days to Weeks |
| Customization | Limited and Costly | Extensive and Affordable |
| Material Waste | High | Low |
| Initial Investment | High | Medium |
| Scalability | Challenging for Small Batches | Easy and Flexible |
The eyewear industry stands at a crossroads in which innovation meets way of life. While traditional manufacturing methods have served well for many years, they warfare to keep pace with cutting-edge demands for pace, customization, and sustainability. SLS 3D printing gives a feasible and interesting opportunity that now not only addresses those challenges however additionally opens new avenues for creativity and performance.
Benefits of SLS 3D Printing for Eyewear Manufacturers
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing is more than just an advanced manufacturing technique—it’s a game-changer for the eyewear industry. From customization to sustainability, the benefits of SLS 3D printing are multifaceted and powerful. Let’s dive deep into why eyewear manufacturers should seriously consider adopting this technology.
Customization and Personalization
One of the most compelling advantages of SLS 3D printing is its ability to offer unparalleled customization.
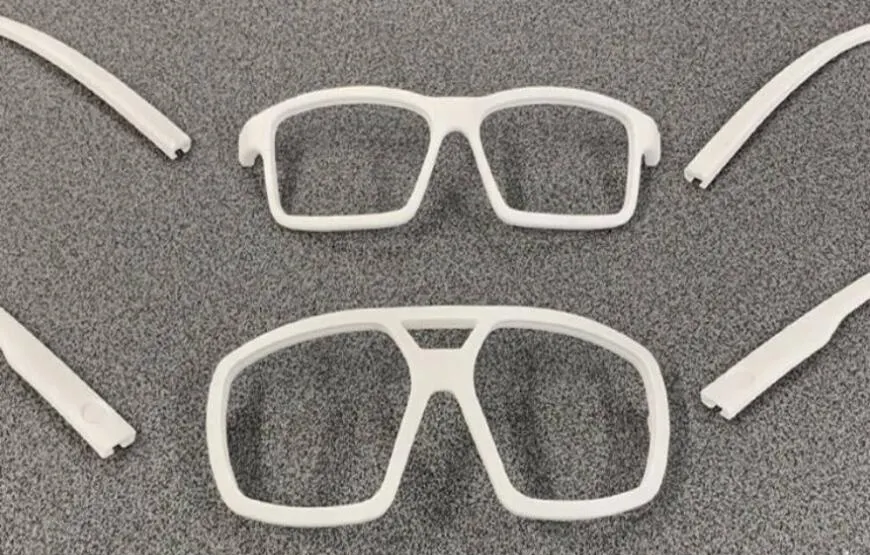

- Tailored Designs: Create eyewear tailored to the exact measurements and preferences of individual customers. This level of personalization can significantly enhance comfort and satisfaction.
- Unlimited Design Possibilities: Intricate designs, complex geometries, and unique textures are easily achievable, allowing designers to push the boundaries of creativity.
Example
Imagine a customer walks into your store and undergoes a quick 3D scan. Within days, they receive a pair of glasses that fit perfectly, featuring their preferred style and color. This is the future that SLS 3D printing promises.
Speed and Efficiency
Time is money, and SLS 3D printing excels in both areas.
- Faster Prototyping: Quickly iterate designs and prototypes, reducing the time from concept to market.
- On-Demand Production: Manufacture eyewear as needed, minimizing inventory and storage costs.
Case Study
A startup eyewear brand implemented SLS 3D printing and reduced their design-to-market cycle by 50%. This agility allowed them to respond swiftly to market trends and customer feedback, giving them a competitive edge.
Design Flexibility
The versatility of SLS 3D printing allows for incredible design flexibility.
- Complex Geometries: Produce intricate designs and lightweight structures that are impossible with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Functional Features: Integrate functional elements directly into the design, such as flexible hinges or ergonomic grips.
Design Capabilities Comparison
| Feature | Traditional Methods | SLS 3D Printing |
| Complex Geometries | Limited | Extensive |
| Integrated Functional Parts | Challenging | Easily Achievable |
| Lightweight Structures | Difficult | Readily Possible |
Cost-Effectiveness
While the initial investment in SLS 3D printing technology can be significant, the long-term cost benefits are substantial.
- Reduced Material Waste: Since unused powder can often be recycled, material costs are lower.
- Lower Production Costs for Small Batches: Economically viable for small-scale production, making it ideal for limited edition or custom eyewear.
Example
A mid-sized eyewear manufacturer transitioned to SLS 3D printing and saw a 30% reduction in material costs and a 20% decrease in overall production expenses.
Sustainability
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, sustainability in manufacturing is no longer optional—it’s essential.
- Eco-Friendly Materials: Use sustainable and recyclable materials, reducing the environmental footprint.
- Minimized Overproduction: On-demand manufacturing reduces the risk of overproduction and excess inventory.
Environmental Impact
| Aspect | Traditional Methods | SLS 3D Printing |
| Material Waste | High | Low |
| Energy Consumption | Variable | Efficient |
| Recyclability | Limited | High |
The advantages of SLS 3D printing for eyewear manufacturers are clear and compelling. From rapid prototyping to sustainable production, this technology gives answers to the various demanding situations confronted by using traditional manufacturing methods. By embracing SLS, eyewear manufacturers can’t most effective decorate their product services however also improve their operational performance and environmental impact.
Real-World Case Studies of SLS 3D Printing in Eyewear
To truly understand the transformative potential of Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing in the eyewear industry, we need to look at real-world examples. These case studies highlight how various companies have successfully integrated SLS technology into their production processes, showcasing the tangible benefits and innovative possibilities it offers.
Case Study 1: Adidas – Performance and Precision
Overview: Adidas, a global leader in sportswear, has ventured into eyewear with a focus on performance and durability. By leveraging SLS 3D printing, Adidas has been able to produce lightweight, strong, and ergonomically designed sports eyewear.
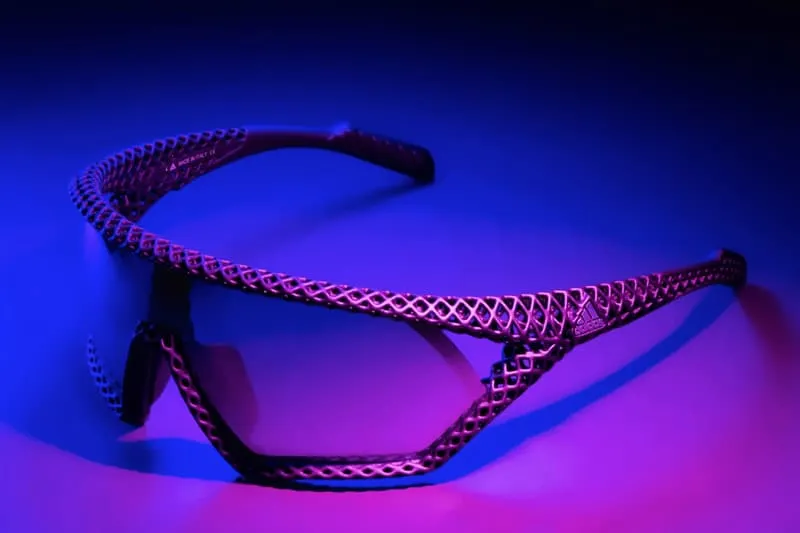

Implementation:
- Material Selection: Adidas uses durable and flexible nylon (PA12) for their eyewear frames.
- Prototyping Speed: SLS 3D printing allows Adidas to quickly iterate on designs, ensuring optimal performance and comfort.
Benefits:
- Enhanced Performance: The lightweight frames reduce fatigue for athletes.
- Customization: Athletes can get eyewear tailored to their specific needs and preferences.
- Durability: The use of strong materials ensures that the eyewear can withstand rigorous physical activity.
| Aspect | Traditional Methods | SLS 3D Printing |
| Prototyping Time | Weeks | Days |
| Weight | Higher | Lower |
| Customization | Limited | Extensive |
Case Study 2: Hoet – Luxury and Customization
Overview: Hoet, a Belgian luxury eyewear brand, has embraced SLS 3D printing to offer bespoke eyewear that combines elegance with precision engineering.
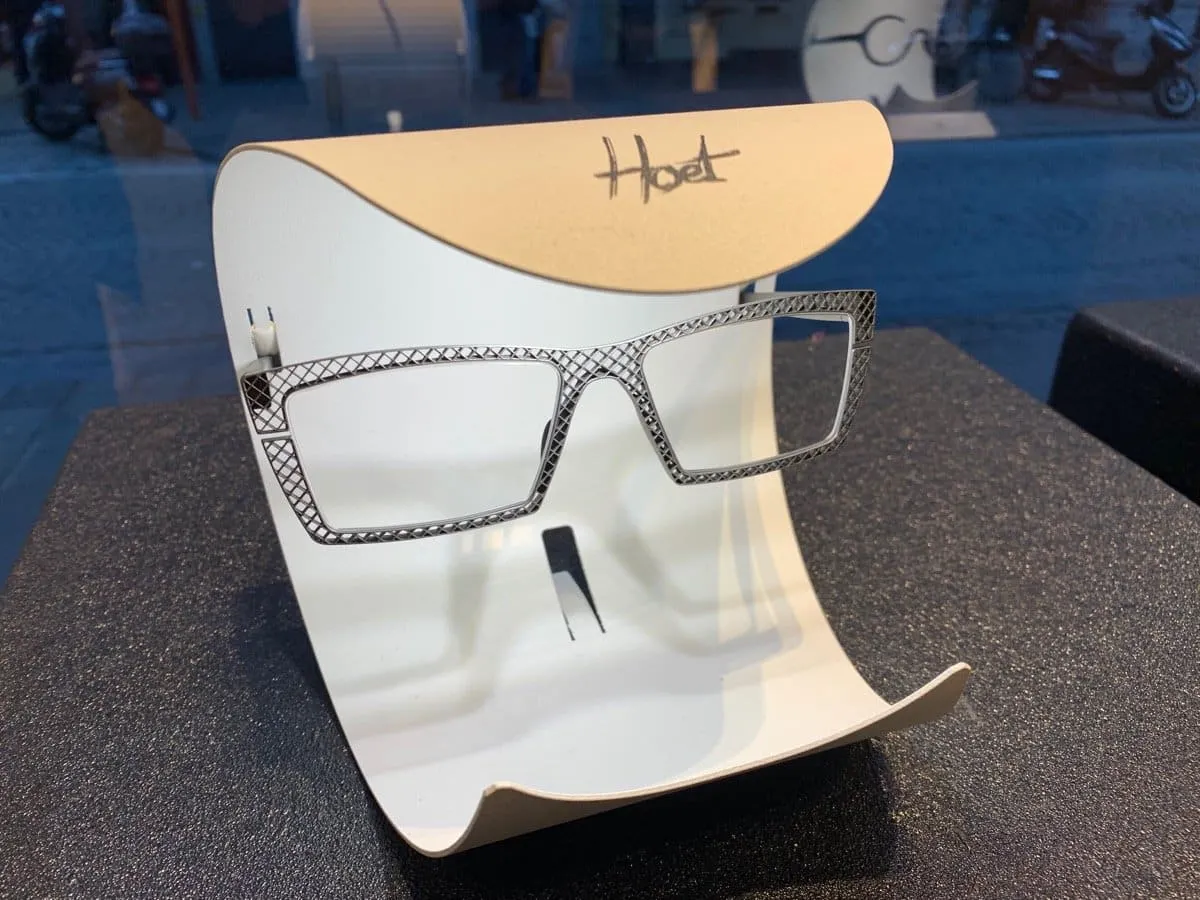

Implementation:
- Design Innovation: Hoet uses SLS to create complex, delicate designs that stand out in the luxury market.
- Custom Fit: Each pair of glasses can be custom-fitted to the wearer’s facial measurements, providing unparalleled comfort.
Benefits:
- Unique Designs: The design freedom offered by SLS allows Hoet to create eyewear that is both aesthetically pleasing and functionally superior.
- Customer Satisfaction: The custom-fit approach results in high levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Reduced Waste: By producing on-demand, Hoet minimizes material waste and overproduction.
| Aspect | Traditional Methods | SLS 3D Printing |
| Design Complexity | Limited | Extensive |
| Customer Fit | Standard Sizes | Custom-Fit |
| Material Waste | High | Low |
Case Study 3: Mykita – Innovation and Style

Overview: Mykita, an innovative eyewear brand, is known for its stylish and modern designs. By integrating SLS 3D printing, Mykita has been able to push the boundaries of what is possible in eyewear design.
Implementation:
- Material Flexibility: Mykita uses various materials, including flexible TPU, to create frames that are both stylish and durable.
- Functional Prototyping: Rapid prototyping with SLS allows Mykita to test and refine functional elements, such as hinges and ergonomic grips.
Benefits:
- Design Versatility: The ability to produce complex geometries and integrated functional parts sets Mykita apart in the competitive eyewear market.
- Speed to Market: Faster design iterations and production cycles allow Mykita to bring new designs to market more quickly.
- Sustainability: Efficient use of materials and on-demand production align with Mykita’s commitment to sustainability.
| Aspect | Traditional Methods | SLS 3D Printing |
| Functional Prototyping | Limited | Extensive |
| Speed to Market | Slow | Fast |
| Sustainability | Variable | High |
These real-world case studies illustrate the profound effect of SLS 3D printing at the eyewear enterprise. Brands like Adidas, Hoet, and Mykita are leveraging this technology to beautify performance, offer unheard of customization, and push the limits of design. The blessings are clean: quicker prototyping, reduced waste, and the potential to supply complex, custom-healthy eyewear that meets the high requirements of nowadays’s purchasers.
Technical Considerations and Best Practices for Integrating SLS 3D Printing in Eyewear Manufacturing
Integrating Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing into eyewear manufacturing isn’t just about acquiring the technology—it’s about understanding how to effectively utilize it for optimal results. This section will provide a comprehensive guide on the technical considerations and best practices for seamlessly incorporating SLS 3D printing into your eyewear production process.
Understanding the Technical Requirements
Before diving into SLS 3D printing, it’s crucial to understand the key technical requirements:
- Choosing the Right Printer
- Build Volume: Ensure the printer has a sufficient build volume to accommodate your designs.
- Resolution: High resolution is essential for producing finely detailed eyewear.
- Reliability: Look for reputable brands known for consistent performance.
- Material Selection
- Compatibility: Verify that the materials you intend to use are compatible with the chosen SLS printer.
- Properties: Consider mechanical properties such as flexibility, strength, and durability.
- Finishing: Some materials may require specific post-processing steps to achieve the desired finish.
- Software and Design Tools
- CAD Software: Invest in robust CAD software capable of creating detailed and complex models.
- Slicing Software: Use slicing software compatible with your SLS printer to convert 3D models into printable layers.
- Simulation Tools: Employ simulation tools to predict and mitigate potential printing issues.
Best Practices for Design and Prototyping
Effective design and prototyping are critical to maximizing the benefits of SLS 3D printing:
- Design for Additive Manufacturing (DfAM)
- Optimize Geometry: Design parts to take full advantage of SLS capabilities, such as complex geometries and integrated features.
- Material Efficiency: Minimize material usage by designing lightweight structures without compromising strength.
- Iterative Prototyping
- Rapid Iteration: Use the speed of SLS 3D printing to quickly iterate and refine designs.
- Functional Prototypes: Produce functional prototypes to test fit, comfort, and performance before final production.
- Post-Processing Techniques
- Surface Finishing: Employ techniques like tumbling, polishing, or coating to achieve the desired surface finish.
- Dyeing and Painting: Customize the appearance of your eyewear through dyeing or painting processes.
Design and Prototyping Best Practices
| Aspect | Best Practice | Benefit |
| Geometry Optimization | Design for SLS capabilities | Enhanced functionality and aesthetics |
| Material Efficiency | Lightweight, strong structures | Reduced material costs |
| Rapid Iteration | Quick prototype cycles | Faster time-to-market |
| Functional Prototypes | Test and refine designs | Improved product quality |
| Surface Finishing | Tumbling, polishing, coating | High-quality final product |
Implementing Quality Control
Maintaining high quality is paramount in eyewear manufacturing. Here are some best practices for quality control:
- Inspection Protocols
- Dimensional Accuracy: Use precision measuring tools to ensure dimensional accuracy of printed parts.
- Visual Inspection: Perform thorough visual inspections to identify surface defects or inconsistencies.
- Testing
- Mechanical Testing: Conduct tests to assess the strength, flexibility, and durability of the eyewear.
- Wear Testing: Simulate real-world usage scenarios to ensure the eyewear meets user expectations.
- Documentation
- Maintain Records: Keep detailed records of design iterations, material batches, and testing results for traceability and continuous improvement.
Quality Control Best Practices
| Aspect | Best Practice | Benefit |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Precision measuring tools | Consistent product quality |
| Visual Inspection | Thorough surface checks | Identify defects early |
| Mechanical Testing | Strength and durability assessments | Ensure product reliability |
| Wear Testing | Simulate real-world usage | Meet user expectations |
| Documentation | Detailed records | Traceability and improvement |
Streamlining Production Workflow
To fully capitalize on SLS 3D printing, it’s essential to streamline your production workflow:
- Automate Where Possible
- Automated Material Handling: Implement systems for automated material loading and recycling.
- Workflow Automation: Use software to automate repetitive tasks, such as slicing and job scheduling.
- Integrate with Existing Systems
- ERP Systems: Integrate SLS 3D printing workflows with your existing ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems for seamless operations.
- Quality Management Systems: Ensure that your quality control protocols are integrated into your overall production workflow.
- Continuous Improvement
- Feedback Loops: Establish feedback loops between design, production, and quality control teams for continuous improvement.
- Training: Invest in ongoing training for your team to keep up with the latest advancements in SLS 3D printing technology.
Production Workflow Best Practices
| Aspect | Best Practice | Benefit |
| Automation | Material and workflow automation | Increased efficiency |
| System Integration | ERP and quality management integration | Seamless operations |
| Continuous Improvement | Feedback loops and training | Ongoing optimization |
Successful integration of SLS 3D printing into eyewear manufacturing requires careful consideration of technical requirements, optimal design and prototyping, rigorous quality control procedures, and manufacturing processes operating flexibility Adherence to these guidelines allows eyewear manufacturers to fully reap the benefits of SLS 3D printing, from customization to injuries and durability
Future Trends and Innovations in SLS 3D Printing for Eyewear
The world of selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing continues to evolve, and new materials continue to revolutionize the eyewear industry as technology advances and new materials and advances are poised to change the way eyewear is made, make and customize again. This section will explore future developments and innovations in SLS 3D printing and their potential impact on the eyewear industry.
Advanced Materials
One of the most exciting areas of innovation in SLS 3D printing is the development of advanced materials. These materials offer enhanced properties that can significantly improve eyewear performance and aesthetics.
- High-Performance Polymers
- Bio-Based Polymers: Environmentally friendly options that reduce carbon footprint.
- Enhanced Durability: Polymers with improved impact resistance and flexibility.
- Thermal Stability: Materials that can withstand extreme temperatures, ideal for sports or industrial use.
- Composite Materials
- Carbon Fiber Composites: Combining lightweight properties with exceptional strength.
- Metal-Polymer Hybrids: Offering the aesthetics and durability of metal with the flexibility of polymer.
Advanced Materials
| Material Type | Properties | Applications |
| Bio-Based Polymers | Eco-friendly, sustainable | General eyewear, eco-conscious brands |
| High-Performance Polymers | Impact-resistant, flexible | Sports, industrial eyewear |
| Carbon Fiber Composites | Lightweight, strong | High-end, performance eyewear |
| Metal-Polymer Hybrids | Durable, flexible | Luxury, custom designs |
Smart Eyewear Integration
The fusion of SLS 3D printing and smart technology is set to create a new category of eyewear that offers more than just vision correction or style.
- Embedded Sensors
- Health Monitoring: Sensors that monitor vital signs, UV exposure, and more.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Integrating AR displays for navigation, notifications, and interactive experiences.
- Connectivity Features
- Bluetooth and Wi-Fi: Seamless connectivity with smartphones and other devices.
- Voice Assistants: Integration with voice-activated assistants for hands-free control.
Example
Imagine a pair of glasses that not only corrects your vision but also tracks your heart rate, provides real-time navigation through AR, and connects to your smartphone to display notifications. This is the future of smart eyewear with SLS 3D printing.
Automation and AI Integration
Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are set to play a significant role in optimizing SLS 3D printing processes.
- Automated Quality Control
- AI-Driven Inspections: Using machine learning algorithms to detect defects and ensure consistent quality.
- Predictive Maintenance: AI systems that predict and prevent machine breakdowns before they occur.
- Design Optimization
- Generative Design: AI algorithms that create optimized designs based on specific performance criteria.
- Topology Optimization: Advanced software that reduces material usage while maintaining structural integrity.
Automation and AI Integration
| Aspect | Innovation | Benefit |
| Quality Control | AI-driven inspections | Consistent product quality |
| Predictive Maintenance | Machine learning algorithms | Reduced downtime and maintenance costs |
| Generative Design | AI-created optimized designs | Enhanced performance and aesthetics |
| Topology Optimization | Material-efficient designs | Lower material costs, sustainability |
Sustainable Manufacturing
Sustainability is a growing concern across all industries, and the eyewear sector is no exception. Future innovations in SLS 3D printing will likely focus on creating more sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Recycled Materials
- Post-Consumer Recycled Polymers: Using recycled plastics to produce new eyewear frames.
- Closed-Loop Systems: Systems that recycle unused powder and minimize waste.
- Energy Efficiency
- Solar-Powered Printers: Incorporating renewable energy sources to power 3D printers.
- Energy-Efficient Processes: Optimizing printing processes to reduce energy consumption.
Sustainable Manufacturing
| Aspect | Innovation | Benefit |
| Recycled Materials | Post-consumer recycled polymers | Reduced environmental impact |
| Closed-Loop Systems | Recycling unused powder | Minimized material waste |
| Solar-Powered Printers | Renewable energy sources | Lower carbon footprint |
| Energy-Efficient Processes | Optimized printing methods | Reduced energy consumption |
The future of SLS 3D printing in eyewear manufacturing is brimming with possibilities. Advanced materials, smart eyewear integration, AI-driven automation, and sustainable manufacturing practices are all set to redefine the industry. By staying ahead of these trends, eyewear manufacturers can continue to innovate and meet the evolving demands of consumers.



