Choosing the right resin for your DLP (Digital Light Processing) 3D printer is of paramount importance. The type of resin you select can immensely influence the output of your 3D printing projects. It’s a critical factor that can affect the durability, finish, acuity and even the color of your final product.
There’s a dazzling array of 3D printer resins available in the market today, each featuring unique properties and catering to specific applications. From crafting intricate jewelry to creating high precision industrial prototypes – there’s a resin for every need. But, how do you make the right choice? How do you discern which resin will best serve your project’s requirements? That’s precisely what we’ll be exploring in this comprehensive guide.
In the subsequent sections, we dive deep to understand the different resin properties, factors to consider when choosing a resin, popular resin types for DLP 3D printing, and much more. Whether you’re a hobbyist, a professional or a specialist in dentistry, engineering, or jewelry, this guide will arm you with the knowledge and insights to make an informed decision in selecting the right resin for your DLP 3D printer.
Understanding Resin Properties
Choosing the right resin for your DLP 3D printer is not just about the brand or price; it’s about understanding the different properties that make a particular type of resin the best fit for your specific requirement. Each resin possesses diverse properties that impact how your final 3D printed object will look, feel, and function. Today, we’re going deep into the world of resin properties, exploring what they mean, and how they affect your 3D prints.
Mechanical Properties

Mechanical properties define how resin responds to physical forces. These are some key mechanical properties worth considering:
- Tensile strength: This is the resin’s resistance against breaking under tension. A higher tensile strength translates into stronger 3D prints that can withstand pulling forces without breaking.
- Elongation at break: Indicative of a resin’s flexibility, it is the degree to which a 3D printed object can stretch or deform before it breaks. Greater elongation at break means better flexibility.
- Flexural strength: The maximum amount of bending stress that a material can endure without deforming permanently. Higher flexural strength ensures that your prints won’t warp or bend easily.
- Impact resistance: This defines a 3D print’s ability to resist sudden, forceful impacts. If your print needs to endure shocks or impacts, choose a resin with high impact resistance.
Thermal Properties
In 3D printing, the thermal properties of the resin come into play considering the heat exposure during the curing process and potential applications involving high temperatures.

- Heat deflection temperature (HDT): HDT is the temperature at which a resin deforms under a specified load. Resins with high HDT are suitable for applications that require heat resistance.
- Glass transition temperature (Tg): Tg is the temperature at which the resin changes from a hard, glassy state to a rubbery state. A higher Tg means a higher operating temperature for your prints.
Optical Properties
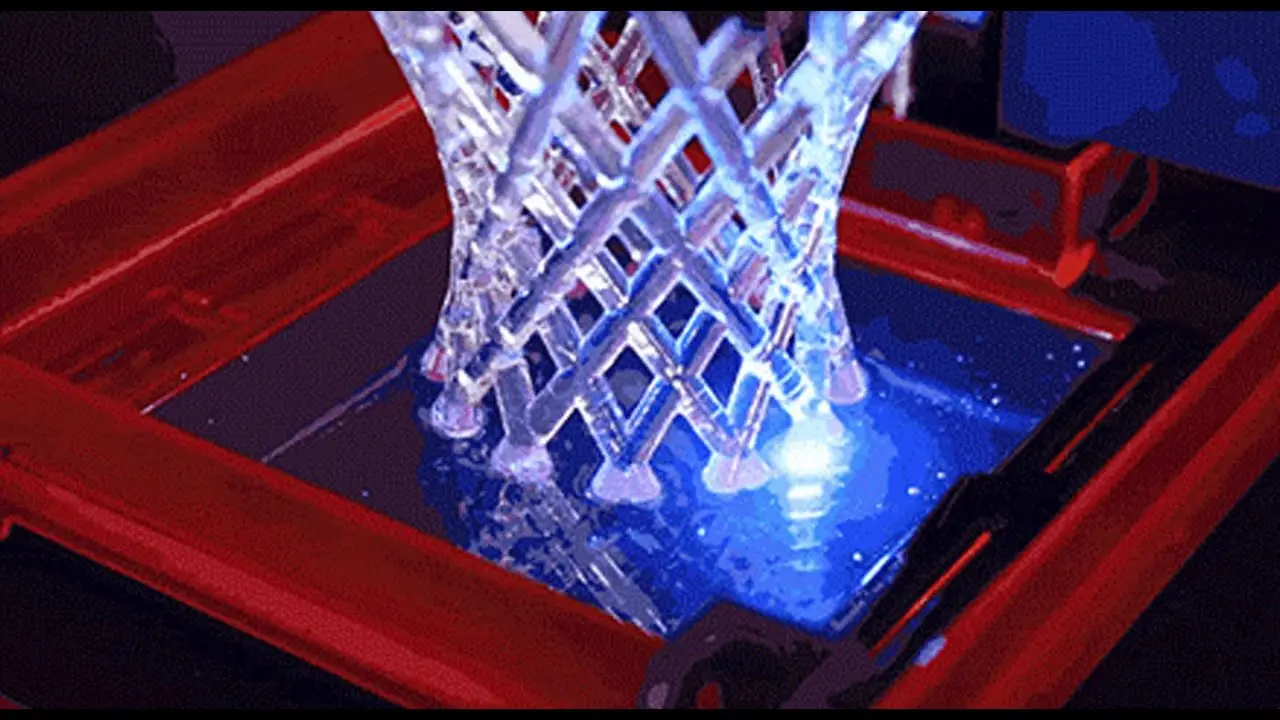
Optical properties govern how your 3D print interacts with light and color.
- Transparency: Select a clear resin if you’re aiming for transparent or see-through prints.
- Color: Resins are available in a wide array of colors, and some resins can even be painted or dyed post-printing.
Other Properties
Beyond mechanical, thermal, and optical properties, there are a few other characteristics that can influence your printing experience and the final outcome:
- Viscosity: The thickness of the resin can impact its flow and leveling during printing, affecting the final surface finish.
- Cure time: How quickly a resin cures under the DLP printer’s light source can affect your printing speed and the ultimate strength of the prints.
- Biocompatibility: If you’re printing something that will come in contact with skin or is intended for medical use, the resin must be biocompatible.
Understanding these properties allows you to make an informed decision about the best resin for your specific 3D printing project. Whether you’re crafting detailed miniatures, producing robust mechanical parts, or designing intricate jewelry, there’s a perfect resin out there just waiting to bring your ideas to life.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Resin
Once you’ve acquainted yourself with the properties of resin, the next logical step is to discern which type of resin is best suited to your specific needs. This might seem like a daunting task, given the broad spectrum of resins available, each touting unique attributes and advantages. However, by taking into consideration your project’s application, quality requirements, post-processing needs, environmental conditions, and your budget, you can make an informed choice.
Application and End-Use
Perhaps the most critical factor in choosing a resin is the intended application and end-use of your 3D printed object.
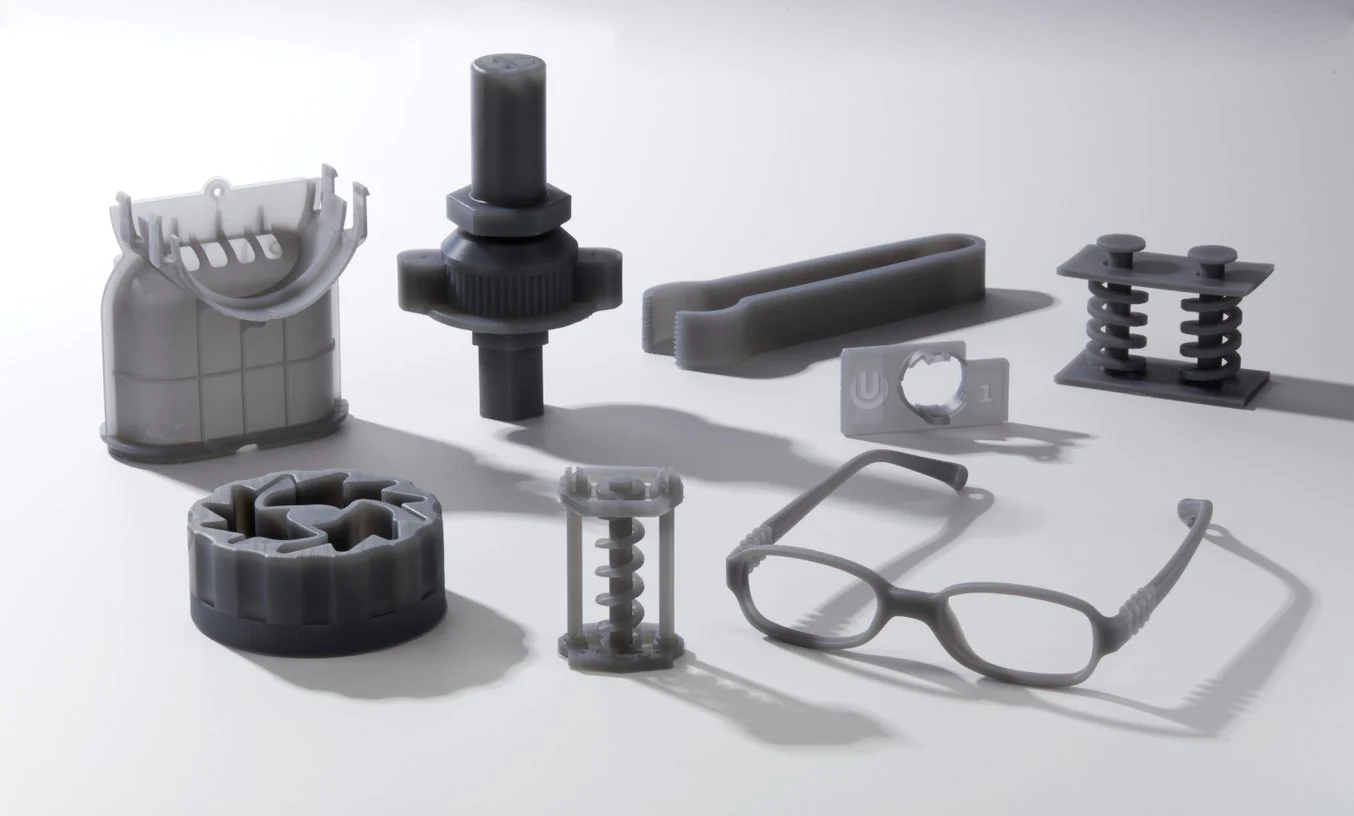

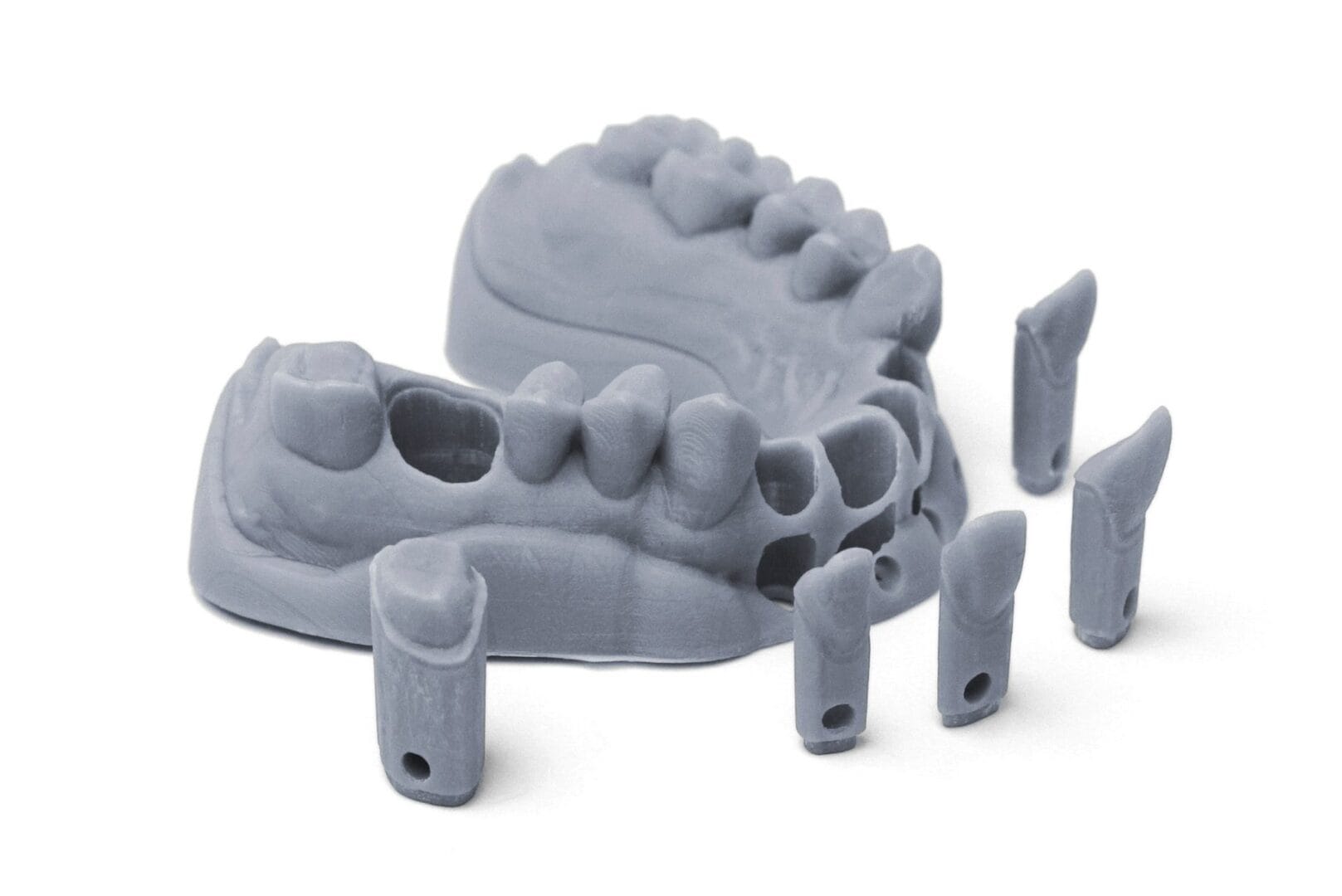

- Prototyping vs. functional parts: Prototyping resins, often more affordable, are perfect for models and prototypes where detail and aesthetics are paramount. However, if you’re printing functional parts that need to withstand wear and tear, opt for engineering or durable resins.
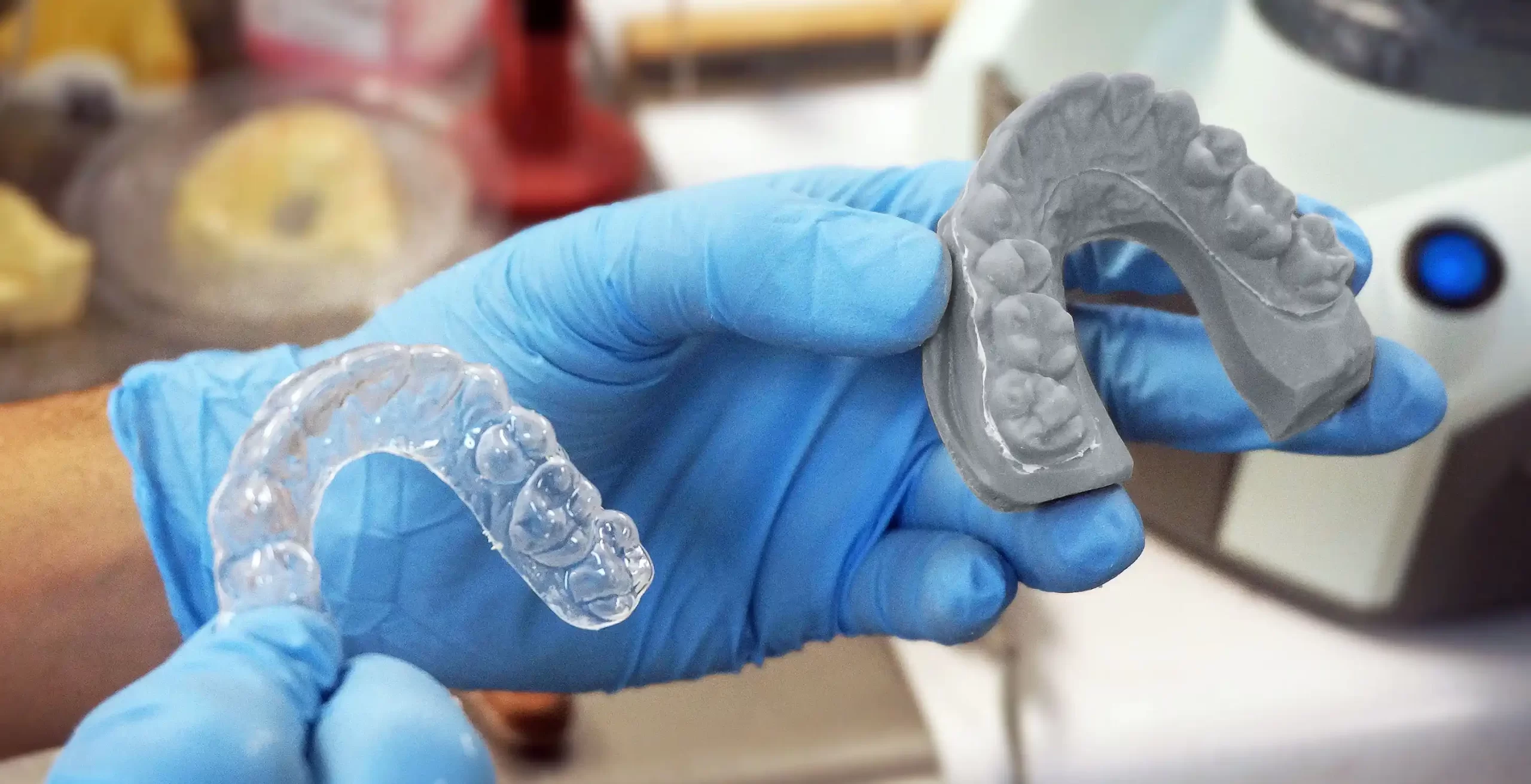
- Dental/medical applications: For dental and medical applications, it’s paramount to choose biocompatible resins that are safe for human contact.
- Jewelry casting: Castable resins, as the name suggests, are perfect for jewelry-making and other casting applications.
- Consumer products: If you’re making consumer products, consider factors like durability, finish, and safety, and choose a resin that ticks all these boxes.
Print Quality Requirements
Different resins will produce varying levels of print quality, affecting not just aesthetics, but also functionality.
- Resolution: Your choice of resin can impact print resolution. If your print needs to capture subtle details, select a resin designed for high-resolution printing.
- Surface finish: Different resins can deliver different surface finishes- from glossy and smooth to matte and textured.
- Dimensional accuracy: For precise, tightly-fitted parts, opt for resins that offer high dimensional accuracy.
Post-Processing Needs
The post-processing steps required can vary considerably between different resins.
- Sanding/polishing: Some resins are easier to sand and polish than others, an important factor if you’re aiming for a smooth, high-gloss finish.
- Painting/dyeing: If you plan to paint or dye your prints, choose a resin that adheres well to your chosen paints and dyes.
- Infiltration: Some porous prints may require infiltration with a sealant to reach their full strength and water-resistance.
Environmental Conditions
Consider the environment where your prints will be kept. For example, if the prints will be exposed to sunlight, choose UV-resistant resins.
Cost and Availability
Lastly, consider the cost and accessibility of your chosen resin.
- Price per liter: Different resins come at different prices. Always take into account your budget constraints.
- Supplier reliability: Take into account the reputation and reliability of your chosen supplier.
- Shipping and storage: Factor in shipping costs and storage requirements when selecting a resin.
Choosing the right resin is a vital step in the 3D printing process. The type of resin you choose can significantly impact the quality of your prints, and understanding how to make this selection is a skill worth mastering. Remember, the key is to understand your requirements and choose a resin that best fits those needs.
Popular Resin Types for DLP 3D Printing
The versatility of DLP 3D printing lies in the extensive array of resins available, each engineered to exhibit unique characteristics tailored for specific applications. Whether you’re crafting intricate jewelry, producing sturdy mechanical parts, or printing biocompatible dental models, there is a resin designed just for you. In this section, we will introduce some of the most popular resin types, their characteristics, and ideal applications.
Standard Resins
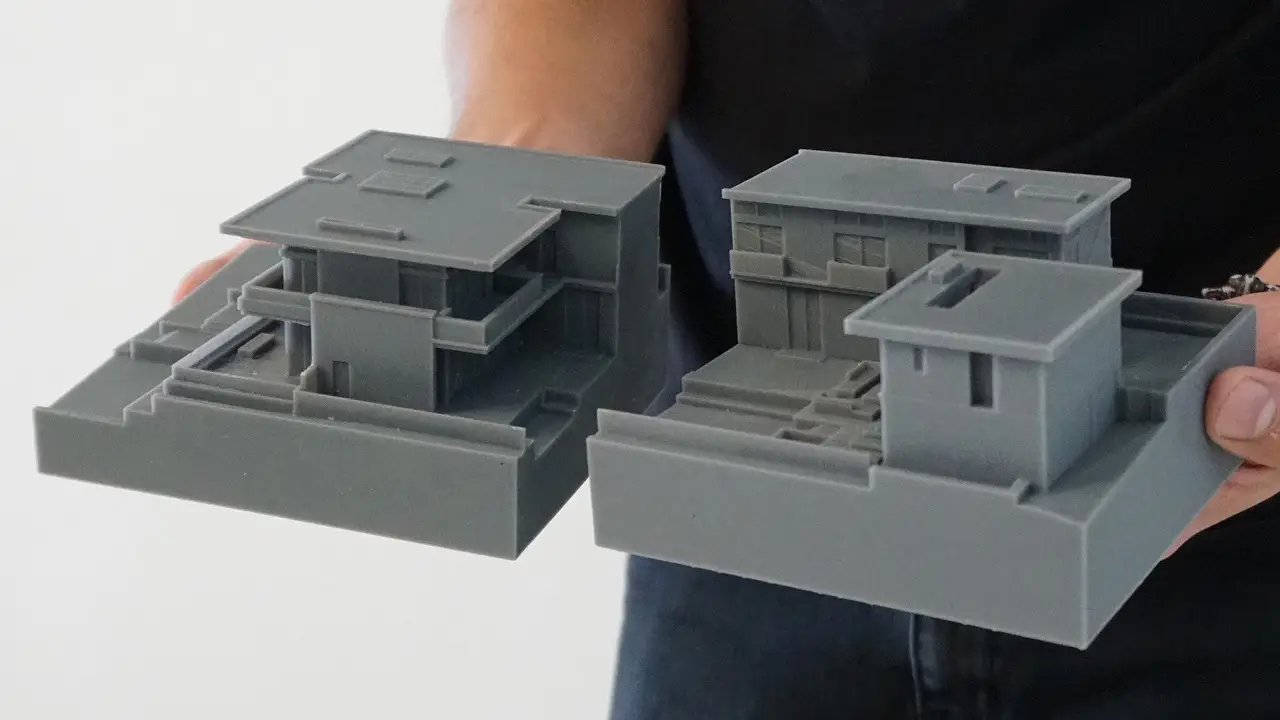
Standard resins are your trusty, go-to resins when you’re looking for a balance of detail, strength, and affordability. As the jack of all trades, they can be used for a broad range of applications, including prototyping, educational projects, and hobby modeling.
Tough Resins
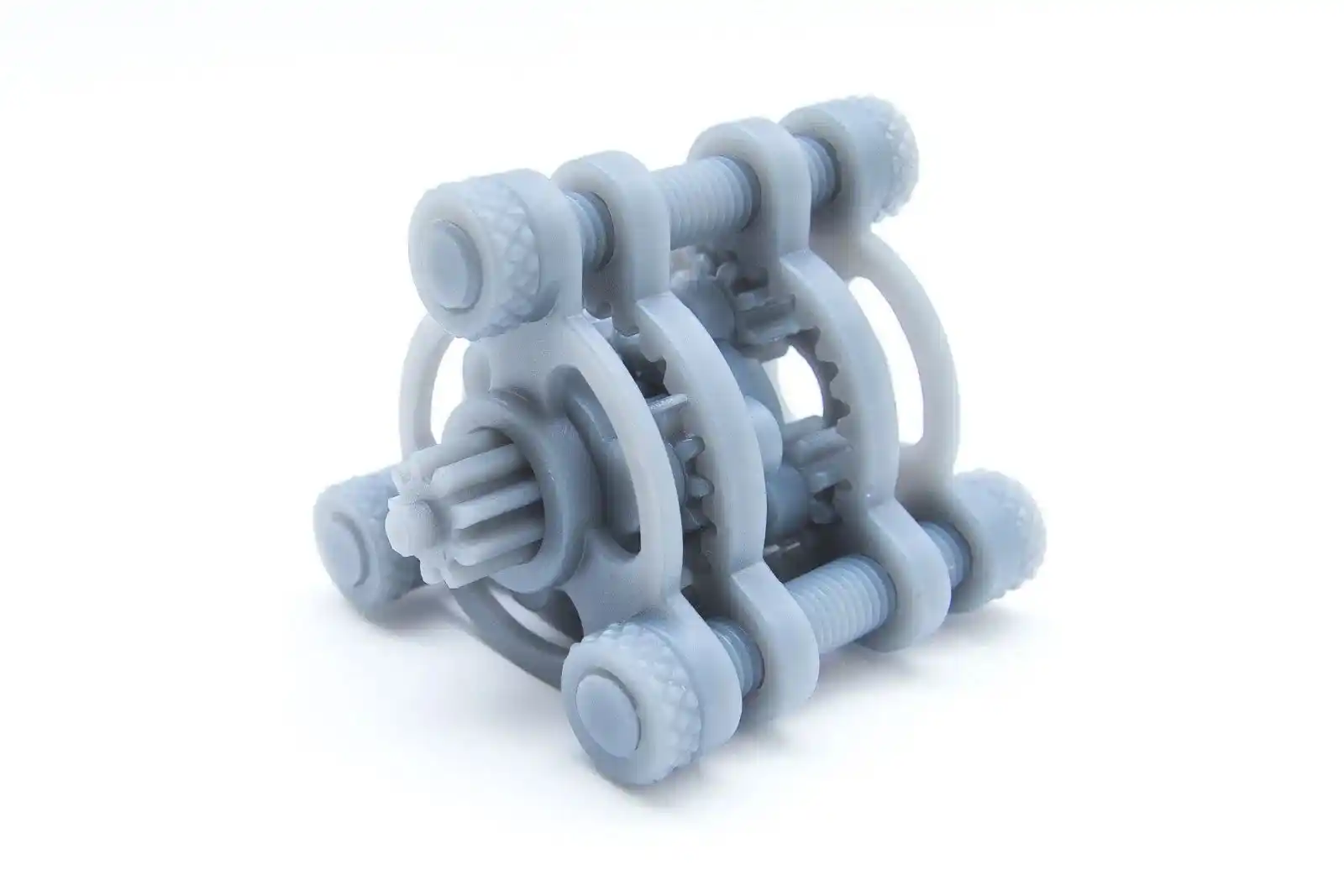
Tough resins are designed to endure high stress and strain. With their superior tensile and flexural strength, they’re excellent for printing functional parts, enclosures for electronic devices, and mechanical assemblies exposed to repetitive stresses.
Flexible Resins
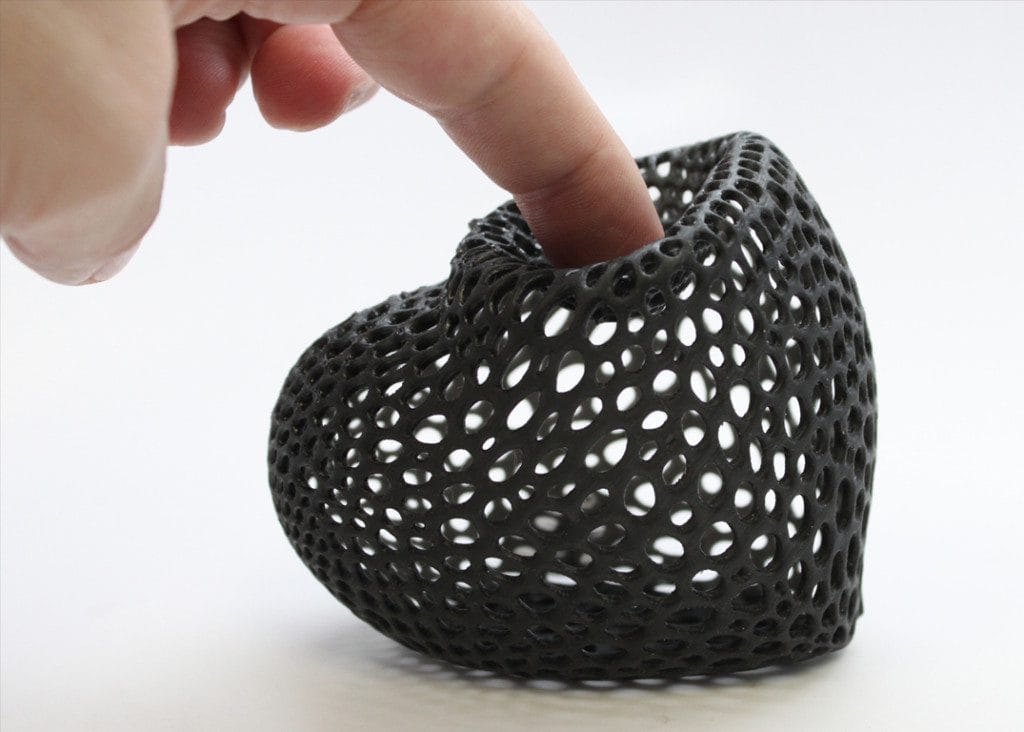

Flexible resins allow for prints with a soft, rubber-like finish. These are perfect for producing bendable models, protective cases, or components requiring a high degree of flexibility and impact resistance.
Castable Resins
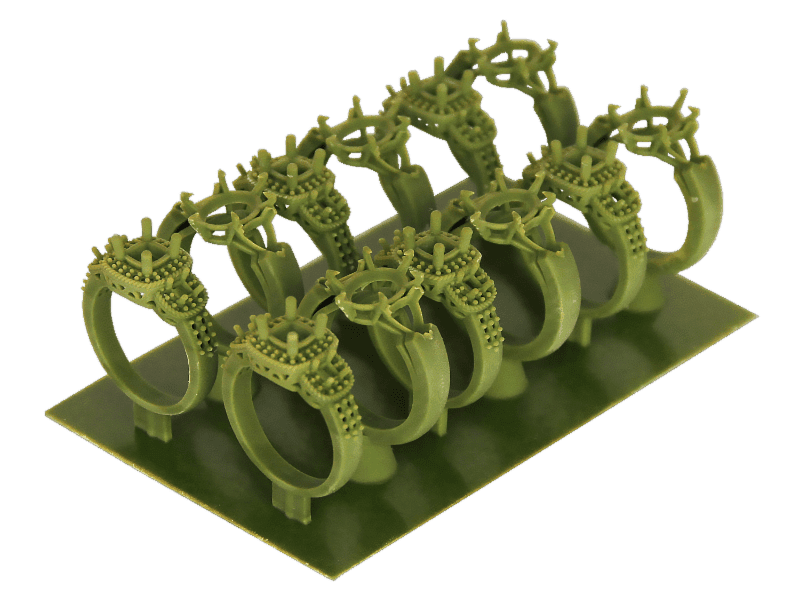
Geared towards professionals in the jewelry and dental sector, castable resins are designed for lost-wax casting/investment casting. They’re ideal for creating molds for metal casting in intricate designs.
Dental Resins
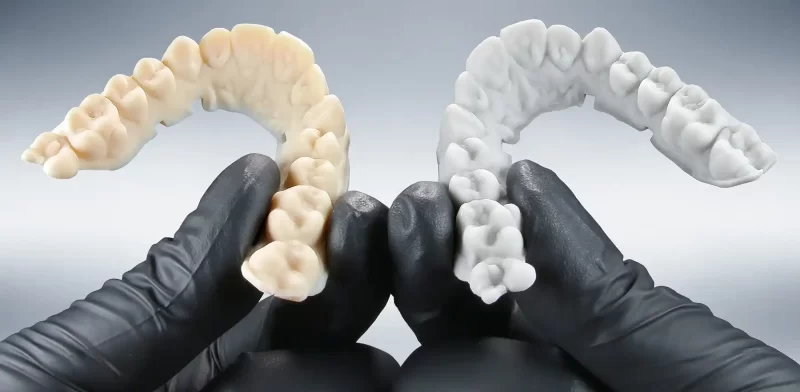
Dental resins usher 3D printing into the realm of dentistry. These biocompatible resins are used to print dental models, surgical guides, dental trays, and more, revolutionizing dental practices.
Engineering Resins
Engineering resins cater to advanced applications demanding specific material properties, such as extreme toughness, high temperature resistance, or even a combination of both.
Choosing the right resin for your applications can make all the difference in your 3D printing projects. Understanding each type’s unique characteristics allows you to select the optimal resin that meets your specific needs.
Resin Handling and Safety
Practice safe handling procedures, store them properly, and dispose of them conscientiously when it comes to 3D printer resins. Ignoring these steps could lead to compromised print quality, shortened resin life, and even potential health and safety risks.
Proper Storage and Shelf Life
Resin storage conditions can significantly impact their performance and shelf life.
- Light exposure: Resins are photosensitive, meaning they react to light. Store your resin in a place that is dark, or where it won’t be exposed to UV light, to delay the curing process.
- Temperature: Storage temperature is essential too. Generally, it’s advisable to store resins in a cool place, approximately 20°C, unless recommended otherwise by the manufacturer.
- Sealing: Always reseal your resin containers promptly after each use to avoid contamination.
- Shelf life: Check the manufacturer’s guidelines for the shelf life of the resin. Resins may deteriorate or change in properties over time if kept beyond their shelf life.
Safety Precautions
- Skin and eye contact: Always wear protective gloves when handling resins, and avoid contact with skin and eyes. If contact occurs, rinse thoroughly with water and seek medical advice if necessary.
- Inhalation: While most resins are designed to be low odor, it’s always a good idea to work in a well-ventilated area.
- PPE: Personal protective equipment, such as gloves and safety glasses, should always be used when handling resins.
Disposal and Environmental Considerations
When disposing of resins, whether in their liquid form or as part of failed prints, consult your local regulations on disposal of chemicals. Some resins may need to be treated as hazardous waste, while others can be cured thoroughly and disposed of as normal waste.
Remember, the key to working with resins is respect. Understanding that they are chemicals and treating them with the necessary precautions ensures a safe and enjoyable 3D printing experience.
Understanding Resin Profiles and Printer Settings
Configuring your 3D printer settings correctly is crucial for a successful print. Each resin has its own unique set of properties and responds differently to light exposure, making it necessary to have tailored settings for each resin – this is what we call a resin profile. In this section, we’ll delve into the essentials of resin profiles and 3D printer settings.
What is a Resin Profile?
A resin profile is essentially a set of printer settings optimized for a specific type of resin. It takes into account factors like the resin’s light sensitivity, color, and intended use to determine the ideal curing time, lift speeds, and other parameters.
Getting the right profile for your resin is crucial as it affects print quality, success rate, and the lifespan of your printer.
Key Parameters in Resin Profiles
When configuring a resin profile, these are some of the key parameters you’d need to consider:
- Layer height: This is the thickness of each layer of the print. Lower values result in higher resolution prints but increase print time.
- Exposure time: This is the time each layer is exposed to light. Too little exposure and your print might not cure properly; too much, and you might over-cure your print.
- Lift speed and distance: These determine how fast and how high the build plate lifts after each layer is printed.
Remember, these parameters are interdependent. Adjusting one might require adjustments to the others to maintain a successful print.
Configure and Test Your Resin Profile
Most resin manufacturers provide recommended settings or a starting point for their resins. However, depending on your specific printer, you may need to tweak these settings.
To configure and validate your resin profile:
- Use the resin manufacturer’s recommended settings as a starting point.
- Do a series of test prints, altering one parameter at a time.
- Observe the results of each test print, noting over-exposure or under-exposure, print failure, or other issues.
- Adjust your settings based on these observations and continue testing until you find your optimal settings.
This iterative process can take time, but the results are rewarding: an optimized printing process, high-quality prints, and reduced failures.
Setting the right resin profile is truly an intimate dance between your printer and the resin, striking the perfect balance to create the object of your desire in all its three-dimensional glory.
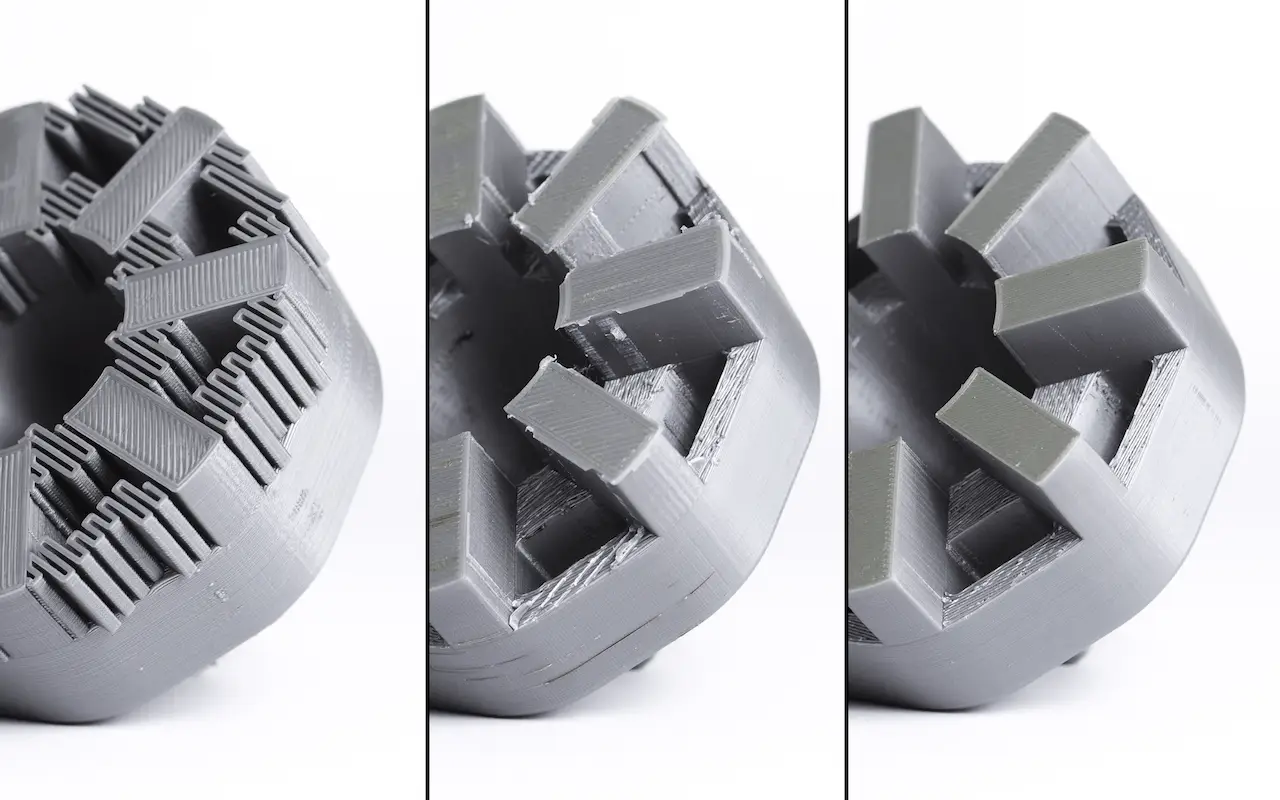
Troubleshooting Common Resin Issues
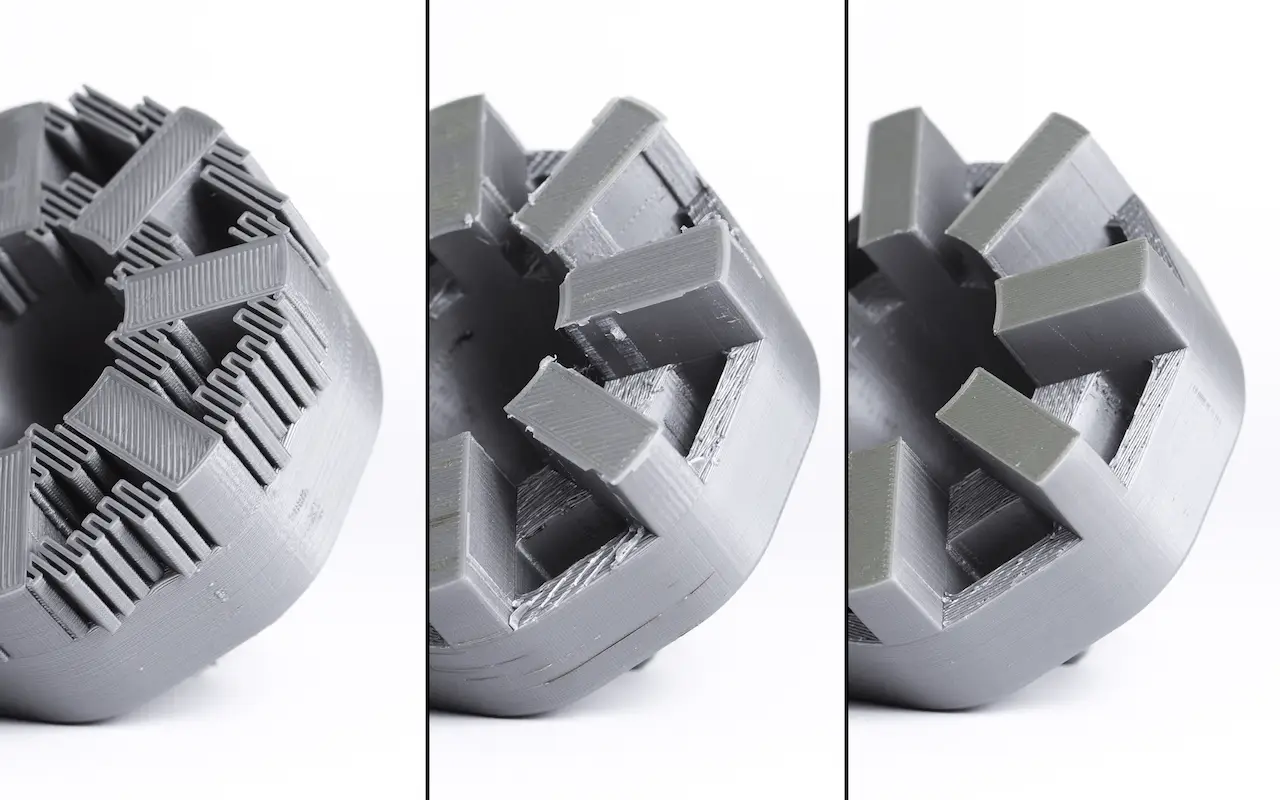
3D printing with resin is an intricate process that is often subject to a variety of potential issues. These issues can stem from the resin itself, the 3D printer, or even the external environment. To ensure the best quality prints, understanding how to diagnose and resolve common problems is essential. Let’s delve into a few common resin issues and discuss how to troubleshoot them.
Incomplete Curing
Incomplete curing is one of the most common issues encountered in resin 3D printing. This generally leads to prints that are not fully solidified and can yield parts that are lacking in detail, strength, or both.
Solution: Adjust Exposure Settings
The most straightforward way to combat incomplete curing is to adjust your printer’s exposure settings. If your prints are consistently under-cured, incrementally increase the exposure time for each layer until you achieve the desired result. However, too much exposure can lead to over-curing, so balance is key.
Warping and Deformation
Warping and deformation is another common issue that can arise. This can lead to parts that are skewed or have dimensions that do not match the original design.
Solution: Optimize Supports and Printing Orientation
Warping can often be mitigated by using adequate supports, especially for larger prints that might sag under their own weight. Additionally, adjusting the orientation of your print can also help minimize warping.
Brittleness
Brittleness is a resin issue where the printed objects lack flexibility and break easily. This is particularly problematic for parts that need to endure any form of stress or tension.
Solution: Use Appropriate Resin
The primary way to combat brittleness is to use a resin that is designed for toughness and flexibility. If you are already using such a resin and are still facing issues, consider post-curing the print to further enhance its strength and durability.
Discoloration
Discoloration involves prints looking differently colored than expected. This can result from various factors, including incorrect exposure, the resin’s natural color, or post-processing methods.
Solution: Calibrate your Printer and Post-Processing
Proper printer calibration and paying careful attention to post-processing can address many discoloration issues. Using the correct exposure settings and ensuring your resin is mixed thoroughly before printing can also help.
By understanding and addressing these common resin 3D printing issues
Conclusion
Resin 3D printing is a versatile technique that offers endless possibilities for creatives, professionals, hobbyists, and innovators. By understanding how to select the right resin for your project and how to manage common issues, you can unlock the full potential of this technology.
Recap of Key Factors in Resin Selection
Selecting the right resin isn’t just about the cost; it involves understanding a wide range of properties and how they relate to your project needs:
- Mechanical Properties: Ensure the resin has sufficient tensile strength, elongation at break, flexural strength, and impact resistance for your project.
- Thermal Properties: Check that the resin’s heat deflection temperature and glass transition temperature are suitable.
- Optical Properties: Consider the resin’s transparency and color.
- Other Properties: Take into account factors like the resin’s viscosity, cure time, and biocompatibility.
Importance of Testing and Experimentation
Every resin behaves differently, and every printer has its nuances. Therefore, there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to 3D printing. Don’t shy away from testing and experimentation, as these efforts will guide you towards more reliable and consistent print results.
Future Developments in Resin Technology
The field of resin 3D printing is still evolving, with new resins and technologies being introduced on an ongoing basis:
- New Resins: Manufacturers are continually developing new resins with unique properties, opening up entirely new applications for 3D printing.
- Improved Technologies: Improvements in DLP technology are enabling faster print times, higher resolutions, and even full-color resin prints.
In summary, understanding the complexity of resins, experimenting, and staying updated with new developments is key to harnessing the full potential of resin 3D printing. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro, continually refine your technique, and most importantly, never stop learning!


