Imagine stepping into a world where your footwear is not just a product but a reflection of your unique style and comfort. In the ever-evolving footwear industry, the mold-making process plays a crucial role in transforming innovative designs into tangible products. Traditionally, creating shoe molds has relied on time-honored methods that involve meticulous craftsmanship, often using materials like wood or metal. While these methods have served the industry well for decades, they come with significant costs and limitations.
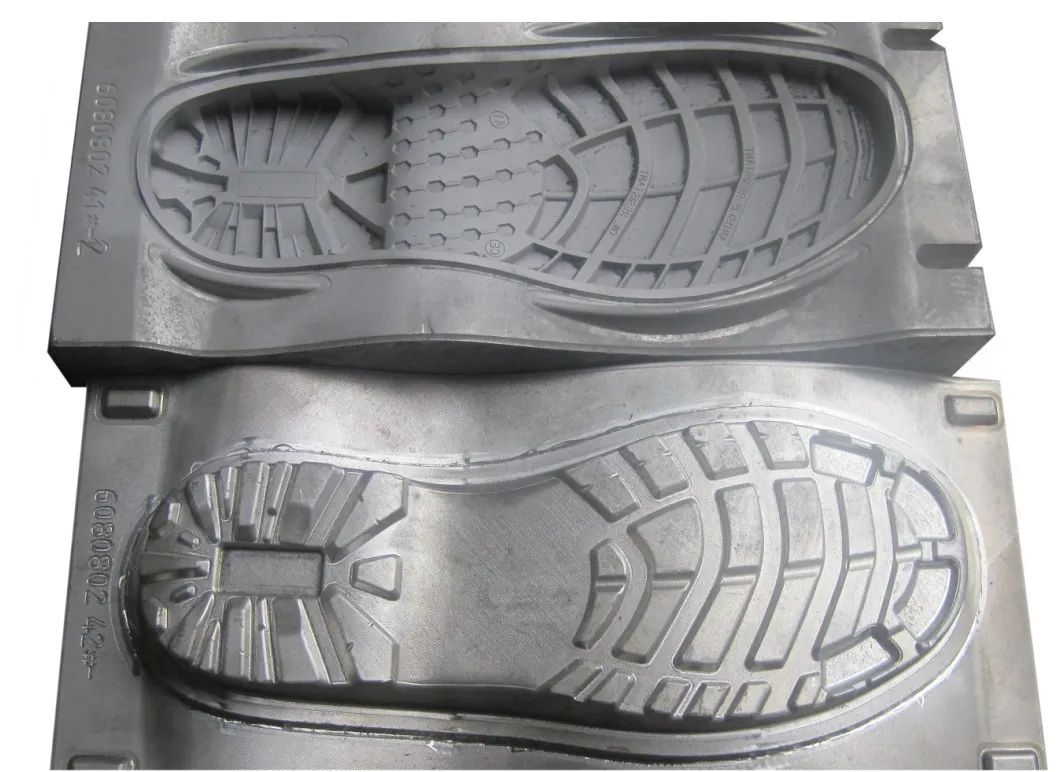

Enter 3D printing—a technology that has revolutionized manufacturing across various sectors, including footwear. With its ability to create complex shapes and designs quickly and cost-effectively, 3D printing is challenging the status quo of traditional mold-making methods. But how do the costs of 3D printed shoe molds stack up against conventional techniques?
This article aims to delve deep into this question, providing a comprehensive comparison of the costs associated with 3D printed shoe molds versus traditional methods. We’ll explore the intricacies of shoe molds, the advantages and disadvantages of each method, and the long-term implications for manufacturers. By the end of this exploration, you’ll have a clearer understanding of whether 3D printing is the future of shoe mold production or if traditional methods still hold their ground in a rapidly changing industry.
Understanding Shoe Molds
1.1 What are Shoe Molds?
Shoe molds are the unsung heroes of the footwear industry, serving as the foundation upon which every shoe is built. Essentially, a shoe mold is a hollow form that shapes the materials—such as leather, rubber, or synthetic fabrics—into the final design of the shoe. These molds are crucial for ensuring that each pair of shoes is consistent in shape, fit, and overall quality.
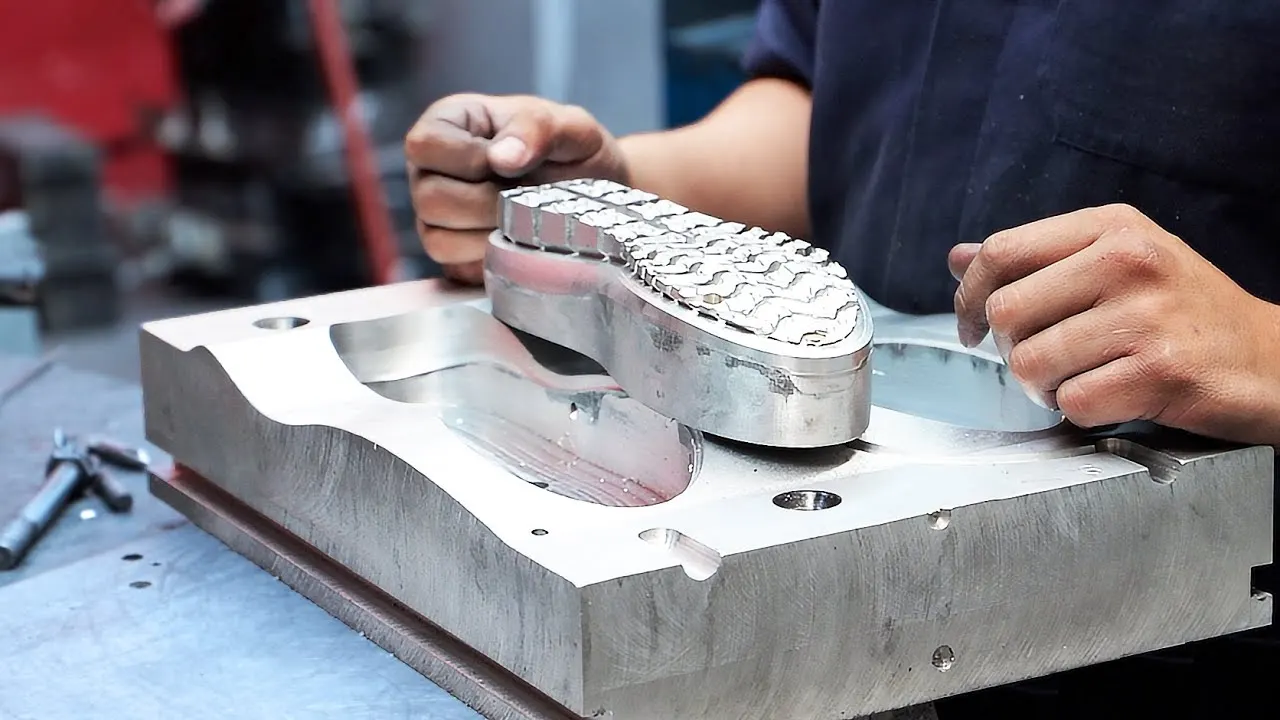

Types of Shoe Molds
Shoe molds can be categorized into several types, each serving a specific purpose in the manufacturing process:
- Lasting Molds: Used to shape the upper part of the shoe, ensuring it fits snugly around the foot.
- Injection Molds: Designed for producing soles, often used in conjunction with materials like polyurethane or thermoplastic rubber.
- Forming Molds: These molds help shape the shoe’s overall structure, particularly in creating unique designs.
1.2 Importance of Shoe Molds in Footwear Production
The significance of shoe molds in footwear production cannot be overstated. They not only dictate the aesthetic appeal of the shoe but also play a vital role in its functionality and comfort. Here are some key points to consider:
Quality Control
- Consistency: Molds ensure that each shoe produced is identical to the last, maintaining quality across large production runs.
- Precision: A well-crafted mold allows for more accurate fitting, which is crucial for customer satisfaction.
Design Flexibility
- Innovation: Shoe molds enable designers to experiment with new shapes and styles, pushing the boundaries of traditional footwear design.
- Customization: With advanced mold-making techniques, brands can offer personalized footwear options, catering to individual customer preferences.
Cost Efficiency
- Reduced Waste: Efficient mold production minimizes material waste, which is particularly important in an industry where margins can be tight.
- Faster Production Times: High-quality molds can significantly speed up the manufacturing process, allowing brands to respond quickly to market demands.
Understanding shoe molds is essential for grasping the broader context of footwear production. As we move forward in this article, we will explore how traditional methods of creating these molds compare to innovative 3D printing techniques. The next section will delve into the traditional methods of shoe mold creation, shedding light on the costs, advantages, and challenges associated with these time-honored practices.
Traditional Methods of Creating Shoe Molds
When it comes to creating shoe molds, traditional methods have stood the test of time, relying on craftsmanship and established techniques that have been honed over decades. While these methods have their merits, they also come with specific costs and limitations. In this section, we’ll explore the various traditional methods of shoe mold creation, break down their costs, and examine their advantages and disadvantages.
2.1 Overview of Traditional Methods
Traditional shoe mold-making typically involves several techniques, each with its own set of materials and processes. Here are the most common methods:
1. CNC Machining
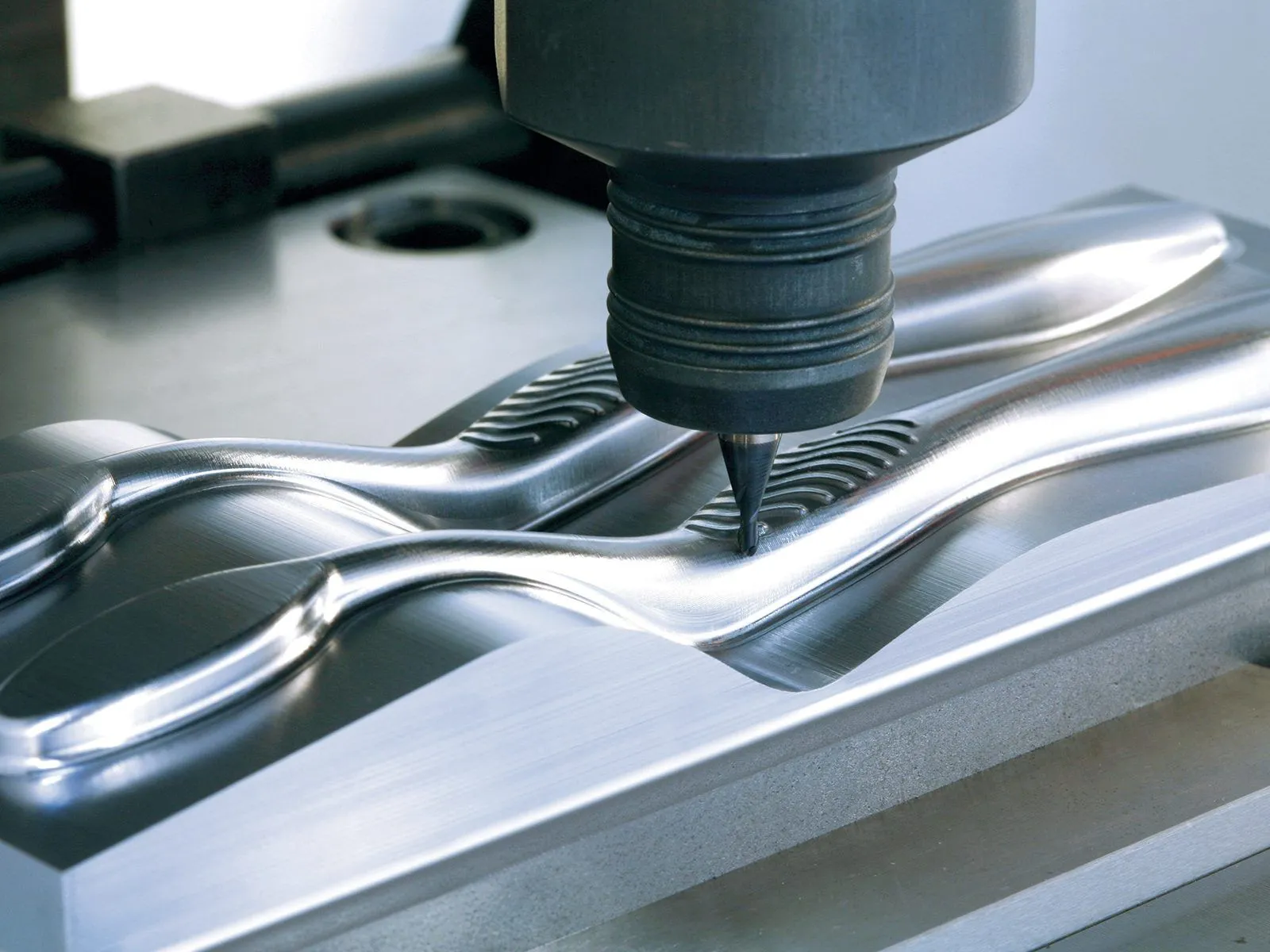

Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining is a modern approach that utilizes computer-controlled machines to carve molds from solid blocks of material.
- Materials Used: Aluminum, steel, or high-density foam.
- Process:
- Design is created using CAD software.
- The CNC machine cuts the mold based on the digital design.
2. Manual Carving
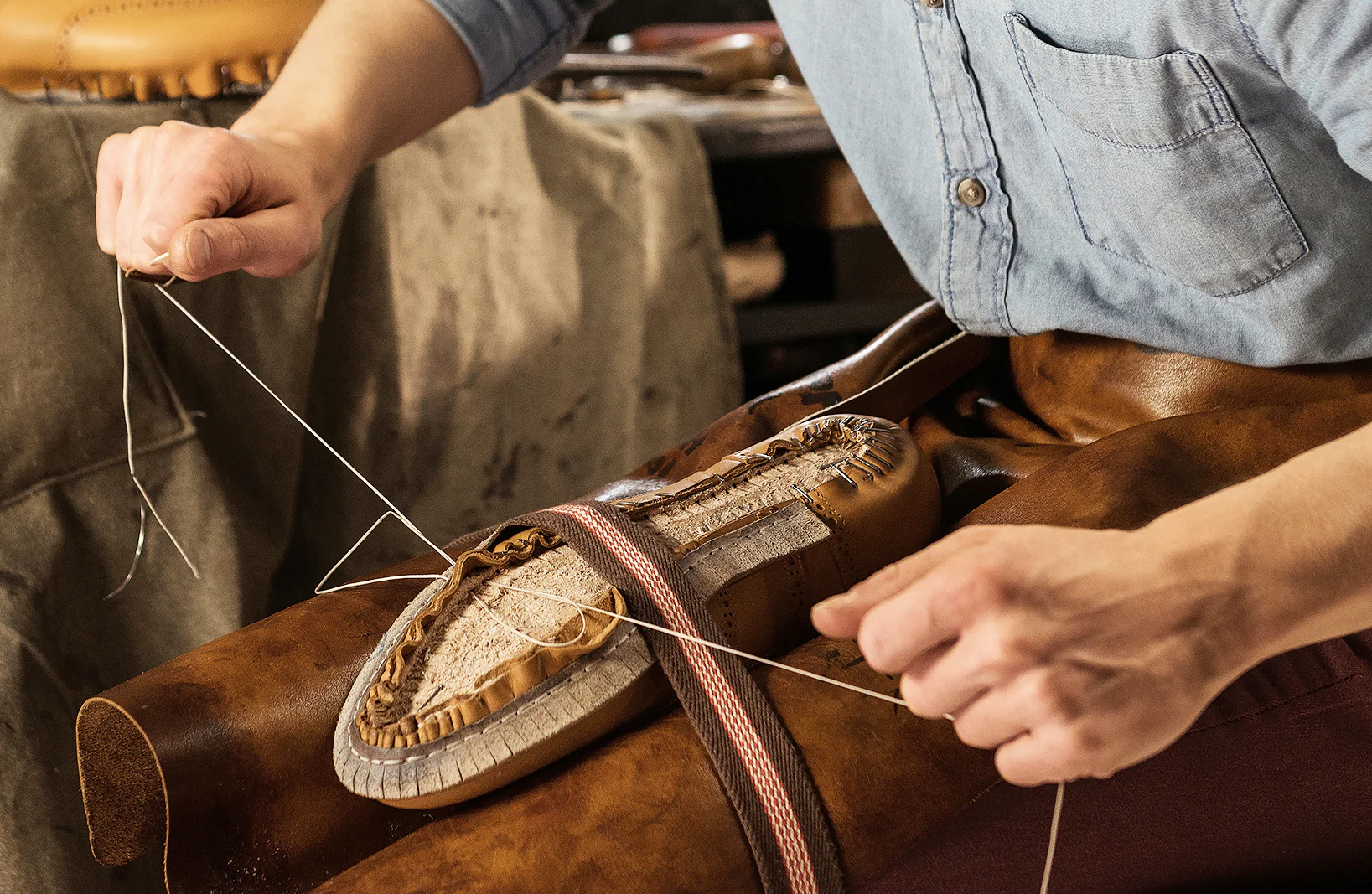

This age-old technique involves skilled artisans manually shaping molds from materials such as wood or metal.
- Materials Used: Wood, metal, or composite materials.
- Process:
- Artisans use tools like chisels and saws to carve the mold.
- This method requires extensive skill and experience.
3. Casting
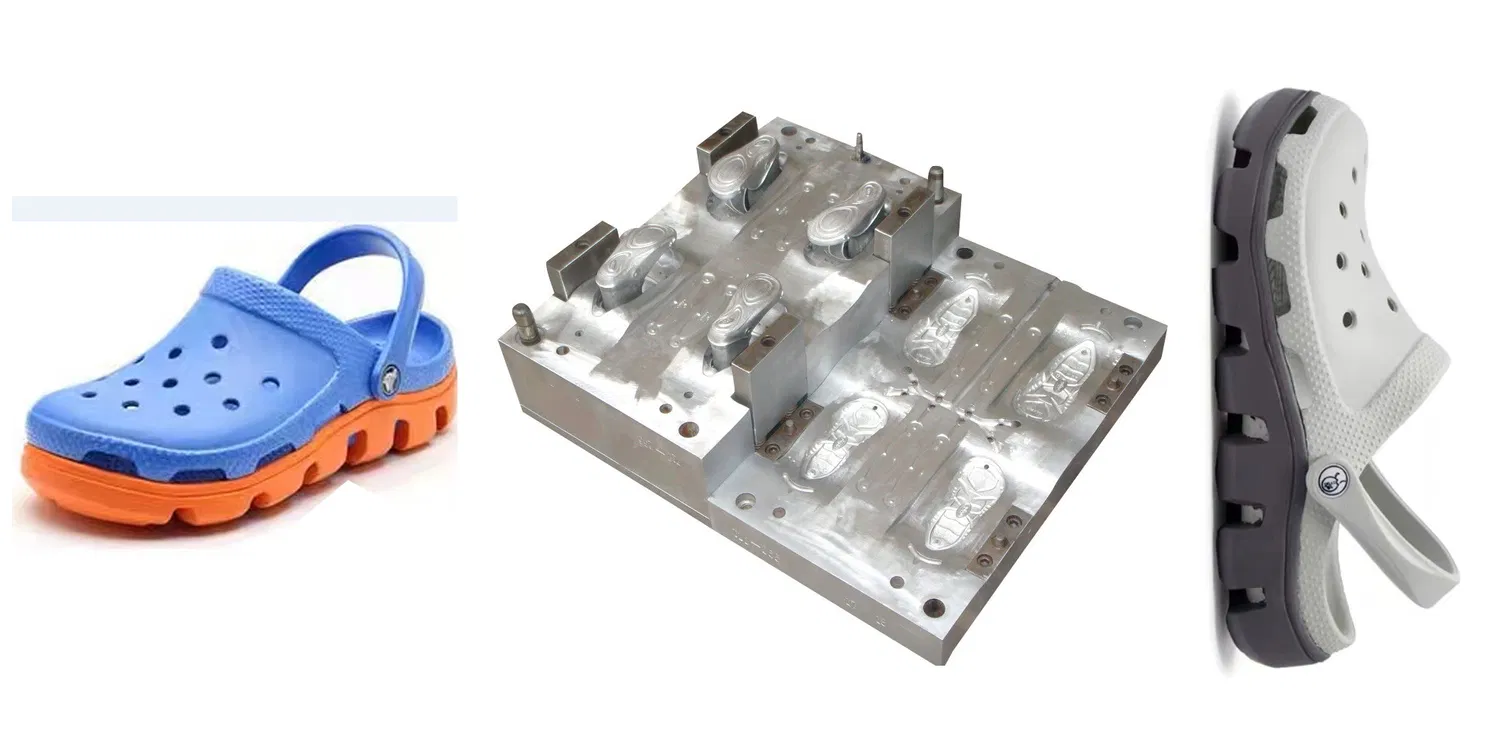
In casting, a master mold is created, which is then used to produce multiple copies.
- Materials Used: Silicone or polyurethane.
- Process:
- A master mold is made, often using CNC machining or manual carving.
- Liquid material is poured into the master mold to create duplicates.
2.2 Cost Breakdown of Traditional Methods
Understanding the costs associated with traditional mold-making methods is crucial for manufacturers. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
| Cost Element | CNC Machining | Manual Carving | Casting |
| Initial Setup Costs | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Material Costs | Moderate to High | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Labor Costs | Low (skilled operator) | High (artisanal skill) | Low to Moderate |
| Production Time | Moderate | High | Low |
| Maintenance Costs | Moderate | Low | Low |
2.3 Advantages and Disadvantages of Traditional Methods
Advantages
- Durability:
- Traditional molds, especially those made from metal, can withstand extensive use and wear.
- Quality Finish:
- Manual carving and CNC machining often yield high-quality finishes, which can be crucial for aesthetic appeal.
- Established Techniques:
- Many manufacturers have decades of experience with traditional methods, leading to reliability and consistency.
Disadvantages
- Longer Lead Times:
- Traditional methods often require significant time for mold creation, which can delay production schedules.
- Higher Costs for Low Volumes:
- The initial setup and material costs can be prohibitive, especially for small production runs.
- Limited Design Flexibility:
- While traditional methods allow for some customization, they often struggle to accommodate highly intricate designs compared to modern techniques.
Traditional methods of creating shoe molds have their strengths and weaknesses. While they offer durability and quality, they also come with higher costs and longer lead times, especially for smaller production runs. As we transition to the next section, we will explore the innovative world of 3D printing technology and how it is reshaping the landscape of shoe mold production.
3D Printing Technology in Shoe Mold Production
As technology advances, so too do the methods we use to create shoe molds. One of the most exciting developments in recent years is the rise of **3D printing**. This innovative manufacturing technique has opened new doors for the footwear industry, allowing for greater design freedom, faster production times, and potentially lower costs. In this section, we’ll explore the ins and outs of 3D printing for shoe molds, including how it works, the costs involved, and its advantages and disadvantages.
3.1 What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, involves creating three-dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital model. This technology has transformed various industries, including aerospace, automotive, and healthcare, and is now making significant inroads in footwear.
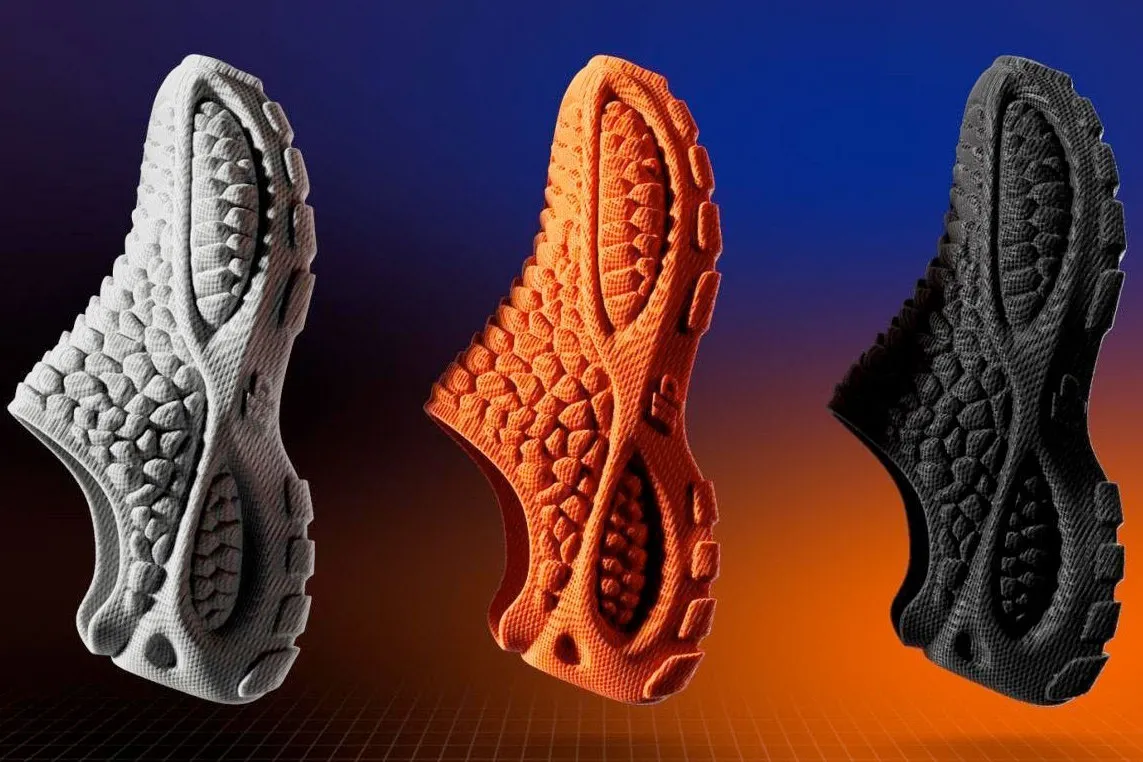

Common 3D Printing Methods for Shoe Molds
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Process: A laser fuses powdered material (often nylon) layer by layer to create a solid object.
- Advantages: Excellent for creating complex geometries and strong parts.
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Process: A thermoplastic filament is melted and extruded layer by layer to build a part.
- Advantages: Cost-effective and widely accessible, making it popular for prototyping.
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- Process: A UV laser cures liquid resin into solid plastic, layer by layer.
- Advantages: Produces high-resolution parts with smooth finishes.
3.2 Cost Breakdown of 3D Printed Shoe Molds
When considering the costs associated with 3D printing shoe molds, it’s essential to break down the various elements involved. Here’s a detailed overview:
| Cost Element | SLS | FDM | SLA |
| Initial Setup Costs | Moderate | Low | Moderate |
| Material Costs | Moderate | Low | Moderate |
| Labor Costs | Low (automated) | Low (easy operation) | Moderate |
| Production Time | Fast | Moderate | Fast |
| Maintenance Costs | Moderate | Low | Moderate |
3.3 Advantages and Disadvantages of 3D Printing
Advantages
- Rapid Prototyping:
- 3D printing allows for quick iterations of designs, enabling manufacturers to test and refine their molds faster than traditional methods.
- Customization:
- Each mold can be tailored to specific designs or individual customer needs, offering unparalleled flexibility.
- Reduced Material Waste:
- Since 3D printing is an additive process, it generates less waste compared to subtractive methods like CNC machining or manual carving.
- Complex Designs:
- 3D printing can produce intricate shapes and structures that would be challenging or impossible to create using traditional methods.
Disadvantages
- Material Limitations:
- While advancements are being made, the range of materials suitable for 3D printing is still more limited compared to traditional methods.
- Surface Finish:
- Parts produced through 3D printing may require post-processing to achieve a smooth finish, which can add time and costs.
- Initial Investment:
- Although costs are decreasing, high-quality 3D printers can still require a significant initial investment.
3D printing technology is reshaping the landscape of shoe mold production, offering numerous advantages such as rapid prototyping, customization, and reduced waste. However, it also comes with its own set of challenges, including material limitations and the need for post-processing. As we move forward in this article, we will compare the costs of 3D printed shoe molds to those produced through traditional methods, providing a clearer picture of which approach may be more beneficial for manufacturers in today’s competitive footwear market.
Cost Comparison
In the ever-evolving landscape of footwear manufacturing, understanding the cost implications of different mold-making methods is crucial for brands aiming to stay competitive. With traditional methods and 3D printing both offering unique advantages, this section will provide a detailed cost comparison between the two approaches. We will analyze direct costs, indirect costs, and long-term implications to help manufacturers make informed decisions.
4.1 Direct Cost Comparison
When comparing the direct costs associated with traditional methods and 3D printing for shoe molds, it’s essential to consider several key factors. Here’s a side-by-side comparison:
| Cost Element | Traditional Methods | 3D Printing |
| Initial Setup Costs | High | Moderate |
| Material Costs | Moderate to High | Moderate |
| Labor Costs | High | Low |
| Production Time | Long | Short |
| Cost per Unit (Low Volume) | High | Moderate to Low |
| Cost per Unit (High Volume) | Moderate | Moderate |
4.2 Indirect Costs
Beyond direct costs, it’s essential to consider indirect costs that can impact the overall financial picture:
- Lead Times:
- Traditional Methods: Longer lead times can delay production schedules and impact time-to-market.
- 3D Printing: Faster production allows brands to respond quickly to market demands, potentially leading to increased sales.
- Inventory Costs:
- Traditional Methods: High initial production runs may require significant inventory, increasing storage costs.
- 3D Printing: On-demand production reduces the need for large inventories, minimizing storage costs.
- Flexibility and Scalability:
- Traditional Methods: Scaling up production can be challenging and costly, especially for custom designs.
- 3D Printing: Easily adaptable for small or large runs, allowing for rapid changes in design without significant cost implications.
4.3 Long-Term Cost Implications
When evaluating the long-term costs of each method, several factors come into play:
- Maintenance Costs:
- Traditional Methods: Molds can wear out over time and require maintenance or replacement, adding to long-term costs.
- 3D Printing: While printers also require maintenance, the molds created can be more easily updated or modified without starting from scratch.
- Adaptability:
- Traditional Methods: Adapting to new designs often requires new molds, which can be expensive and time-consuming.
- 3D Printing: Designers can modify digital files quickly, allowing for easy adaptations and updates to existing molds.
- Sustainability Considerations:
- Traditional Methods: Higher material waste and energy consumption can lead to increased costs and environmental impact.
- 3D Printing: Generally produces less waste and allows for more sustainable practices, which can be a selling point for eco-conscious consumers.
The cost comparison between traditional methods and 3D printing for shoe molds reveals significant differences that can influence a manufacturer’s decision-making process. While traditional methods may offer durability and quality, they often come with higher initial and long-term costs. In contrast, 3D printing provides a more flexible, cost-effective solution that is well-suited for today’s fast-paced market. As we move to the next section, we will explore real-world case studies that highlight the successful implementation of 3D printed shoe molds, providing further insights into the practical applications of this innovative technology.
Case Studies
As we delve into the practical applications of 3D printing in shoe mold production, real-world case studies can provide valuable insights into how brands are leveraging this technology to enhance their manufacturing processes. In this section, we will explore successful implementations of 3D printed shoe molds, analyze the outcomes, and compare them with traditional methods. Additionally, we will look at examples of companies that continue to rely on traditional methods and the results they achieve.
5.1 Successful Implementation of 3D Printed Shoe Molds
Case Study 1: Adidas
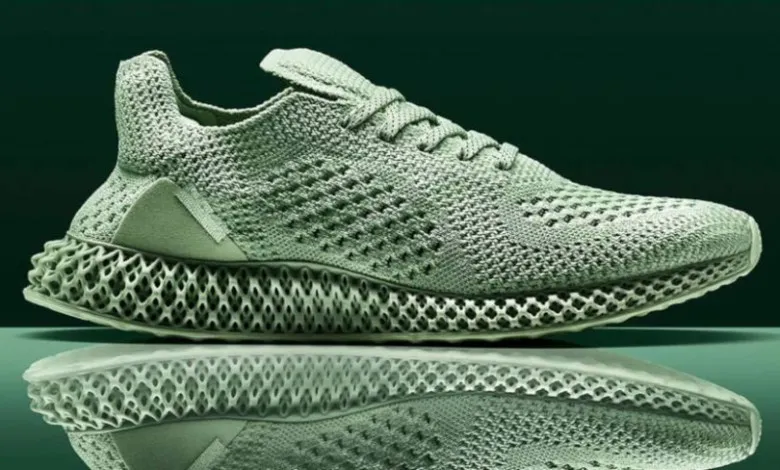

Overview:
Adidas has been at the forefront of integrating 3D printing technology into its footwear production. The company launched its “Futurecraft” initiative, which focuses on customizing shoes using 3D-printed molds.
- Technology Used: Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Key Benefits:
- Customization: Adidas can produce personalized shoe molds that cater to individual customer preferences.
- Reduced Lead Times: The time from design to production has significantly decreased, allowing Adidas to respond quickly to market trends.
- Sustainability: The company has reduced material waste by utilizing 3D printing, aligning with its environmental goals.
Results:
Adidas reported a significant reduction in production costs and lead times, enabling them to launch new products faster and with higher customer satisfaction. The Futurecraft line has received positive feedback for its fit and performance.
Case Study 2: New Balance
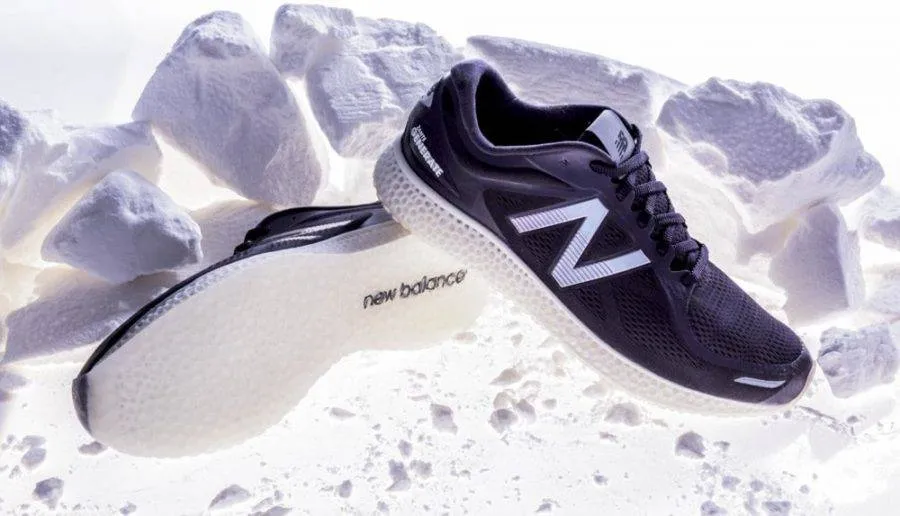

Overview:
New Balance has embraced 3D printing to enhance its manufacturing capabilities, particularly in producing custom insoles and shoe molds.
- Technology Used: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Key Benefits:
- Rapid Prototyping: New Balance can quickly iterate on designs, leading to improved product development cycles.
- Cost Efficiency: The ability to produce molds on-demand reduces inventory costs and waste.
Results:
By integrating 3D printing, New Balance has improved its ability to offer customized footwear solutions, resulting in increased sales and customer loyalty. The company has also reported lower production costs due to reduced waste and faster turnaround times.
5.2 Traditional Methods in Practice
Case Study 3: Nike

Overview:
Nike has long relied on traditional mold-making techniques to produce its footwear. While the company is exploring 3D printing, it still maintains a robust traditional manufacturing process.
- Technology Used: CNC Machining and Manual Carving
- Key Benefits:
- Quality Control: Nike’s established methods ensure high-quality finishes and durability.
- Brand Legacy: The company’s reputation for quality has been built over decades of traditional craftsmanship.
Results:
While Nike continues to produce high-quality footwear, the company faces challenges in terms of lead times and adaptability. The reliance on traditional methods has led to longer production cycles, which can hinder responsiveness to market changes.
Case Study 4: Puma

Overview:
Puma has also maintained traditional methods for creating shoe molds, focusing on quality and craftsmanship.
- Technology Used: Manual Carving and Casting
- Key Benefits:
- Artisanal Quality: The company emphasizes the craftsmanship involved in its mold-making process.
- Consistency: Established processes ensure that molds are consistently produced.
Results:
Puma’s commitment to traditional methods has resulted in high-quality products, but like Nike, the company has experienced challenges with scalability and speed. As consumer demand for rapid customization grows, Puma may need to explore integrating 3D printing into its processes.
The case studies presented illustrate the diverse approaches brands are taking in mold production. Companies like Adidas and New Balance have successfully adopted 3D printing, reaping the benefits of customization, reduced lead times, and sustainability. In contrast, traditional brands like Nike and Puma continue to rely on established methods, which provide quality but may limit their agility in a fast-paced market. As we look towards the future, the footwear industry may see an increasing blend of both methods, leveraging the strengths of each to meet evolving consumer demands. In the next section, we will explore future trends in shoe mold production, including innovations in 3D printing and sustainability considerations.
Future Trends
As the footwear industry continues to evolve, the methods used for producing shoe molds are also undergoing significant transformations. With advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on sustainability, the future of shoe mold production is poised for exciting changes. In this section, we will explore the innovations in 3D printing for footwear, the role of sustainability, and predictions for what lies ahead in the industry.
6.1 Innovations in 3D Printing for Footwear
The field of 3D printing is rapidly advancing, and several key innovations are shaping the future of shoe mold production:

1. Advanced Materials
- New Filaments and Resins: Innovations in materials are making 3D printing more versatile. For example, flexible filaments and durable resins are now available, allowing for the production of molds that can withstand the rigors of footwear manufacturing.
- Bio-based Materials: Sustainable materials derived from renewable sources are gaining traction, enabling brands to reduce their environmental footprint.
2. Multi-Material Printing
- Combining Properties: Multi-material 3D printing allows manufacturers to create molds with varying properties, such as flexibility and rigidity, within a single print. This capability can lead to more functional and comfortable footwear designs.
3. Enhanced Speed and Efficiency
- Faster Printing Technologies: New printing technologies, such as Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP), offer significantly faster printing speeds compared to traditional methods, reducing lead times and costs.
- Automation in Production: The integration of automated systems in 3D printing processes can streamline production workflows, making it easier for manufacturers to scale operations.
6.2 The Role of Sustainability
Sustainability is becoming a central focus in the footwear industry, and 3D printing offers several advantages in this regard:
1. Reduced Material Waste
- Additive Manufacturing Benefits: Unlike traditional subtractive methods, 3D printing uses only the material necessary for production, significantly minimizing waste. This is particularly important in an industry where material costs can be high.
2. Eco-Friendly Materials
- Sustainable Sourcing: The development of eco-friendly materials, such as biodegradable filaments and recycled plastics, aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products. Brands that adopt these materials can enhance their market appeal.
3. Localized Production
- On-Demand Manufacturing: 3D printing enables on-demand production, allowing brands to manufacture shoes closer to their target markets. This reduces transportation emissions and aligns with the principles of sustainability.
6.3 Predictions for the Future of Shoe Mold Production
As we look ahead, several trends are likely to shape the future of shoe mold production:
1. Increased Adoption of 3D Printing
- Mainstream Integration: As the technology becomes more accessible and cost-effective, we can expect a broader adoption of 3D printing in the footwear industry, particularly for custom and limited-edition releases.
2. Hybrid Manufacturing Models
- Combining Techniques: The future may see a hybrid approach where traditional methods are combined with 3D printing to leverage the strengths of both. This could lead to more efficient production processes and enhanced product quality.
3. Greater Customization Options
- Personalized Footwear: Advances in 3D printing technology will likely enable brands to offer even more personalized footwear options, catering to individual customer preferences and foot shapes.
4. Focus on Circular Economy
- Sustainable Practices: As the circular economy gains traction, brands may increasingly focus on designing products that can be easily recycled or repurposed, further reducing waste in the footwear industry.
Conclusion
The future of shoe mold production is bright, with innovations in 3D printing and a strong emphasis on sustainability driving change. As brands adapt to these trends, we can expect to see a more efficient, eco-friendly, and customer-centric footwear industry. The integration of advanced technologies and sustainable practices will not only enhance production capabilities but also resonate with the growing consumer demand for responsible and innovative products. As we conclude this exploration, it’s clear that the footwear industry stands at the cusp of a transformative era, one that promises to redefine the way we think about shoe molds and manufacturing processes.


