In the domain of 3D printing, Stereolithography (SLA) has established a distinct position, offering unparalleled precision and detail. SLA technology can create high – resolution models that capture even the most intricate designs, whether for elaborate prototypes or functional end – use parts. However, the true potential of SLA lies not only in the technology itself but also in the materials used to actualize those designs.
Consider the need to print a dental model with exact accuracy or the task of creating a robust prototype capable of withstanding rigorous testing. The choice of material can significantly influence the outcome. Given the diverse options such as Standard, Engineering, and Dental SLA materials, understanding their unique properties and applications is crucial for achieving optimal results.
This article delves into the realm of SLA materials, exploring the distinct characteristics of Standard, Engineering, and Dental materials. It discusses their specific applications, advantages, and provides guidance on selecting the appropriate material for a project. Whether you are a hobbyist, a professional designer, or involved in the dental field, this comprehensive guide equips you with the knowledge to make informed decisions regarding your SLA printing projects.
Understanding SLA Materials
What is SLA Printing?
Stereolithography (SLA) is a revolutionary 3D printing technology. It uses a laser to cure liquid resin into solid objects. The process involves layering the resin and selectively solidifying it to produce highly detailed and complex models. SLA is renowned for its fine resolution and smooth surface finish, making it a preferred choice for applications demanding high accuracy.
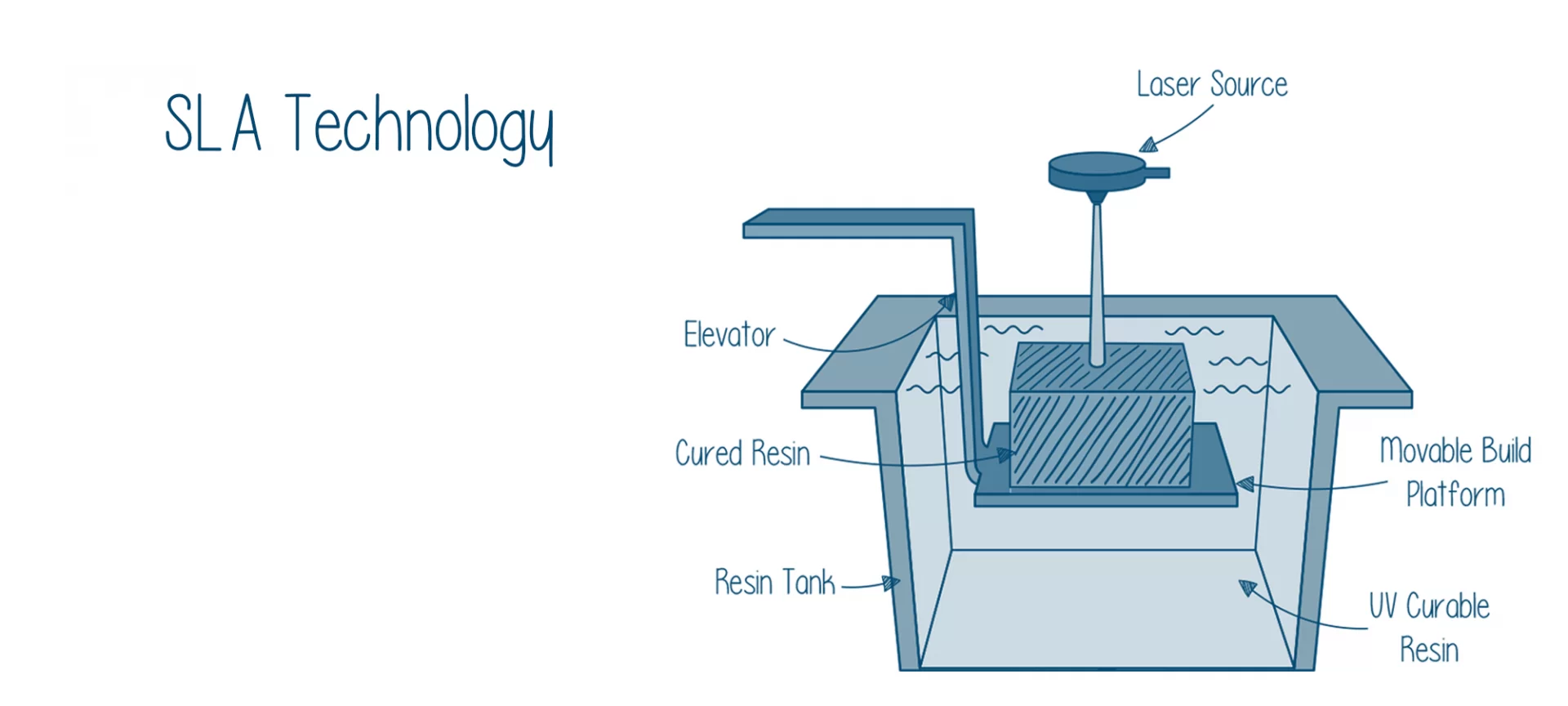
Key Advantages of SLA Printing:
- High Precision: SLA can achieve layer resolutions as fine as 25 microns, making it suitable for detailed designs.
- Smooth Surface Finish: The cured resin results in smooth surfaces, often requiring minimal post – processing.
- Wide Range of Materials: SLA printing supports various resin types, enabling customization based on specific project requirements.
Types of SLA Materials

Material selection is crucial in SLA printing as it directly impacts the final product’s performance, appearance, and suitability for different applications. SLA materials can be broadly classified into three main types: Standard, Engineering, and Dental. Each type has unique properties tailored to meet specific needs.
Why Material Selection Matters
Selecting the appropriate material can affect:
- Performance: Different materials offer varying levels of strength, flexibility, and durability.
- Cost: Material costs can vary significantly, influencing the overall project budget.
- Application Suitability: Some materials are designed for specific industries, ensuring optimal performance in unique scenarios.
To better understand the differences between these material types, the following sections will analyze them in detail.
Overview of SLA Material Categories
| Material Type | Characteristics | Typical Applications |
| Standard | Easy to use, versatile, good detail | Prototyping, visual models |
| Engineering | Durable, heat – resistant, functional | End – use parts, functional prototypes |
| Dental | Biocompatible, high precision | Dental models, surgical guides |
SLA printing is a powerful technology, and careful material selection unlocks its full potential. Understanding the differences between Standard, Engineering, and Dental SLA materials is essential for achieving the best results in projects. Each category serves unique purposes, and knowledge of their characteristics helps in making informed decisions based on specific printing requirements.
Standard SLA Materials
What are Standard SLA Materials?

Standard SLA materials are the most commonly used resins in the 3D printing industry. They are known for their versatility, ease of use, and ability to produce high – quality prints with excellent detail. These materials are ideal for a wide range of applications, especially in the prototyping phase, where speed and fidelity are crucial.
Characteristics of Standard SLA Materials:
- User – Friendly: Standard materials are generally easy to print with, accessible to both beginners and experienced users.
- High Detail and Resolution: They can achieve intricate designs and fine details, making them suitable for visual models.
- Variety of Colors: Available in multiple colors, including clear, grey, and black, allowing for design flexibility.
Applications of Standard SLA Materials
Standard SLA materials have diverse applications across various industries. Some common uses include:

- Prototyping: Ideal for creating quick and accurate prototypes for design validation.
- Model Making: Used in architectural and product design to create detailed visual models.
- Functional Testing: Suitable for parts tested for fit and form, but not necessarily for strength or durability.
Benefits of Using Standard Materials:
- Cost – Effective: Generally more affordable than specialized materials, making them a good choice for initial prototypes.
- Fast Turnaround: Quick printing times due to the simplicity of the materials.
- Ease of Post – Processing: Standard resins typically require minimal finishing, saving time and effort.
Popular Standard SLA Materials
Here are some of the most popular Standard SLA materials and their key properties:
| Material Name | Key Properties | Ideal Applications |
| Clear Resin | High transparency, good detail | Visual models, light guides |
| Grey Resin | Balanced strength and detail | Prototyping, concept models |
| Black Resin | Matte finish, good contrast | Functional parts, aesthetic models |
| White Resin | Good rigidity, easy to paint | Consumer product prototypes |
Mechanical Properties Comparison:
- Tensile Strength: Most Standard materials have a tensile strength ranging from 30 to 50 MPa, making them suitable for non – load – bearing applications.
- Flexural Modulus: A flexural modulus of about 1,500 to 2,500 MPa indicates that while they are not extremely flexible, they can withstand some bending without breaking.
Considerations When Using Standard SLA Materials
Although Standard SLA materials are suitable for various applications, several factors should be considered before choosing them for a project:
- Limitations in Durability: They are not suitable for heavy – duty applications requiring high strength or heat resistance.
- Surface Finish: Although they provide a smooth finish, the clarity and detail may not be as high as those of specialized materials.
- Environmental Sensitivity: Standard resins can be affected by UV light and moisture, which may impact long – term use.
Standard SLA materials are fundamental in the 3D printing industry, offering versatility and quality for various applications. Their ease of use and cost – effectiveness make them excellent choices for prototyping and model making. However, it is essential to be aware of their limitations when considering them for specific projects.
Engineering SLA Materials
What are Engineering SLA Materials?
Engineering SLA materials are specifically formulated to meet the demanding requirements of industrial applications. Unlike Standard materials, which are mainly suitable for prototyping and visual models, Engineering materials offer enhanced mechanical properties such as strength, durability, and thermal resistance. This makes them ideal for functional prototypes and end – use parts that must withstand real – world conditions.
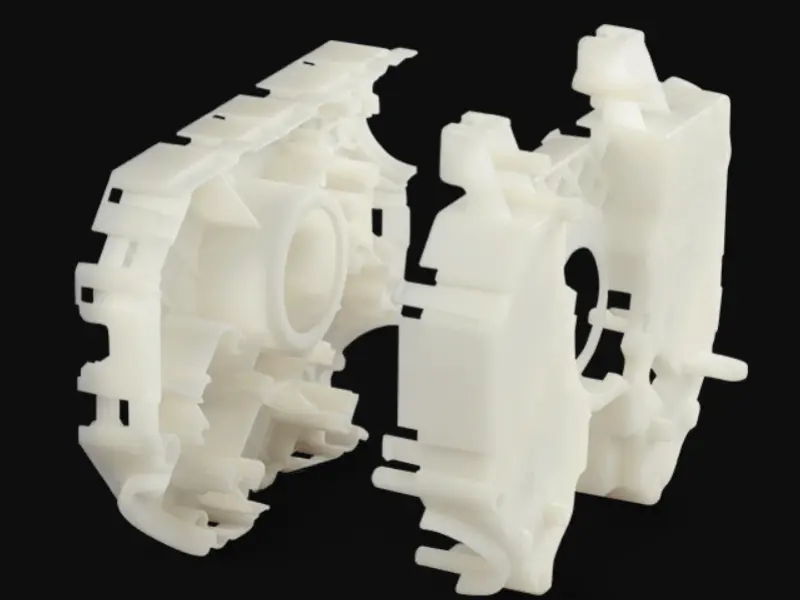

Characteristics of Engineering SLA Materials:
- High Strength and Toughness: These materials are designed to have superior mechanical properties, making them suitable for parts that require durability and impact resistance.
- Heat Resistance: Many Engineering materials can withstand elevated temperatures, making them useful for applications where heat exposure is a concern.
- Precision: They maintain high dimensional accuracy even under stress, ensuring that parts fit together as intended.
Applications of Engineering SLA Materials
Engineering SLA materials are used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer products. Some key applications include:
- Functional Prototypes: Used for testing form, fit, and function in real – world scenarios.
- End – Use Parts: Suitable for producing components ready for market use, such as brackets, housings, and enclosures.
- Tooling and Jigs: Often used to create custom tools and fixtures that require high precision and durability.
Benefits of Using Engineering Materials:
- Enhanced Performance: Designed to withstand mechanical stress, heat, and environmental factors.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for expensive tooling or machining processes, enabling on – demand production.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wider range of applications than Standard materials.
Popular Engineering SLA Materials
Here are some of the most widely used Engineering SLA materials and their key properties:
| Material Name | Key Properties | Ideal Applications |
| Tough Resin | High impact resistance | Functional prototypes, housings |
| High Temp Resin | Heat resistance up to 200°C | Automotive and aerospace parts |
| Flexible Resin | Rubber – like flexibility | Seals, gaskets, and ergonomic grips |
| Durable Resin | Excellent tensile strength | End – use parts and functional testing |
Mechanical Properties Comparison:
- Tensile Strength: Engineering materials typically have a tensile strength ranging from 50 to 100 MPa, allowing them to handle higher loads.
- Flexural Modulus: A flexural modulus of about 2,500 to 5,000 MPa indicates improved stiffness compared to Standard materials.
Considerations When Using Engineering SLA Materials
Although Engineering SLA materials offer numerous advantages, some factors should be kept in mind:
- Cost: Generally more expensive than Standard materials, which may impact budget considerations for large – scale projects.
- Print Complexity: Some Engineering materials may require specific printing parameters or conditions to achieve optimal results.
- Post – Processing Needs: Depending on the material, additional post – processing steps may be necessary to achieve the desired surface finish or mechanical properties.
Engineering SLA materials represent a significant advancement in 3D printing technology, providing the strength, durability, and heat resistance required for demanding applications. They are suitable for those looking to create functional prototypes or end – use parts that can withstand real – world challenges.
Dental SLA Materials
What are Dental SLA Materials?
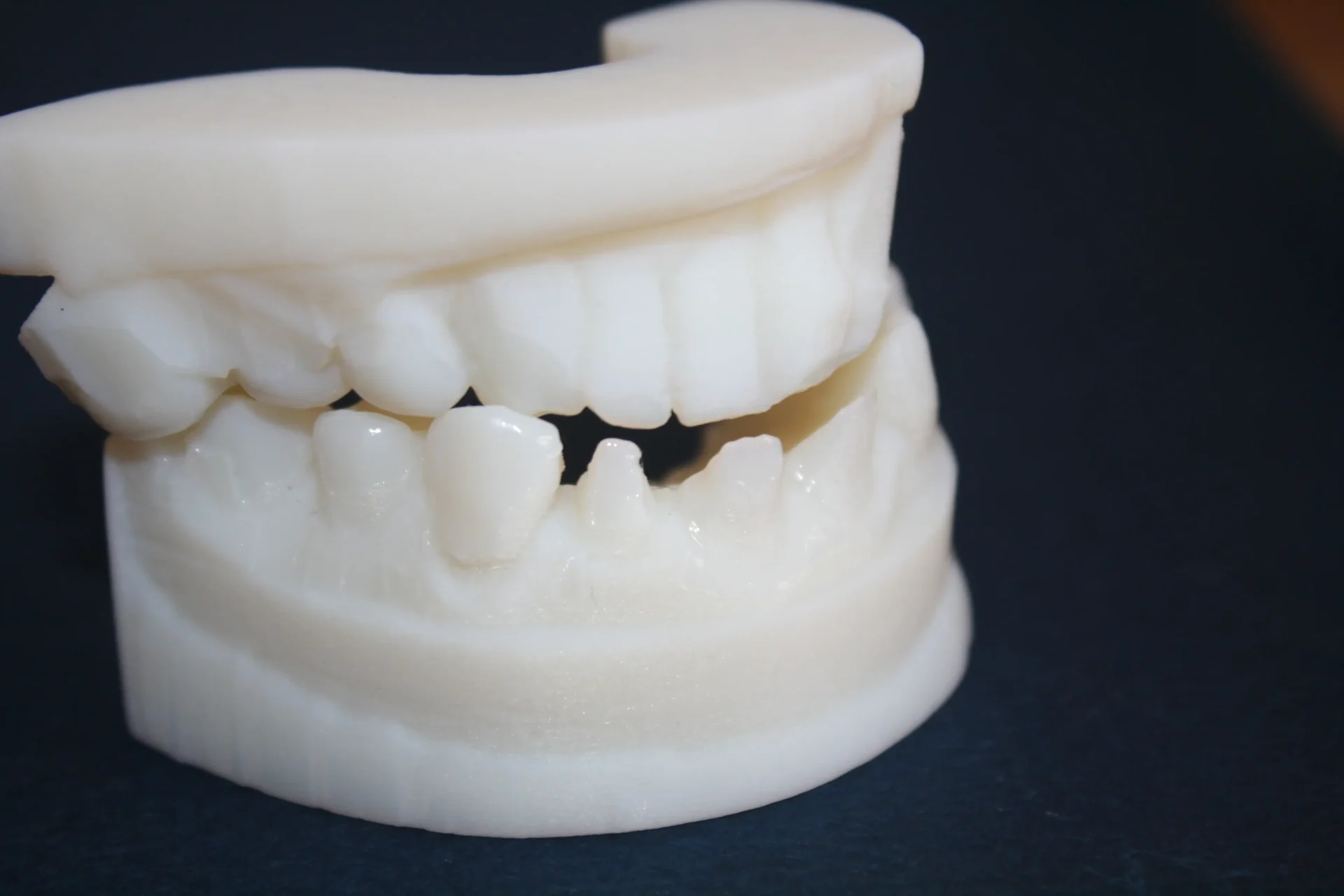
Dental SLA materials are specifically engineered resins designed to meet the strict requirements of the dental industry. These materials are characterized by their biocompatibility, precision, and ability to produce highly detailed models, making them essential for dental applications such as crowns, bridges, and surgical guides. Accuracy is of utmost importance in dental work, and Dental SLA materials are formulated to meet this need.
Characteristics of Dental SLA Materials:
- Biocompatibility: Dental materials must be safe for use in the human body, ensuring that they do not cause adverse reactions.
- High Precision and Detail: These resins can produce intricate designs with exceptional accuracy, crucial for the perfect fit of dental appliances.
- Stability and Durability: Dental materials need to withstand oral conditions, including moisture and temperature variations.
Applications of Dental SLA Materials
Dental SLA materials are used in various applications within the dental field, where precision and quality are critical. Some common applications include:
- Dental Models: Used to create accurate representations of patients’ teeth and gums for planning and communication.
- Crowns and Bridges: These materials are ideal for producing prosthetic dental restorations that require a perfect fit and aesthetic appeal.
- Surgical Guides: Custom surgical guides are made to assist dentists in performing precise implant surgeries.
- Orthodontic Appliances: Used to create clear aligners and other orthodontic devices that require high accuracy.
Benefits of Using Dental Materials:
- Enhanced Patient Outcomes: The precision of Dental SLA materials leads to better – fitting appliances, improving patient satisfaction.
- Reduced Turnaround Time: Quick printing capabilities allow dental practices to provide faster service to patients.
- Versatility: Suitable for a range of applications, from models to functional restorations.
Popular Dental SLA Materials
Here are some of the most widely used Dental SLA materials and their key properties:
| Material Name | Key Properties | Ideal Applications |
| Dental Model Resin | High detail, smooth finish | Models for diagnosis and planning |
| Dental Surgical Guide Resin | Biocompatible, high precision | Surgical guides for implant placements |
| Dental Crown Resin | Aesthetic, durable, and strong | Crowns and bridges |
| Orthodontic Clear Aligners Resin | Flexible and transparent | Clear aligners and retainers |
Mechanical Properties Comparison:
- Tensile Strength: Dental materials typically have a tensile strength ranging from 40 to 80 MPa, ensuring sufficient strength for dental applications.
- Flexural Modulus: A flexural modulus of around 1,500 to 2,500 MPa provides the necessary rigidity for dental restorations.
Considerations When Using Dental SLA Materials
Although Dental SLA materials are tailored for the dental industry, several factors should be considered:

- Regulatory Compliance: Dental materials must meet specific regulatory standards to ensure patient safety. It is essential to choose materials that are certified for dental use.
- Cost Considerations: Dental materials can be more expensive than standard resins, impacting the overall cost of dental services.
- Post – Processing Requirements: Many dental materials require post – processing steps such as washing and curing to ensure optimal mechanical properties and biocompatibility.
Dental SLA materials are crucial for the dental industry, offering the precision and biocompatibility necessary for creating high – quality dental restorations and models. Their unique properties enable dental professionals to enhance patient outcomes and streamline workflows.
Comparative Analysis of SLA Materials
Key Differences Between the Material Types
When selecting the right SLA material for a project, understanding the key differences between Standard, Engineering, and Dental materials is crucial. Each type has distinct characteristics tailored to specific applications, and knowledge of these differences helps in making informed decisions.
Summary Table of SLA Material Types:
| Material Type | Primary Characteristics | Typical Applications | Cost Range | Biocompatibility |
| Standard | Easy to use, versatile, good detail | Prototyping, visual models | Low to Moderate | No |
| Engineering | High strength, heat – resistant | Functional prototypes, end – use parts | Moderate to High | No |
| Dental | Biocompatible, high precision | Dental models, crowns, surgical guides | Moderate to High | Yes |
Choosing the Right Material for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate SLA material depends on several factors, including the intended application, required properties, and budget constraints. The following guide helps determine the most suitable material:
1. Application Needs
- Prototyping and Visual Models: If the primary goal is to create a visual representation or prototype, Standard SLA materials are ideal due to their ease of use and cost – effectiveness.
- Functional Parts and Prototypes: For projects requiring durability and performance, Engineering materials are a better choice, offering enhanced mechanical properties.
- Dental Applications: If creating dental models, crowns, or surgical guides, Dental materials are essential due to their biocompatibility and precision.
2. Mechanical Properties Required
- Strength and Durability: If the project demands high strength and durability, choose Engineering SLA materials that can withstand stress and heat.
- Detail and Precision: For applications needing high detail and precision, Dental materials are excellent for producing intricate designs suitable for dental work.
3. Budget Considerations
- Cost Efficiency: If budget is a primary concern, Standard materials provide the most cost – effective solution for prototyping and non – functional designs.
- Investment in Quality: For end – use parts or critical applications, investing in Engineering or Dental materials may be justified despite higher costs.
Case Studies: Material Selection in Action
To illustrate the importance of material selection, the following case studies demonstrate how different materials were chosen based on project requirements:
- Case Study 1: Prototyping a Consumer Product
- Objective: Develop a prototype for a new consumer gadget.
- Material Chosen: Standard SLA material (Grey Resin)
- Reasoning: The project required quick turnaround and visual fidelity, making Standard materials the best choice. The prototype was produced with detailed features, perfect for design evaluation.
- Case Study 2: Creating a Dental Crown
- Objective: Fabricate a custom dental crown for a patient.
- Material Chosen: Dental SLA material (Dental Crown Resin)
- Reasoning: The biocompatibility and precision of the Dental resin were critical to ensure a perfect fit and safety in the patient’s mouth. The material allowed for high – detail printing, essential for dental applications.
Understanding the differences between Standard, Engineering, and Dental SLA materials is vital for achieving optimal results in 3D printing projects. Each material type has unique advantages tailored to specific applications, and making the right choice can significantly impact the success of a project.
Future Trends in SLA Materials
Advancements in Material Science
The field of 3D printing, especially in SLA technology, is evolving rapidly. Innovations in material science are creating new possibilities and applications. Some notable trends include:
1. Development of High – Performance Resins
- New Formulations: Researchers are continuously developing new resin formulations that enhance properties such as strength, flexibility, and heat resistance. These advancements open up opportunities for applications in demanding industries like aerospace and automotive.
- Multi – Material Printing: Advances in multi – material printing enable the combination of different resin types within a single print, allowing the creation of parts with varying mechanical properties. This is particularly beneficial for applications requiring both rigidity and flexibility.
2. Improved Biocompatibility
- Medical Applications: With the increasing demand for personalized medicine and dental solutions, the development of biocompatible materials is becoming more important. New resins that mimic the properties of natural tissues are being researched for applications in dental, orthopedic, and surgical solutions.
- Regulatory Compliance: As biocompatible materials become more common, manufacturers are focusing on ensuring that these materials meet strict regulatory requirements for use in healthcare.
3. Enhanced Surface Finishes
- Post – Processing Innovations: Advances in post – processing techniques are being explored to improve the surface finish of SLA – printed parts. New methods, such as automated polishing or coating technologies, can significantly reduce the need for manual finishing and enhance the overall appearance and functionality of the printed objects.
Sustainability in SLA Materials
As environmental concerns become more significant, sustainability is a critical focus in the development of SLA materials. The industry is exploring several ways to reduce its ecological footprint:
1. Eco – Friendly Resins
- Bio – Based Materials: An increasing number of manufacturers are developing bio – based resins derived from renewable resources. These materials aim to minimize reliance on petroleum products and reduce the overall environmental impact.
- Recyclability and Reusability: Innovations in resin formulations are being explored to create materials that can be recycled or reused, promoting a more sustainable lifecycle for 3D – printed parts.
2. Energy Efficiency in Printing
- Lower Energy Consumption: New SLA printers are being designed to operate more efficiently, consuming less energy during the printing process. This includes advancements in light source technologies that require less power while maintaining high printing speeds and quality. For instance, some printers now use LED light sources instead of traditional lasers, which not only reduces energy consumption but also offers better control over the curing process.
- Waste Reduction: Efforts are being made to minimize waste during the printing process. This involves the development of systems that recycle unused resin or support structures. Some printers are equipped with built – in recycling mechanisms that can filter and reuse excess resin, while others use soluble support materials that can be easily removed and recycled, reducing the amount of waste sent to landfills.
Conclusion
The future of SLA materials is promising, with continuous progress in material science and a strong emphasis on sustainability. The development of new high – performance resins and eco – friendly solutions will expand the capabilities of SLA 3D printing. This, in turn, will open up new opportunities for innovation across a wide range of industries. For example, in the automotive industry, high – strength and heat – resistant SLA materials could enable the production of lightweight, complex parts that improve fuel efficiency. In the medical field, enhanced biocompatible materials will support the growth of personalized medicine and more advanced dental and surgical procedures. As these trends continue to develop, SLA 3D printing is likely to become an even more integral part of modern manufacturing and product development processes.
High temperature resin
Need 3D printed parts that can handle the heat? Look no further than SLA printing with 355 High-Temperature Resin.



 العربية
العربية 简体中文
简体中文 繁體中文
繁體中文 Nederlands
Nederlands English
English Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch हिन्दी
हिन्दी Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latin
Latin Polski
Polski Português
Português Русский
Русский Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ไทย
ไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt