In the vast and ever-evolving world of 3D printing, a striking technology that is transforming the landscape of additive manufacturing is Digital Light Processing (DLP). As we remove the veil of this innovative technology, you’ll discover just how pivotal it is, and why it’s taking the 3D printing industry by storm.

Crafted from the fusion of digital technology and fine artistry, DLP 3D printing brings to life intricate models, boasting precision, speed, and versatility. It is truly a feast for the eyes, both in the process and the results, and is widely appreciated for its high-quality output and efficiency.
In this comprehensive guide, we will journey through the multifaceted realm of DLP 3D printing. Starting from its quintessential definition and history, we’ll delve into the technicalities of how it works and the core components that drive it. We’ll compare DLP with other 3D printing technologies, highlight its strengths, and address its limitations.
Understanding DLP 3D Printing
A. Definition and History
Digital Light Processing, popularly known as DLP is a kind of stereolithography (SLA) technology that utilizes digital projectors to solidify photo-sensitive resin, layer by layer, to form a 3D object. Its inception traces back to the late 1980s, with the Texas Instruments pioneering its development.
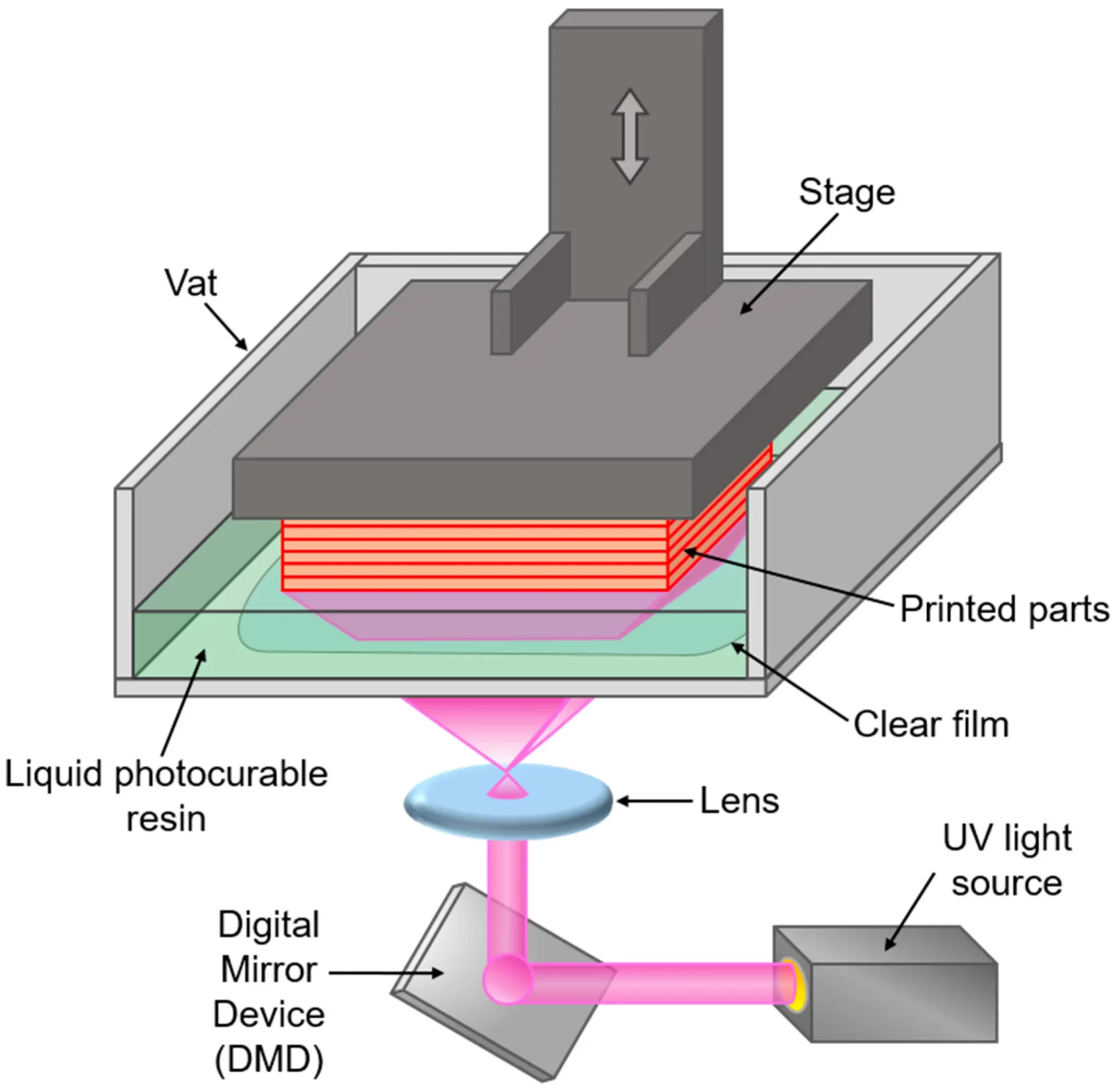
B. How DLP Works
DLP 3D printing, at its core, uses an ultraviolet light source, typically an LED, which projects light onto a vat of photopolymer resin.
Here are the main steps:
- Layer Projection: The image of a single layer is projected onto the resin.
- Exposure: The photosensitive resin solidifies upon absorbing the UV light.
- Lifting: The build platform lifts to detach the freshly printed layer.
- Repeat: The process repeats until the entire object is printed.
The originality of DLP lies in the simultaneous projection of entire layers, allowing for significantly fast printing speeds.
C. Core Components of a DLP 3D Printer
Below is a quick insight into the essential parts of a DLP 3D printer:
Light Source
The most vital part that emits UV light for curing the resin.
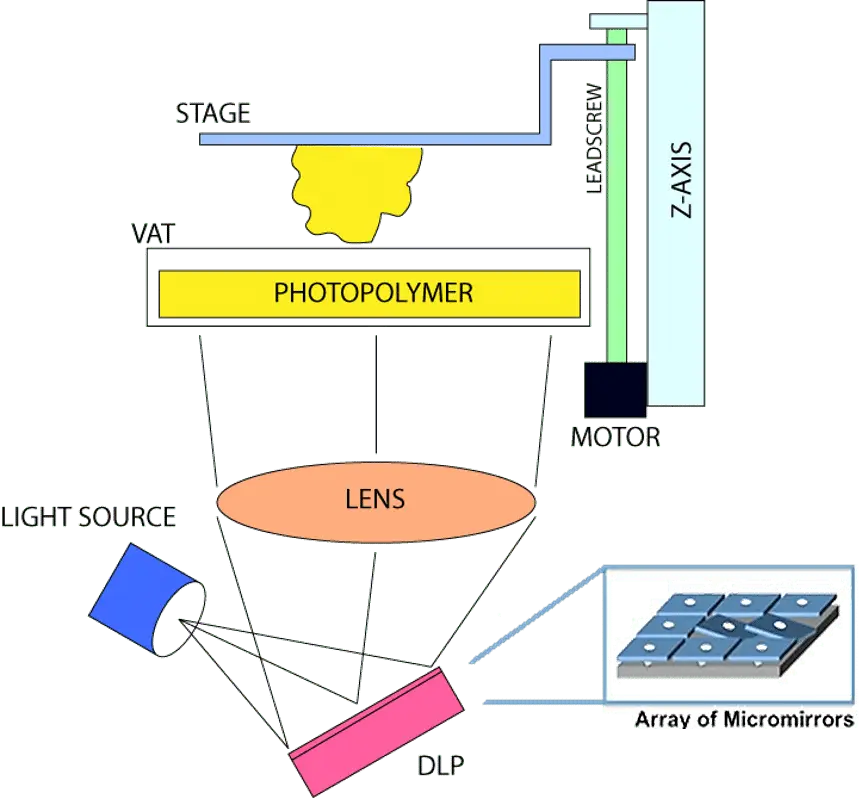
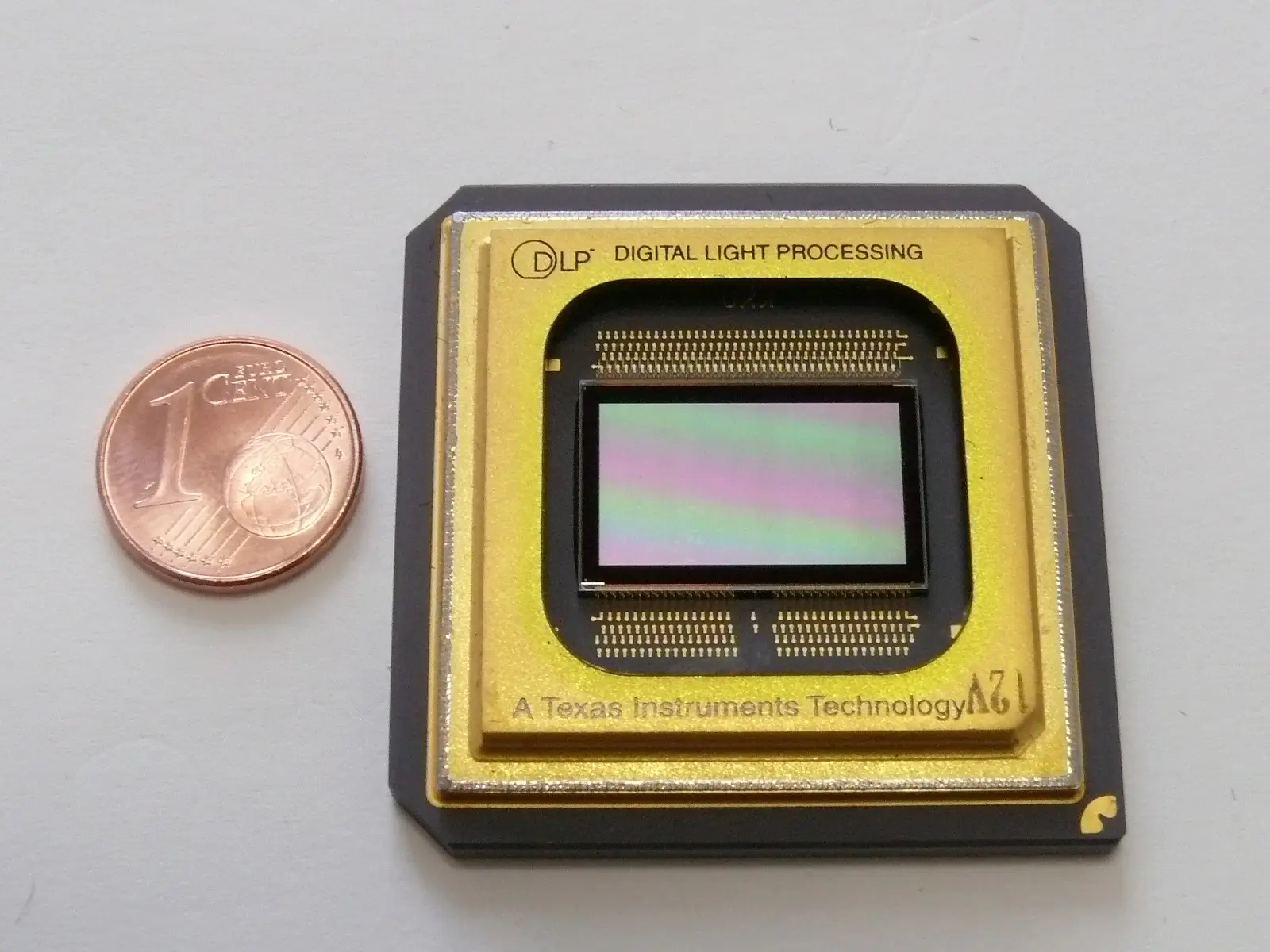
DLP Chip
A digital micromirror device (DMD) made of tiny mirrors, each representing a pixel.
Resin tank
The vessel containing the photopolymer resin.
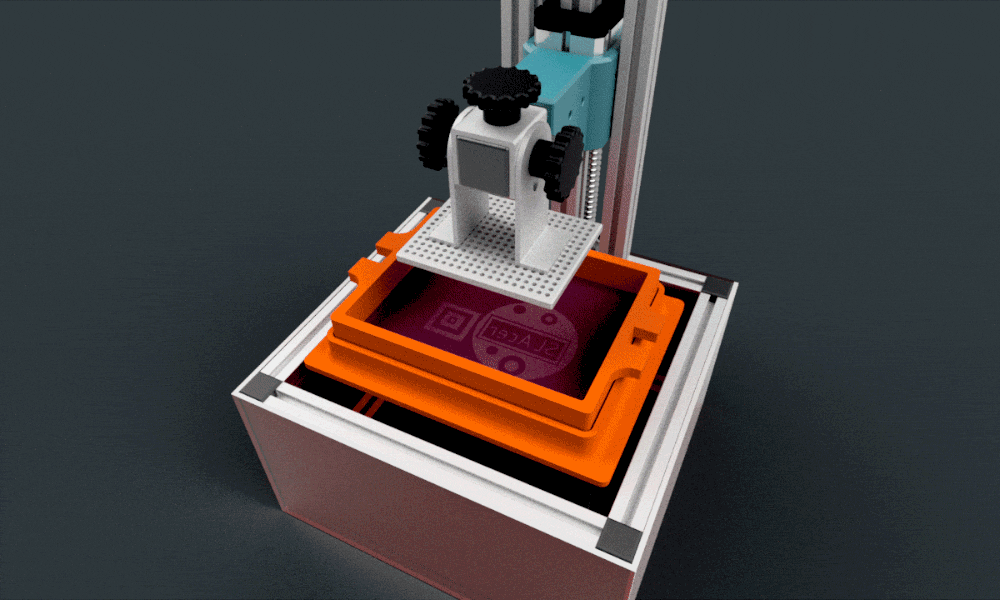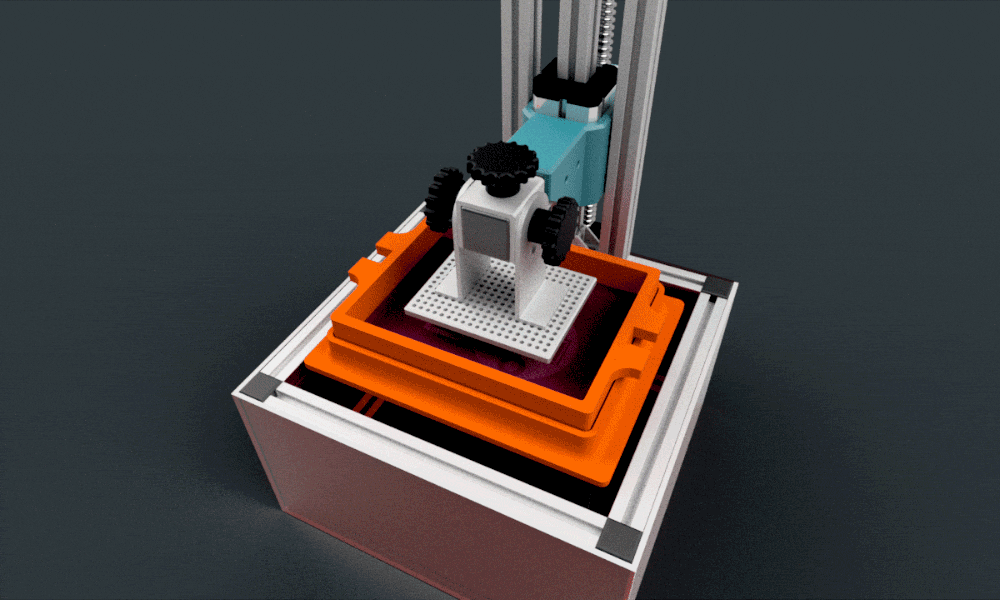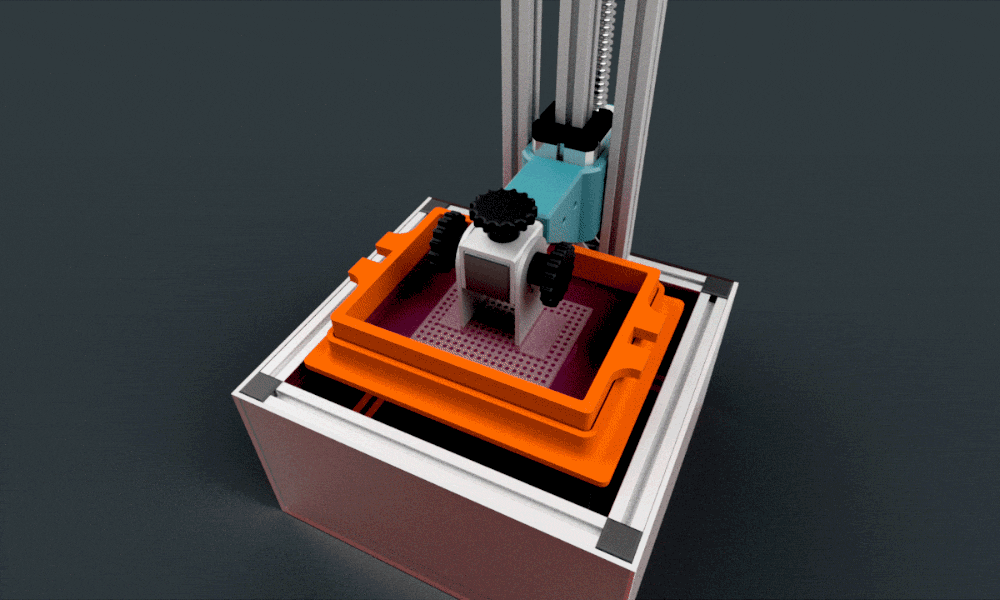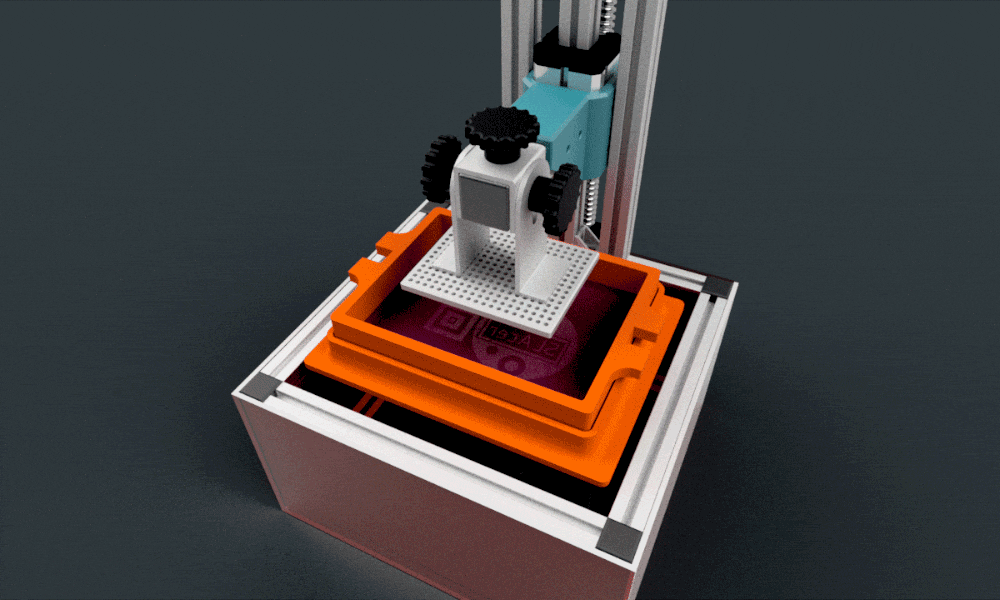
Build Platform
Where the final object takes shape.
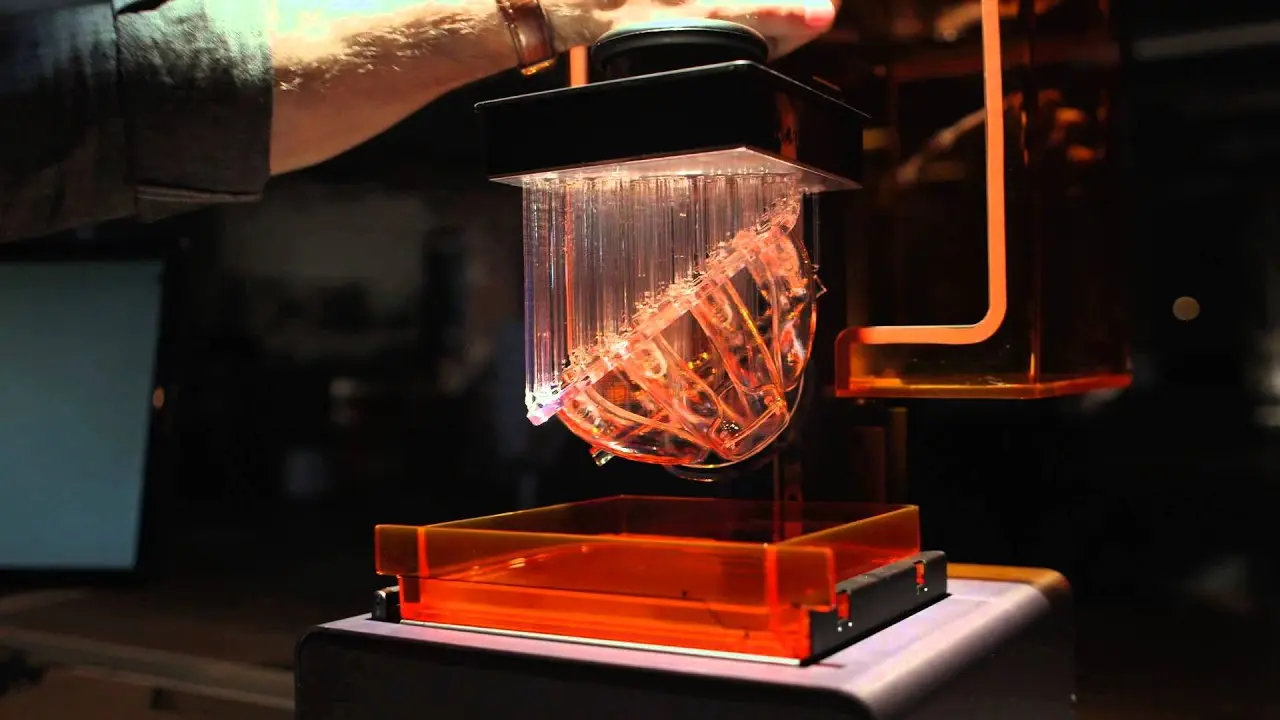

Comparison of DLP with Other 3D Printing Technologies
When it comes to 3D printing, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Different technologies offer unique pros and cons. Understanding these can help determine the best fit for specific applications. In this section, we’ll focus on how DLP compares to other popular 3D printing technologies—namely Stereolithography (SLA) and Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM).
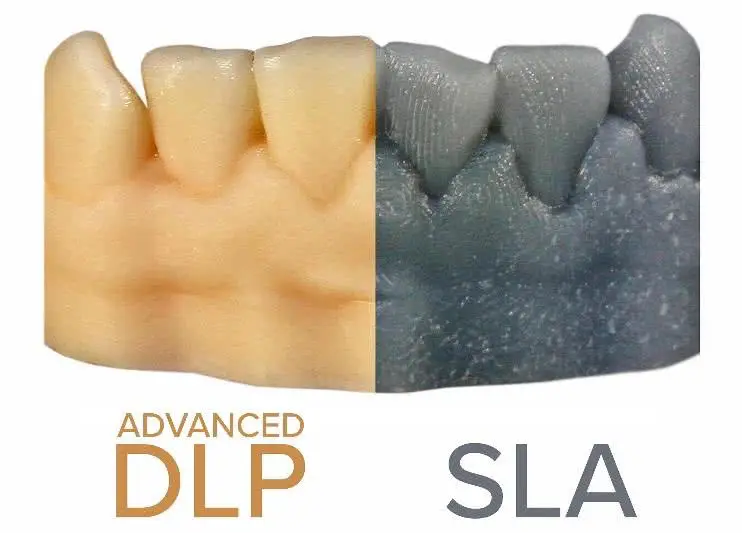
A. DLP vs SLA: What’s the Difference?
SLA, like DLP, uses photopolymers which are solidified with light. Despite the common UV-based technique, the difference lies in how the light is applied.
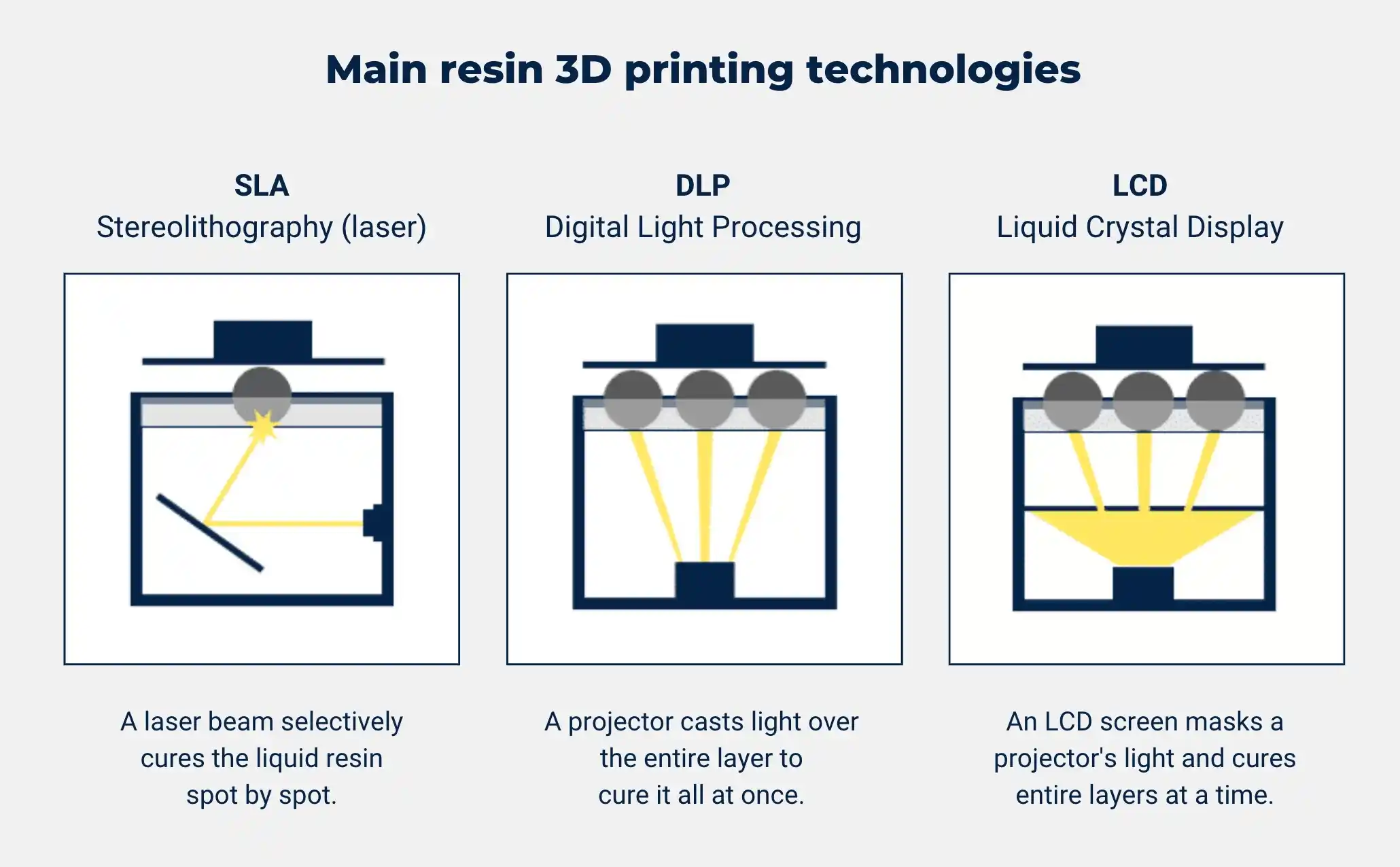
Stereolithography (SLA): Uses a laser beam to trace and solidify each layer, focusing on individual points, which makes the process slower.
Digital Light Processing (DLP): Projects the entire layer in a single shot—thus speeding up the process, especially for larger parts or multiple objects.
B. DLP vs FDM: Distinctions and Characteristics
FDM, short for Fused Deposition Modeling, represents a vastly different approach where a plastic filament is heated, extruded, and layered to form the object.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Ideal for low-cost prototyping with commonly available materials like PLA and ABS. However, the layer lines are often visible, leaving a rough surface finish.
Digital Light Processing (DLP): Known for high resolution and precision, creating smooth, detailed parts impossible with FDM. However, the materials can be costlier and require handling precautions due to their liquid state and sensitivity to UV light.
C. Why Choose DLP over Others
Though your choice will depend on the specific needs of your project, several reasons make DLP a popular choice:
- Speed: DLP’s layer-by-layer approach makes it faster, particularly if you’re printing at high volumes.
- Precision: If your project requires intricate details, DLP’s high resolution can capture these with great accuracy.
- Smooth Finishes: DLP objects require less post-processing giving a cleaner, professional look.
| DLP | SLA | FDM | |
| Speed | Fast | Moderate | Slow |
| Accuracy | High | High | Moderate |
| Finish Quality | Smooth | Smooth | Rough |
| Cost of Materials | High | Moderate | Low |
Advantages and Challenges of DLP 3D Printing
Each 3D printing technique has its strengths and weaknesses. This section digs deeper into the benefits DLP technology offers and the hurdles it faces to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of its capabilities.
A. Advantages of DLP 3D Printing
- Speed and Efficiency: DLP’s unique ability to project entire layers in a single go makes it significantly faster, a vital advantage, especially for large production runs.
- High Resolution and Precision: The digital micromirror device (DMD) in a DLP 3D printer can control every single pixel (or voxel), resulting in exceptional detail and precision in the final print.
- Smooth Surface Finish: DLP offers a superior surface finish compared to FDM, meaning less post-processing and a more professional looking end product.
- Cost-Effective for Bulk Prints: While the initial setup and resin costs may be high, the faster print speed can mean a lower cost-per-part for high-volume productions.
B. Challenges of DLP 3D Printing
- Material Limitations: DLP printers primarily use photopolymer resins which are more expensive and offer less material variety compared to FDM filaments.
- Post Processing Needs: Printed parts need to be cleaned and cured before use. This process requires additional time, space, and equipment.
- Limited Build Volume: DLP printers typically have a smaller build volume due to the size constraints of the digital light projector.
Remember, the right 3D printing technology for your needs depends on your specific requirements, budget, and expertise. As we continue to explore the dynamic world of DLP 3D printing, we hope that this understanding of its potential and constraints guides you in making the best decision. Up next, we will provide a guide to help you choose the best DLP 3D printer for your needs. Stay tuned!
Choosing the Right DLP 3D Printer: A Comprehensive Guide
Making an informed choice when buying a 3D printer can significantly affect both the quality of your final product and your overall printing experience. Here’s a comprehensive guide on crucial factors to consider before investing in a DLP 3D printer.
A. Accuracy and Resolution
Consider the project’s detail level required and ensure the machine’s resolution matches it. Higher resolution printers can recreate intricate details flawlessly but might come with a steeper price tag.
B. Speed and Efficiency
If time is a significant factor, a DLP 3D printer’s speed should be a priority. As we’ve discussed earlier, DLP excels over other 3D printing technologies in terms of speed, especially for bulk printing.
C. Build Volume
The size of the printer’s build volume determines the maximum size of the object it can print. Choose a printer that can accommodate your project’s size requirements.
D. Material Compatibility
Different projects demand different materials, which might not all be supported by a single printer. Check what kinds of resin a printer can use before finalizing your purchase.
E. Post-Processing Capabilities
Consider a machine with smart post-processing features to ease the post-print cleanup and curing process.
F. Budget
Last, but certainly not least, make sure to stay within your spending limits. Higher-spec printers cost more, and so it’s crucial to strike a balance between cost and necessary features.
| Factors | Description |
| Accuracy & Resolution | The level of detail the printer can accurately recreate |
| Speed & Efficiency | The rate at which the printer can complete a print |
| Build Volume | The maximum size of an object that the printer can print |
| Material Compatibility | The types of resin the printer supports |
| Post-Processing Capabilities | The printer’s in-built facilitation for post-print cleanup and curing |
| Budget | The overall cost of the printer, compared to the features it provides |
Choosing a DLP 3D printer involves striking a balance between your project requirements, budget, and the printer’s capabilities. With this comprehensive guide, we hope to ease your decision-making process, bringing you a step closer to your 3D printing ambitions. As we continue to navigate the expansive universe of DLP 3D printing, stay tuned to our next section, where we delve into tips and tricks to perfect your DLP 3D printing process!
Perfecting Your DLP 3D Printing Process: Tips and Tricks
Now that we’ve explored how to choose the best DLP 3D printer, let’s delve into the practical realm. Here are some expert tips for perfecting your DLP 3D printing process.
A. Understanding and Adjusting Parameters
DLP 3D printers offer a range of parameters that you can adjust to perfect your prints, such as layer thickness, exposure time, and lift speed. Understand what each parameter means, and don’t be afraid to experiment to achieve the best results.
B. Proper Maintenance of the Resin Tank
The quality of your 3D prints is directly dependent on the condition of your resin tank. Remember to clean your resin tank after each print job, and ensure there are no cured resin pieces before starting a new job.
C. Optimizing Part Orientation
The orientation of your model can affect both the quality of your print and your printer’s longevity. Angle your parts and use supports to ensure a successful print and minimize stress on the build plate.
D. Mastering Post-Processing
Post-processing is an art in itself. Take the time to learn about cleaning, curing, and finishing techniques to enhance the look and feel of your prints.
E. Keeping Safety Practices in Mind
Always remember, safety first! Wear gloves when handling liquid resin, clean any spills immediately, and keep your workspace ventilated.
Mastering these elements will take time, practice, and a healthy dose of patience, but the pay-off will be high-quality, precision 3D prints. Plus, you’ll have gained additional expertise in the fine art of DLP 3D printing.
Exciting Applications of DLP 3D Printing
DLP 3D printing is not just a fascinating technology – it’s a game-changer in a wide variety of professions and industries. In this section, we’ll explore a few exciting applications.
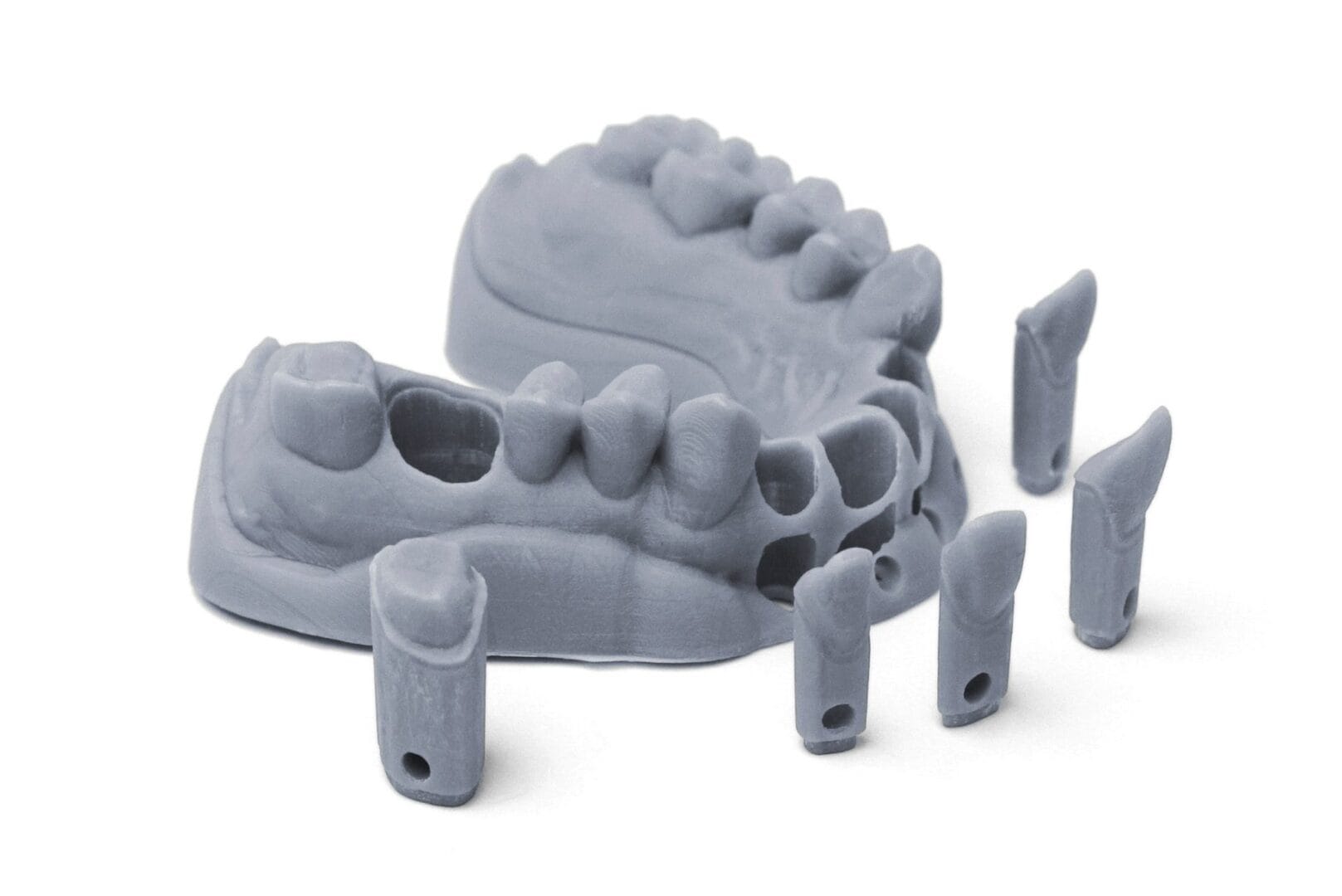
Dentistry
DLP 3D printing is revolutionizing dental practices, with its ability to accurately fabricate crowns, bridges, and a variety of orthodontic appliances using biocompatible resins.
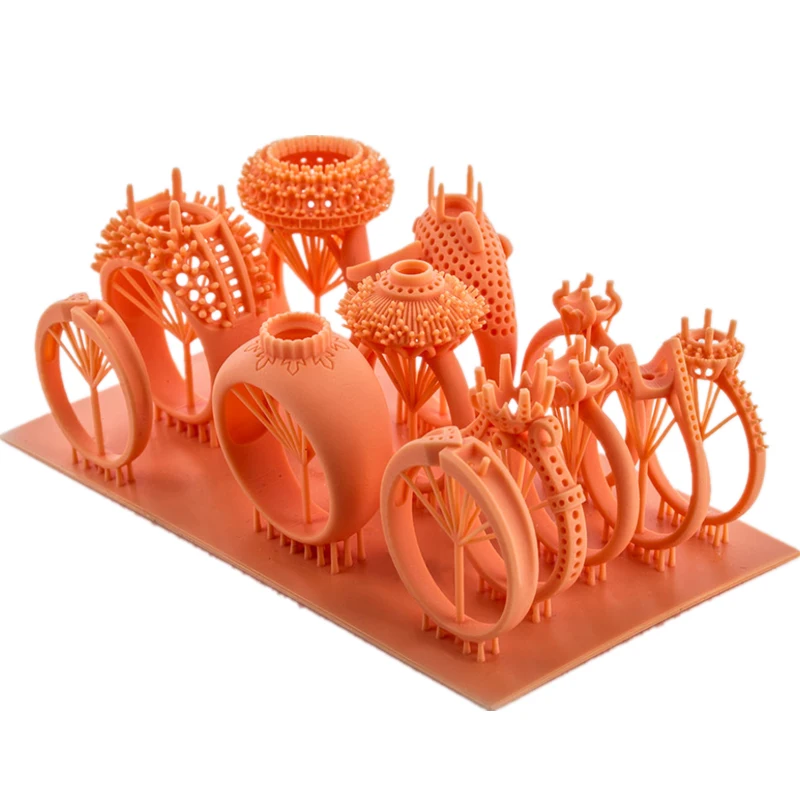
Jewelry Design
With its high resolution and precision, DLP stands as a boon for jewelry designers. They can produce intricate models with a level of detail, previously considered impossible.
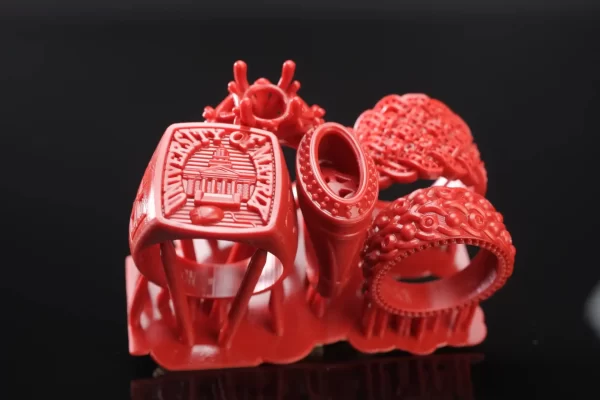

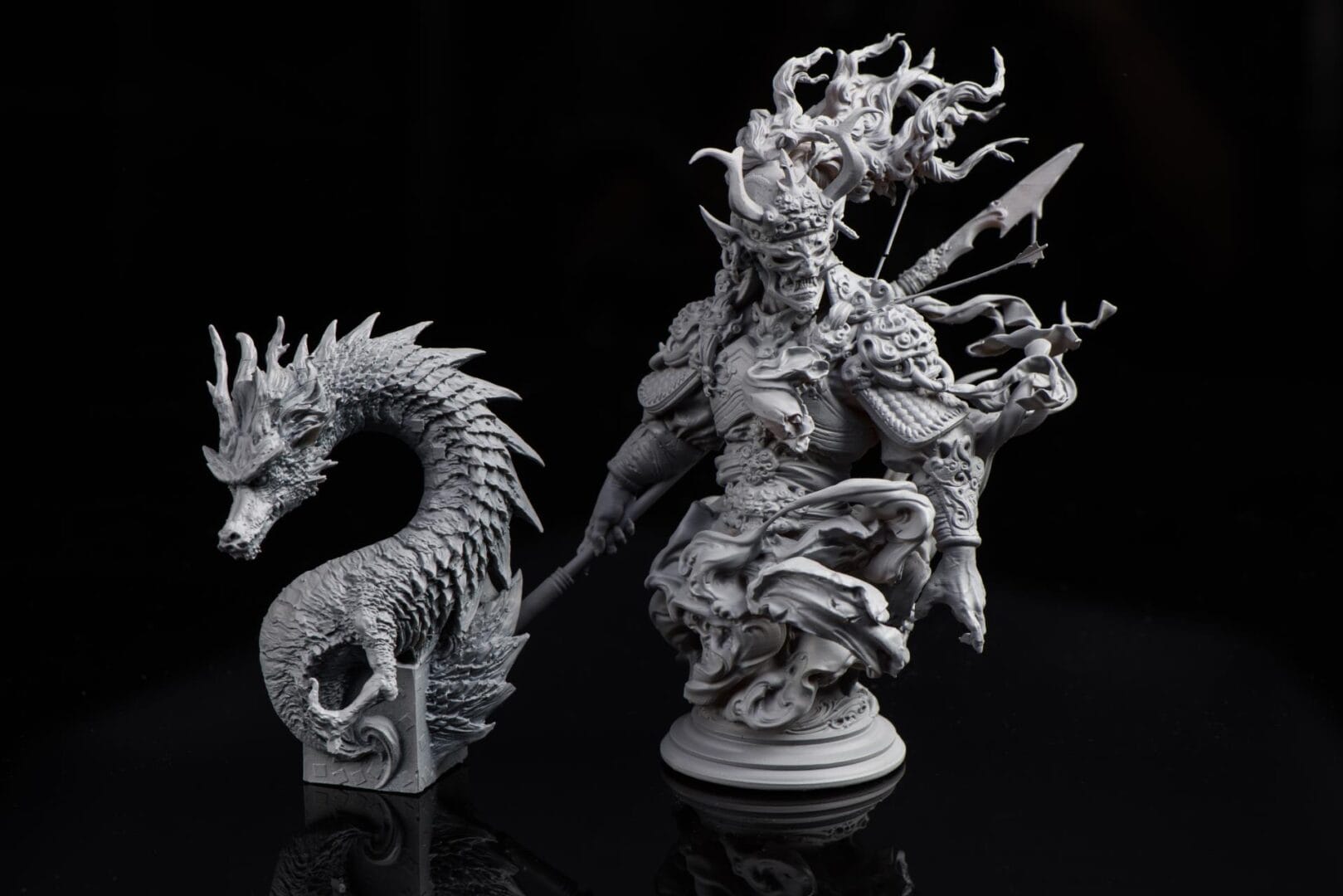
Prototyping
DLP’s speed and efficiency make it a popular choice in rapid prototyping, facilitating faster design iterations and shaving off development time.

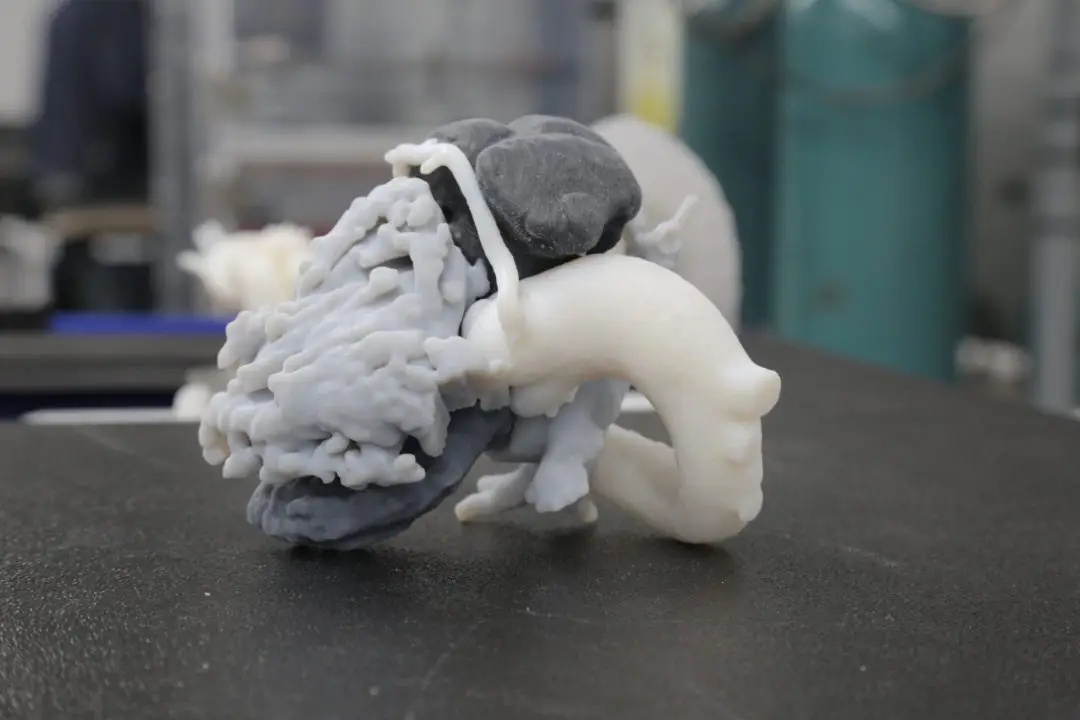
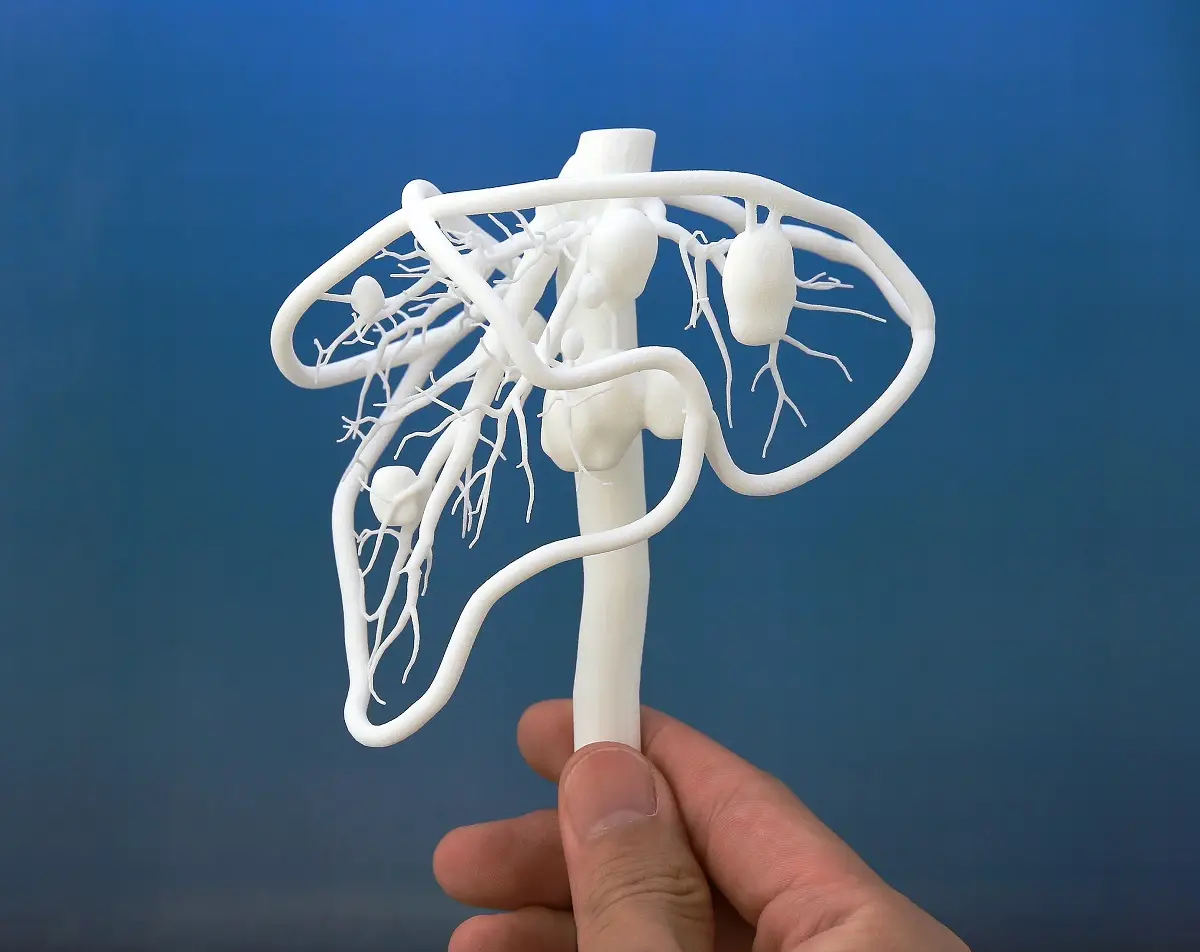
Biomedical Research
In biomedical research, DLP 3D printers are used to create highly accurate tissues and organ models, propelling advances in personalized medicine.

The applications of DLP 3D printing are seemingly endless as the technology continues to mature further. These are just a sampling of the industries where DLP 3D printing is making its remarkable mark.
The Future of DLP 3D Printing: Trends and Predictions
As we’ve seen, DLP 3D printing is already a significant technology, influencing different industrial sectors and bringing about a revolution in manufacturing. But what’s next for DLP 3D printing? This section will cover the trends and predictions shaping the future of this remarkable technology.
More Biocompatible Materials
With the rise of DLP in the medical field, we’ll likely see the development of more biocompatible materials, further enhancing medical applications.
Improved Software Capabilities
Upcoming software enhancements are set to simplify the DLP printing process even more, making it easier for beginners to get high-quality prints.
Expanding Market
With the increasing accessibility of DLP 3D printers, we’re looking at a rapidly expanding market, with more manufacturers entering the scene.
Greater Adoption in Manufacturing
More industries are likely to adopt DLP 3D printing in their manufacturing processes given its advantages in both speed and precision.
Environmental Sustainability
As the technology matures, manufacturers will find ways to make DLP more eco-friendly, contributing to sustainability goals.
The future certainly looks bright for DLP 3D Printing. As we explore this realm further, the developments we’ll experience promise to be nothing short of revolutionary. In our final section, we summarise what we’ve learned so far and suggest further resources for continued learning on this exciting subject! So, stick around.
FAQ
1.What are the requirements for materials used in DLP 3D printing?
Material Compatibility
Different projects demand different materials, which might not all be supported by a single printer. Check what kinds of resin a printer can use before finalizing your purchase. When selecting materials for DLP 3D printing, it’s crucial to consider several key requirements to ensure optimal performance and quality:
- Lower Viscosity: Choose resins with lower viscosity as they allow for faster and more uniform recoating and refilling, enhancing the efficiency of the printing process.
- Low Shrinkage: Opt for materials with low shrinkage to minimize warping. This is especially important for preserving fine details and maintaining the structural integrity of larger prints.
- Material Interaction: Avoid resins that may swell, cloud, or otherwise react negatively with the printer’s window material, as this can compromise both the print quality and the printer’s longevity.
By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure that your DLP 3D printing projects achieve the desired results without compromising on quality or detail.
More About DLP 3D Printing and Resources for Further Learning
Online Forums and Communities
Online 3D printing communities and forums are excellent places to learn. Sites like Reddit and 3D Hubs Talk are full of seasoned 3D printers sharing their experiences.
Blogs and Podcasts
Blogs and podcasts like those from All3DP, 3D Printing Industry, 3Dnatives and The 3D Printing Podcast provide latest news, trends, and insights.
Books and E-books
Books like “3D Printing for Dummies” or “The 3D Printing Handbook” provide detailed, in-depth knowledge and can be acquired in physical or digital format.
Manufacturer Resources
Many 3D printer manufacturers provide rich resources, including tutorials, guides, and technical support. Some notable ones include Formlabs, creality, zongheng3d and AnyCubic.
With these references at your fingertips, your journey into the captivating world of DLP 3D printing is just beginning. As with anything new, the learning might seem daunting at first, but remember that every expert was once a beginner. Embrace the process and have fun exploring!