In a rapidly evolving world, industries strive to stay competitive through innovation and sustainability. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing has emerged as a transformative technology, offering unique design flexibility and efficiency. It enables the creation of complex parts and prototypes at a fraction of the time compared to traditional manufacturing methods, revolutionizing multiple industries. This article delves into SLS technology, exploring its workings, applications, trends, challenges, and future outlook.
Understanding SLS 3D Printing
What is SLS 3D Printing?
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is a revolutionary 3D printing technique. It uses a laser to fuse powdered materials into solid structures. SLS stands out for its ability to produce intricate, functional designs. Key features include:
- Layered Construction: SLS builds parts layer by layer, facilitating the creation of complex geometries.
- Material Versatility: It can work with diverse materials, mainly thermoplastics, and also metals and ceramics.
- No Support Structures Required: Unlike some 3D printing methods, SLS doesn’t need additional support during printing. The surrounding powder serves as a support medium.
How Does SLS Work?
The SLS printing process involves several crucial steps:
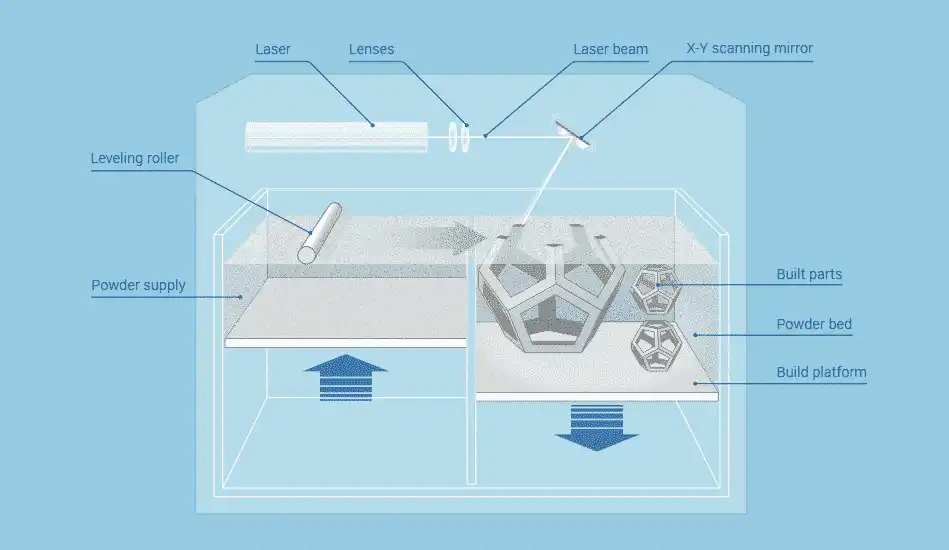
- 3D Model Preparation: Designers create a 3D model using CAD software. Then, slicing software divides the model into thin horizontal layers.
- Powder Layering: A thin layer of powder material is evenly spread across the build platform.
- Laser Sintering: A high – powered laser scans the powder surface. It selectively sinters, or fuses, the powder according to the 3D model. After each layer is complete, the platform lowers slightly, and another powder layer is applied.
- Cooling Phase: Once the build is finished, the machine cools down. Then, the parts can be removed from the unsintered powder.
- Post – Processing: Parts may need cleaning to remove excess powder. They can also undergo additional finishing processes like polishing or dyeing.
| Step | Description |
| Model Preparation | Design and slice the 3D model |
| Layering | Spread powder evenly on the build platform |
| Laser Sintering | Laser fuses powder layer by layer |
| Cooling | Allow the build chamber to cool down |
| Post – Processing | Clean and finish the final parts |
Advantages of SLS 3D Printing

SLS technology offers numerous benefits, making it popular across various fields:
- Design Freedom: SLS enables the production of complex geometries and intricate designs that are often unachievable with traditional methods. For example, it can create parts with internal lattice structures for lightweight yet strong components.
- Material Strength: Parts made via SLS are known for their durability and mechanical strength, making them suitable for functional applications. In the automotive industry, SLS – printed brackets can withstand significant stress.
- Scalability: SLS can handle both low – volume runs and large – batch production without the need for expensive molds. This flexibility is valuable for businesses of different sizes.
- Reduced Waste: The process generates minimal waste as unused powder can be reused in future prints. This not only saves resources but also reduces costs.
- Shorter Lead Times: SLS allows for rapid prototyping. Designers can quickly iterate and test designs, accelerating product development cycles.
Industries Utilizing SLS 3D Printing
SLS 3D printing has found diverse applications across multiple industries, transforming product design, production, and delivery.
Aerospace Industry
The aerospace sector demands lightweight, durable components to meet rigorous standards. SLS 3D printing addresses these needs effectively.
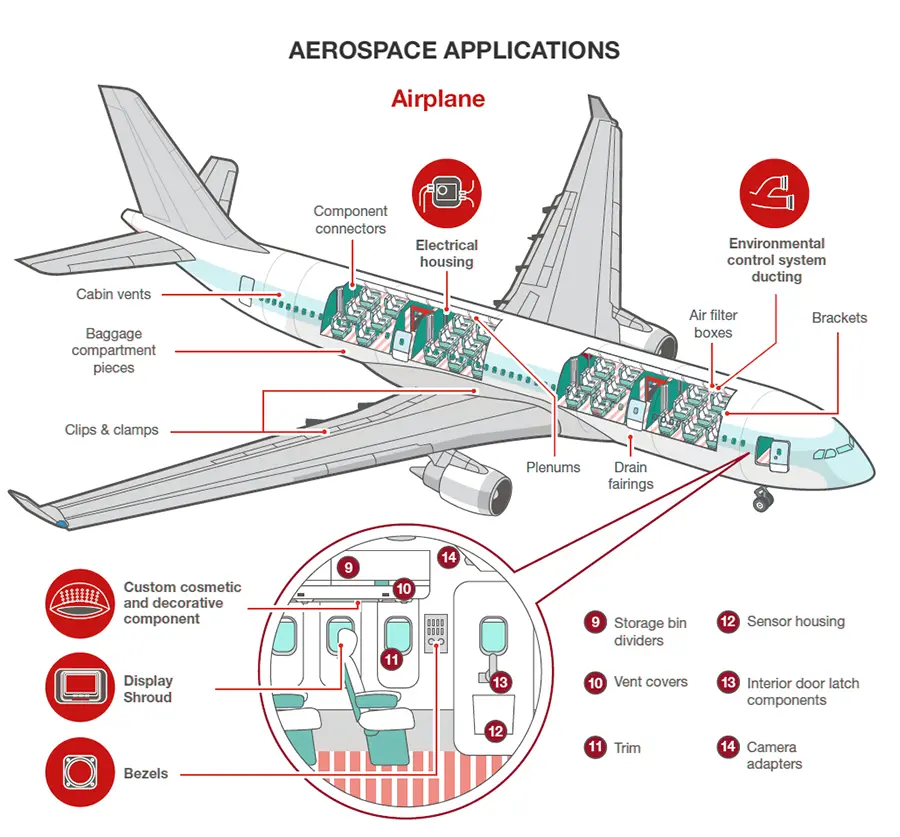
- Key Applications:
- Lightweight Components: SLS can produce complex geometries like internal lattice structures in brackets and fixtures. These structures reduce weight without sacrificing strength, crucial for fuel – efficient aircraft.
- Rapid Prototyping: Aerospace companies can quickly iterate on designs. They can test multiple prototypes in a fraction of the time required for traditional manufacturing, saving both time and costs.
- Case Study: NASA has used SLS to create lightweight components for spacecraft. SLS – enabled rapid prototyping has significantly reduced development time and costs for NASA’s space missions.
Automotive Industry
In the automotive field, SLS 3D printing is a valuable tool for prototyping and production.

- Key Applications:
- Custom Tooling and Fixtures: SLS allows for the production of specialized tools tailored to specific tasks on the assembly line. These tools enhance efficiency and precision during vehicle manufacturing.
- End – Use Parts: Automotive manufacturers can directly produce low – volume production parts, such as custom brackets or housings, using SLS. This offers flexibility in production and reduces the need for large – scale tooling investments.
- Case Study: BMW leverages SLS technology to create prototypes of vehicle parts. By testing and refining designs with SLS – printed prototypes before mass production, BMW shortens development times and minimizes costs associated with traditional tooling.
Healthcare and Medical Devices
SLS technology has brought about significant advancements in the healthcare industry, particularly in medical device and implant production.

- Key Applications:
- Custom Implants: SLS can produce personalized implants that match a patient’s anatomy. This improves comfort and the effectiveness of the implants, enhancing patient outcomes.
- Surgical Tools: Bespoke surgical instruments created using SLS offer improved functionality and precision during surgeries. They can be designed to fit a surgeon’s specific needs for a particular procedure.
- Case Study: Materialise, a medical software and 3D printing company, has developed customized surgical guides and implants using SLS. These products have enhanced the precision of surgeries, leading to better patient recovery and satisfaction.
Consumer Products
SLS 3D printing is revolutionizing the consumer products sector, enabling mass customization in various products.
- Key Applications:
- Personalized Goods: SLS allows customers to personalize products like custom – fit shoes or unique jewelry. This trend caters to individual preferences and enhances the consumer experience.
- Prototyping and Production: Companies can quickly design and produce prototypes for market testing. This speeds up the time – to – market for new products, giving them a competitive edge.
- Case Study: Adidas has utilized SLS to create customized shoe components. These components are tailored to individual customer preferences, such as foot shape and gait, providing a more comfortable and personalized product.
Electronics and Electrical Components
The electronics industry benefits from SLS technology’s ability to produce intricate, lightweight, and durable components.
- Key Applications:
- Enclosures and Housings: SLS is used to create lightweight enclosures that protect electronic components without adding excessive weight. This is important for portable electronic devices.
- Thermal Management Solutions: SLS’s capacity to create complex geometries helps in designing thermal management components. These components can dissipate heat effectively, improving the performance and lifespan of electronic devices.
- Case Study: HP uses SLS to manufacture parts for its printers and other electronic devices. By optimizing the design and weight of these parts with SLS, HP improves product performance and reduces overall product weight.
Architecture and Construction
The architecture and construction industries are exploring SLS for creating complex models and functional tools.
- Key Applications:
- Building Prototypes: SLS can produce detailed architectural models. These models help architects and clients visualize designs, making it easier to communicate and refine concepts.
- Construction Tools: Specialized construction tools can be manufactured using SLS. These tools offer greater precision and efficiency on construction sites.
- Case Study: Zaha Hadid Architects has utilized SLS technology to fabricate complex building models. These models showcase the firm’s innovative and intricate design concepts, highlighting the capabilities of SLS in the architecture field.
| Industry | Key Applications | Notable Case Studies |
| Aerospace | Lightweight components, rapid prototyping | NASA |
| Automotive | Custom tooling, end – use parts | BMW |
| Healthcare | Custom implants, surgical tools | Materialise |
| Consumer Products | Personalized goods, prototyping | Adidas |
| Electronics | Enclosures, thermal management | HP |
| Architecture | Building prototypes, construction tools | Zaha Hadid Architects |
Emerging Trends in SLS 3D Printing
As technology advances, SLS 3D printing is at the forefront of innovation in the manufacturing sector. Here are some of the emerging trends:
Material Innovations

The development of advanced materials is a significant trend in SLS technology. These materials offer greater flexibility and improved performance in printed parts.
- New Powder Materials: Recent advancements include high – performance polymers, metals, and composites. For instance, nylon composites reinforced with carbon fiber provide superior strength and durability, making them suitable for aerospace and automotive applications.
- Biodegradable Materials: The use of eco – friendly materials is on the rise. These materials offer sustainable alternatives for industries aiming to reduce their environmental impact, such as in packaging and consumer products.
- Multi – Material Printing: Progress is being made in the ability to print with multiple materials in a single build. This allows for parts with varying properties and functionalities, like combining a rigid structural material with a flexible component in one part.
| Material Type | Characteristics | Applications |
| Nylon | Lightweight, strong, and flexible | General parts, automotive components |
| Carbon Fiber Nylon | High strength – to – weight ratio | Aerospace, automotive, sporting goods |
| TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) | Rubber – like flexibility | Consumer products, medical devices |
| Biodegradable Plastics | Eco – friendly and sustainable | Packaging, eco – conscious products |
Advances in Technology
Technological advancements are expanding the capabilities of SLS 3D printing.
- Improved Laser Systems: New high – powered lasers enhance the speed and precision of the sintering process. They enable faster production without compromising on quality, making SLS more competitive with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Automation and Smart Manufacturing: Incorporating AI and machine learning into SLS processes enables predictive maintenance, process optimization, and reduced downtime. For example, 3D Systems integrates automation into its SLS systems, reducing manual intervention and increasing production efficiency.
- Enhanced Software Solutions: Advanced slicing software improves the translation of designs into printable objects. It allows for better layer management and support structure optimization, resulting in higher – quality prints.
Environmental Considerations
Sustainability is a crucial focus for many industries, and SLS technology is adapting accordingly.
- Material Reusability: SLS’s ability to reuse unsintered powder significantly reduces waste. Companies are developing more efficient recycling and reuse methods, further minimizing material waste in the production process.
- Energy Efficiency: Advances in machine design are leading to more energy – efficient SLS systems. These systems consume less power, reducing the carbon footprint of the production process.
- Sustainable Material Development: Research into sustainable materials, such as bio – based plastics, is making SLS a more environmentally friendly option in manufacturing.
| Benefit | Description |
| Reduced Material Waste | Unused powder can be reused for future prints |
| Lower Energy Consumption | New designs are optimizing energy use |
| Eco – friendly Material Options | Development of biodegradable and recyclable materials |
Potential New Applications
As SLS technology progresses, its potential applications continue to expand.
- On – Demand Manufacturing: SLS is being used for on – demand manufacturing, where parts are printed as needed. This reduces storage costs and waste associated with overproduction, making it a cost – effective solution for many businesses.
- Aerospace and Defense: Given the ongoing need for lightweight, durable parts in aerospace and defense, SLS has the potential to revolutionize component manufacturing in these critical industries. It can produce parts with complex geometries that meet the high – performance requirements of these sectors.
- Customized Products for E – commerce: The growing demand for personalized shopping experiences is driving the need for customized products. SLS can efficiently produce these customized items, catering to the e – commerce market’s needs.
Challenges and Limitations of SLS 3D Printing
Despite its many advantages, SLS 3D printing faces several challenges that can limit its widespread adoption.
Cost Considerations
The cost of SLS technology can be a significant barrier, especially for smaller operations.
- Equipment Costs: SLS printers are generally more expensive than standard FDM printers. Their advanced technology, including high – powered lasers and specialized build chambers, contributes to the high price.
- Material Expenses: The powders used in SLS, particularly high – performance materials, can be costly. This cost factor can be a deterrent for small businesses and startups with limited budgets.
- Post – Processing Costs: After SLS printing, parts often require additional finishing processes like cleaning and surface treatment. These post – processing steps add to the overall production costs.
| Cost Factor | SLS | FDM | SLA |
| Initial Equipment Cost | High | Low | Medium |
| Material Cost | Moderate to High | Low | Moderate |
| Post – Processing Cost | Moderate | Low | High |
Material Constraints
There are limitations in the types of materials available for SLS and their properties.
- Limited Material Range: Although SLS can work with various materials, the range is narrower compared to other 3D printing technologies. Not all polymers and composites are suitable for SLS, restricting the options for certain applications.
- Material Properties: Some SLS materials may not meet specific requirements for applications involving extreme temperatures or chemical resistance. This limits their use in industries with stringent material property demands.
- Powder Handling Issues: Handling fine powders in SLS can pose health and safety risks. Proper safety measures and equipment are necessary to mitigate these risks during the printing process.
Technical Complexities
SLS technology involves complex processes that can present challenges during operation and production.
- Process Control: Achieving consistent quality in SLS prints is difficult due to factors like variations in laser power, powder quality, and environmental conditions within the build chamber. These variables can affect the final product’s quality.
- Printer Calibration: Regular calibration of SLS printers is essential for optimal performance. Misalignment or calibration errors can lead to failed prints or reduced part quality, increasing production costs and delays.
- Post – Processing Requirements: The extensive post – processing needed for SLS – printed parts can complicate production timelines and add to labor costs, making the overall production process more complex.
Regulatory Hurdles
Regulatory challenges are particularly significant in industries like aerospace and healthcare.
- Certification Regulations: Many industries require certifications for materials and processes used in manufacturing. Navigating these complex regulatory landscapes can slow down the adoption of SLS technology, as companies need to invest time and resources to meet the requirements.
- Quality Assurance Standards: SLS parts must meet strict quality standards. Rigorous testing and validation procedures are necessary, which can be resource – intensive and time – consuming, adding to the cost and complexity of production.
- Intellectual Property Issues: As SLS technology evolves, concerns about intellectual property protection arise. These issues can impact innovation and collaboration among companies in the SLS ecosystem.
The Future Outlook for SLS 3D Printing
The future of SLS 3D printing holds great promise, with several developments expected to reshape industries and manufacturing processes.
Technological Advancements
Ongoing technological innovations will enhance SLS’s efficiency, accuracy, and usability.
- Increased Speed and Efficiency: Advances in laser technology and machine design will likely lead to faster print speeds. This will increase throughput and reduce cycle times, making SLS more competitive with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Automation and AI Integration: Incorporating automation and artificial intelligence into SLS processes will optimize production workflows. AI can predict maintenance needs, improve process control, and enhance overall operational efficiency.
- Cloud Computing and IoT: Integrating cloud – based solutions and the Internet of Things (IoT) will enable remote management of SLS printers. Real – time monitoring of production and data analysis for continuous improvement will also be possible, allowing for more efficient production operations.
| Development | Description |
| Faster Laser Systems | Enhanced laser technology for quicker sintering |
| AI Process Optimization | Use of AI to streamline workflows and reduce errors |
| Remote Monitoring | Cloud – based management for real – time tracking |
Innovations in Materials
Future SLS development will see continued innovation in materials, expanding its applications and capabilities.
- Advanced Polymer Blends: New polymer blends will be developed, offering superior mechanical properties, lightweight characteristics, and enhanced performance in extreme environments. These blends will open up new opportunities in industries such as aerospace and automotive.
- Smart Materials: Research into smart materials that can change properties in response to environmental changes will open new applications in fields like robotics and aerospace. SLS can be used to print these materials into complex structures for various functions.
- Biocompatible Materials: Continued advancements in biocompatible materials for medical applications, such as implants and prosthetics, will drive further adoption of SLS in the healthcare sector. This will improve patient care and outcomes.
Expanding Applications
The versatility of SLS technology will lead to an expansion of its applications across multiple industries.
- On – Demand Manufacturing: The trend towards on – demand manufacturing will accelerate. SLS will enable companies to produce components quickly as needed, reducing waste and storage costs. This will transform the way companies manage their inventory and production processes.
- Customized Consumer Products: The growing consumer demand for personalization will drive growth in sectors like fashion, footwear, and electronics. SLS can provide tailored solutions, offering unique and customized products to meet individual customer preferences.
- Aerospace and Defense Innovations: Continued exploration of lightweight, high – strength components in aerospace and defense applications will strengthen SLS’s role in these industries. SLS – printed parts will contribute to the development of more advanced and efficient aircraft and defense systems.
Market Trends
As SLS technology matures, the market will experience significant trends that will shape its future.
- Increased Competition: More companies entering the SLS space will drive innovation. This competition will also lead to price reductions, making SLS technology more accessible to a wider range of businesses and accelerating its adoption across industries.
- Sustainability Focus: The growing emphasis on sustainability will encourage the development of eco – friendly materials and processes in SLS technology. This will appeal to environmentally conscious consumers and businesses, further promoting the use of SLS in sustainable manufacturing.
- Global Manufacturing Shifts: SLS technology will facilitate the trend towards decentralized manufacturing. Companies can produce components closer to their end – users, reducing supply chain disruptions and improving overall supply chain efficiency.
In conclusion, SLS 3D printing is a powerful technology with the potential to transform multiple industries. While it faces challenges, ongoing advancements


