In the dynamic landscape of manufacturing and design, one technology is leading a disruptive charge – Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D Printing. Revolutionizing the approach to production, it has allowed sectors like aerospace, automotive, and healthcare to create intricate, high-strength components at costs and speeds that traditional manufacturing methods just can’t match.

But what exactly is SLS 3D Printing? How does it make components that are more durable than ones produced by other 3D printing methods, or even traditional manufacturing processes? This article will guide you through the fascinating world of SLS 3D Printing – its process, its unique qualities, the materials it uses, and its versatility in application.

If you’re a business exploring rapid production methods or an individual intrigued by technological advancements, you’re about to discover how SLS 3D Printing could redefine your trajectory. Let’s take a closer look at this game-changing technology and understand how SLS 3D Printing Services can deliver durability like never before.
Understanding SLS 3D Printing
In the vast ecosystem of 3D printing, Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) enjoys a unique status. Unlike other methods that deposit or cure materials layer by layer, SLS uses a high-power laser to fuse small particles of polymer powder into a solid structure.
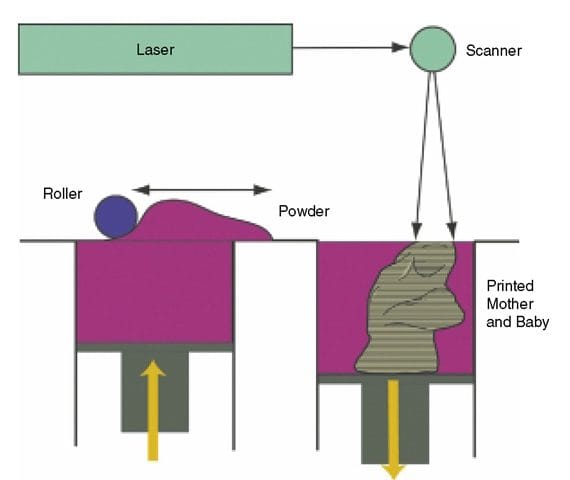
The Basics of SLS 3D Printing
Under the hood of an SLS 3D printer, you will find three key elements:
- A Laser: The laser in an SLS printer serves a critical role. It selectively sinter – or fuse – the powdered material based on the 3D design input.
- A Powder Bed: Here, the chosen powdered material — typically a nylon or polyamide — awaits the laser’s touch. Once the laser sinteres the material, it forms a solid structure layer by layer.
- A Roller: The roller’s work comes into play after each layer is completed. It spreads another layer of fine powder over the top, ready for the next pass of the laser.
This combination and process gives SLS a distinct edge over other 3D printing techniques in producing durable, complex, and high-resolution components.
Material Selection: The Heart of Durability
SLS printing primarily uses nylon powders which imbue the final product with high-impact resistance, stability under thermal stress, flexibility, and water resistance the hallmarks of a durable product meant for real-world use. Some popular materials used in SLS printing include:
- PA 11 & PA 12: Widely chosen for their mechanical properties and stable nature under varied temperature conditions.
- Glass-filled Nylon: A successful response to demands for materials with improved rigidity, low shrinkage, high thermal resistance, and reduced warping.
- Alumide: A blend of nylon and aluminum that achieves excellent tensile strength and metallic sheen.
Why Choose SLS over Other 3D Printing Methods?
While each 3D printing method comes with its strengths, SLS stands out in the crowd for a handful of significant reasons:
Superior Durability: As discussed, the nature of materials and the fusion process gives SLS 3D printed components superior strength and durability.
Design Freedom: SLS does not require support structures that limit design options in other 3D printing techniques. Be it complex geometries, overhangs or inner channels – SLS can create it all.
Production Efficiency: SLS allows for batch production, nesting multiple parts in a single powder bed. This leads to cost-effective and timely production runs.
Surface Finish: While SLS won’t necessarily deliver a glossy finish, it achieves excellent accuracy and surface resolution.
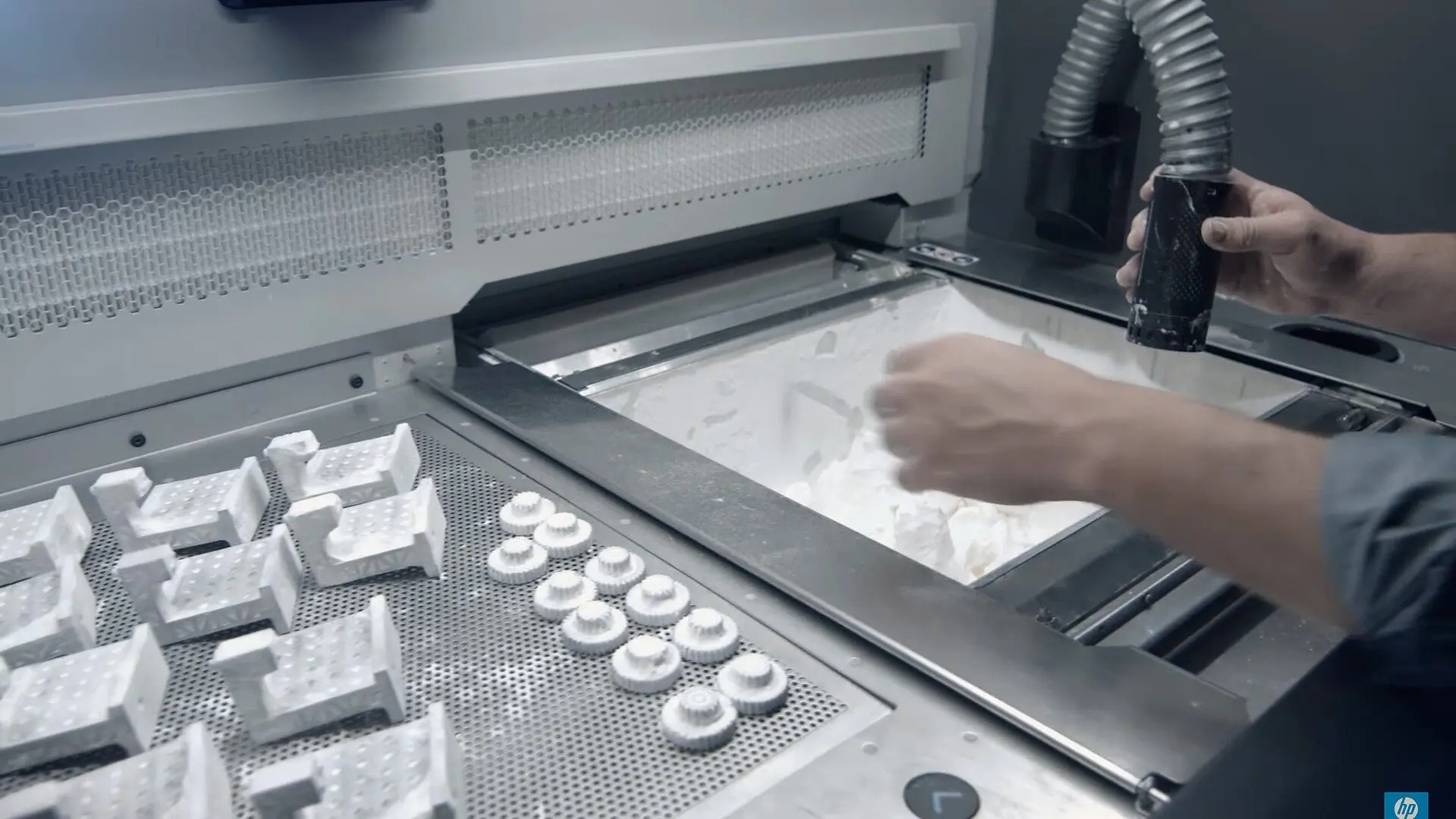

Understanding the mechanics of SLS 3D printing, it’s easy to appreciate its impact in the manufacturing world. From functional prototypes to end-use parts, SLS’s mark is unmistakable and impressive. As we’ll discuss in the next sections, its influence over multiple sectors is a testament to its robustness and versatility.
Applications of SLS 3D Printing
Explore any industry that relies on a balance of speed, strength and precision in its components, and you’ll spot the influence of Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D Printing. The ability to create complex geometries at a rapid pace has led to its adoption in a myriad of sectors.
Aerospace: Flying High with SLS
Imagine an industry where weight is the enemy, and precision is non-negotiable. That’s aerospace in a nutshell. SLS has harnessed these demands and turned them into opportunities. As a result, flight components, small-scale models to intricate cabin fixtures, are now regularly created using this technology. For instance, Airbus has started deploying SLS printed components in its planes, which has resulted in significant weight reduction and cost savings.
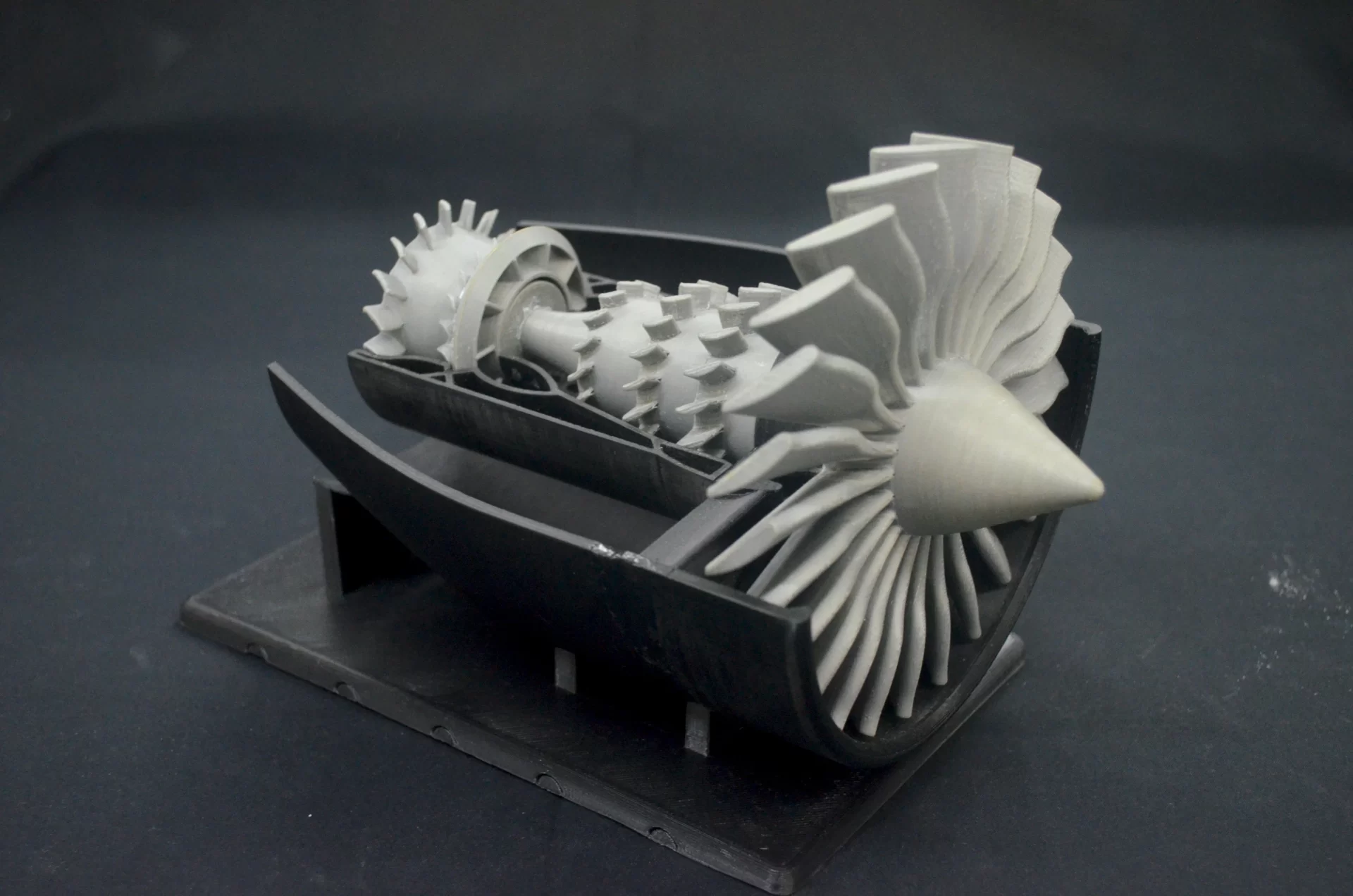

Applications in Aerospace:
- Production of lightweight, durable parts.
- Manufacturing geometrically complex components not achievable through traditional methods.
- Rapid prototyping of aircraft components.
Automotive: Driving Innovation with SLS
The automotive industry is another sector that’s rapidly embracing SLS. With the ability to produce high-strength, durable parts, manufacturers can drastically cut down on production time. BMW, for example, utilized SLS to create window guide rails for the i8 Roadster. The ability to iterate and implement designs within a few days gave them a significant edge in the market.
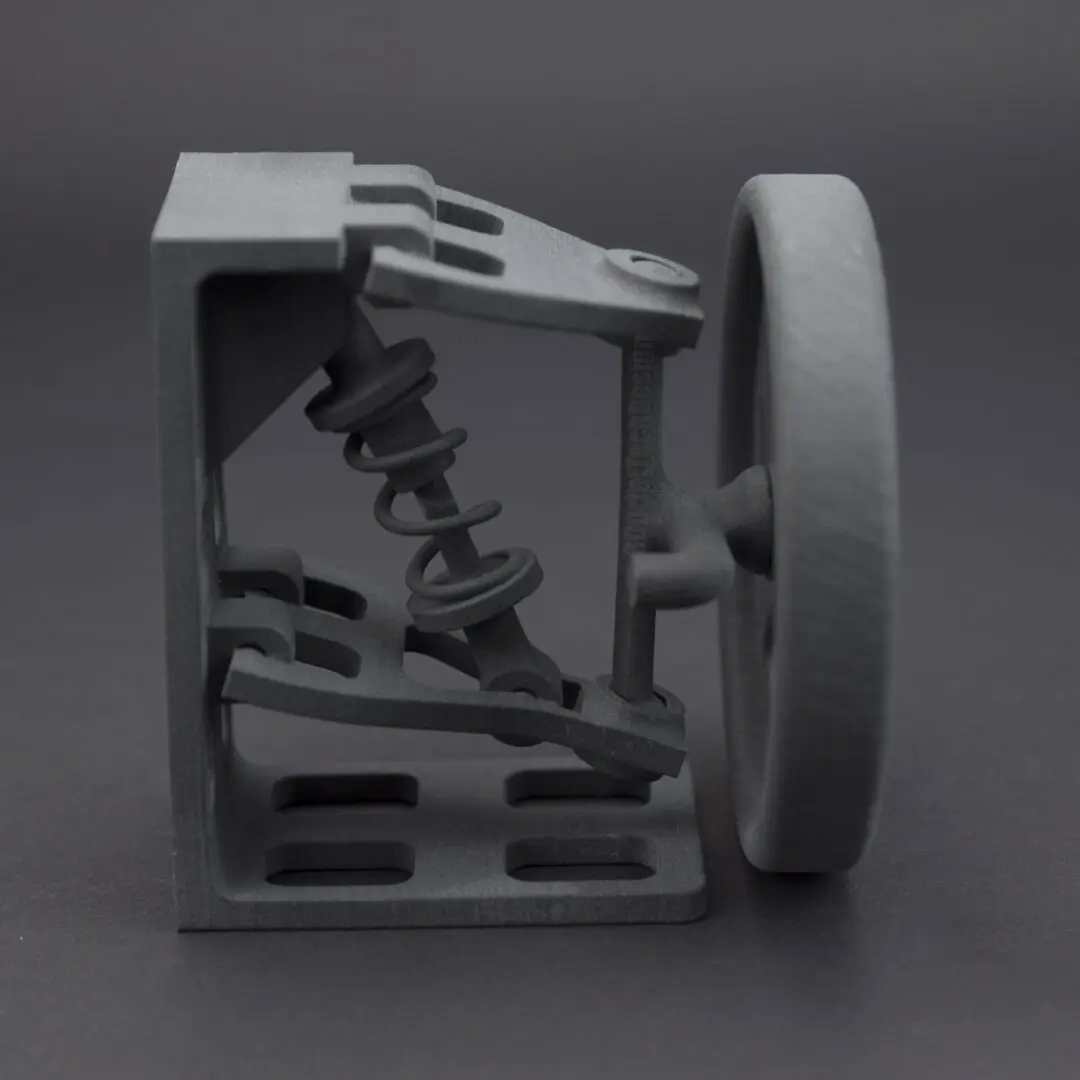

Applications in Automotive:
- Production of end-use parts like fixtures, mounts, and connectors.
- Quick prototyping of complex parts.
- Reduction in tooling costs and production time.
Medicine: Healing with Precision
The medical field can particularly benefit from SLS’s ability to customize and print on-demand. Whether it’s patient-specific models, surgical guides, or even biocompatible prosthetics, SLS allows for personalized healthcare like never before.
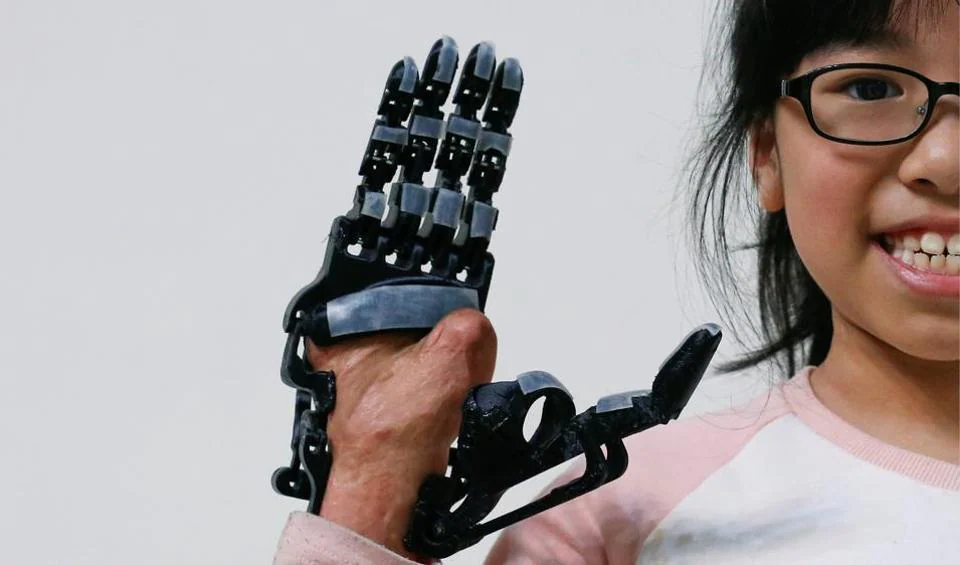

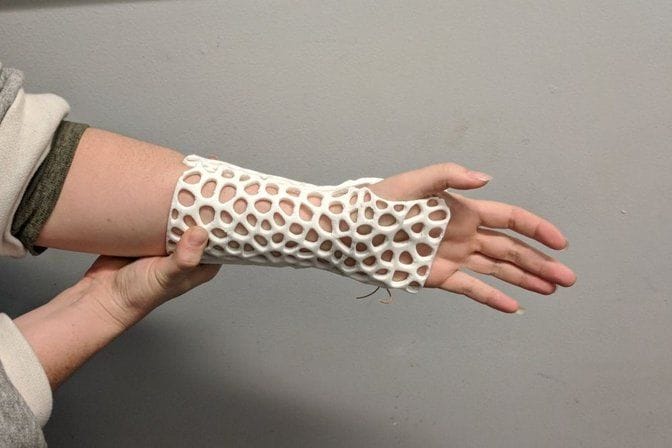
Applications in Medicine:
- Production of patient-specific prosthetics and orthotics.
- Creation of 3D models of patient anatomy for surgical planning.
- Manufacture of biocompatible implants.
Summing it Up: Diverse Industry Applications with SLS
While we delved into three major sectors, myriad other industries, including fashion, architecture, and defense, also capitalize on the capabilities of SLS 3D printing. This technology effectively bridges the gap between design flexibility, production speed, and component durability, making it a go-to solution for a range of applications.
Case Studies of SLS 3D Printing
Real-world examples often illustrate the effectiveness and potential of a technology most vividly. Let’s look at some standout uses of Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing across diverse industries.
Case Study 1: Formlabs in Healthcare

Formlabs, a 3D-printing technology developer and manufacturer, used SLS for creating a range of medical devices. They developed on-demand, patient-specific treatments like surgical guides, orthoses, and prosthetics. Thousands of patients have benefited from this personalized medical care, demonstrating SLS’s potential in healthcare.
Case Study 2: The BMW i8 Roadster
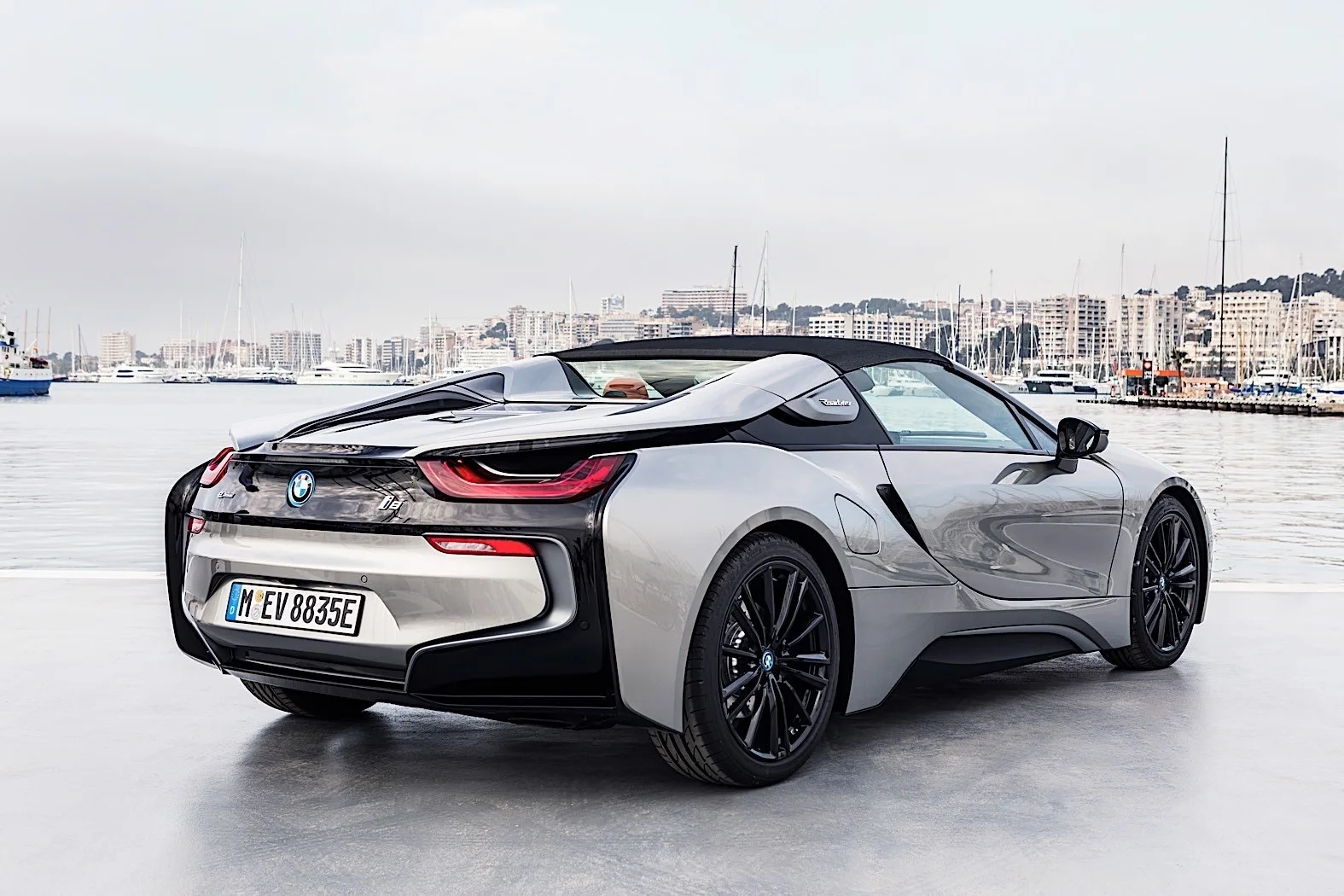

When BMW wanted to implement innovative design components quickly into their i8 Roadster, they turned to SLS. The result? Window-guide rails that were 10% lighter, installed 40% faster, and cost 25% less than traditional components. A triumph in automotive design, this case underscores the power of SLS for manufacturing efficiency.
Case Study 3: SpaceX Rocket Components
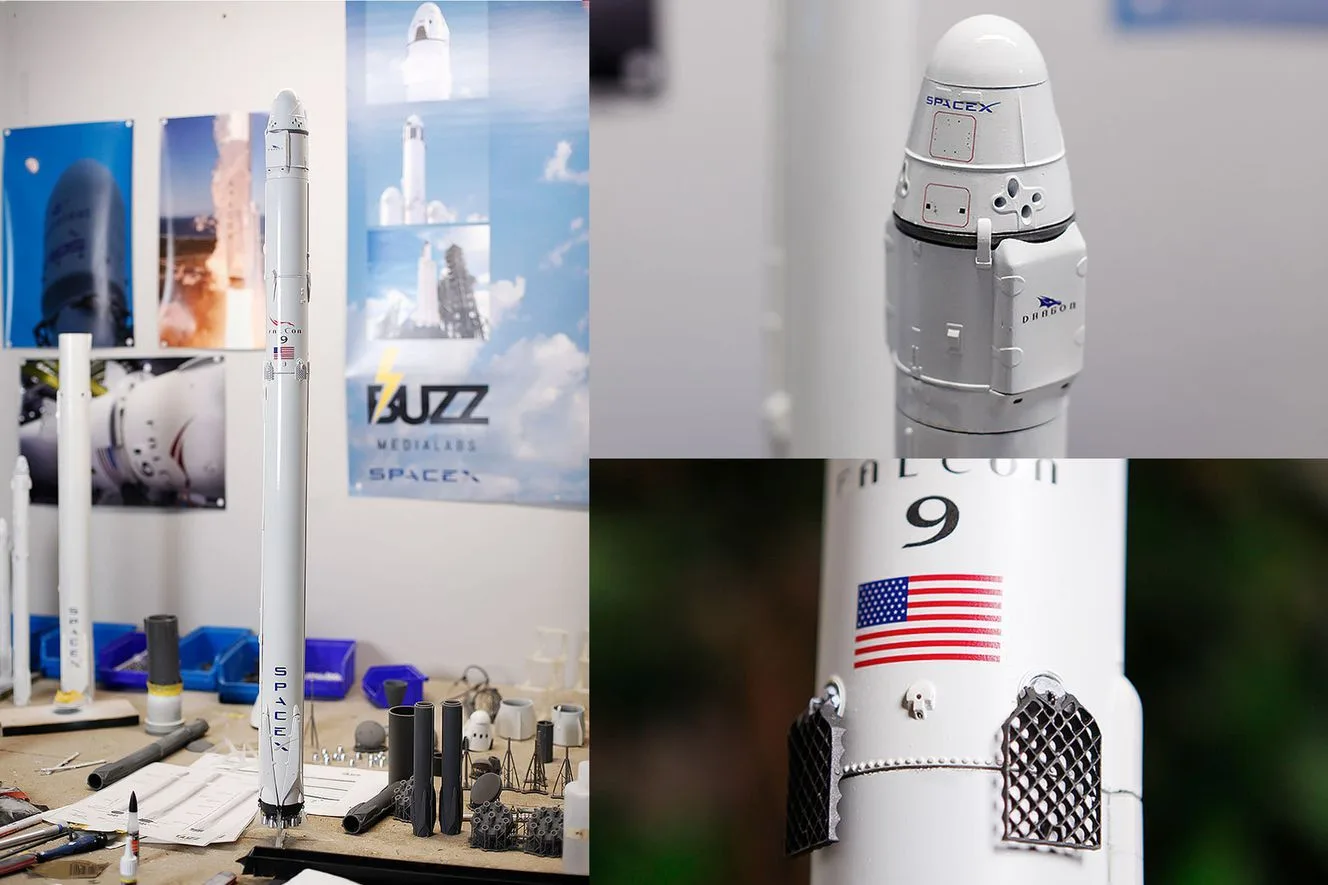

In the quest for the stars, every ounce counts. SpaceX utilized SLS 3D printing to create critical components for its Dragon and Crew Dragon spacecraft. The intricate SuperDraco engine chamber, for instance, was successfully 3D printed using SLS, showcasing the technique’s suitability for high-stress use-cases.
These case studies give a glimpse into the transformative impact SLS 3D printing can have across sectors. Gain insights from these uses to implement SLS more effectively.
As we move ahead, we’ll explore how to approach choosing SLS printing services and unlock the potential of this technology.
Choosing the Right SLS 3D Printing Services
Navigating the world of Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D Printing Services might seem daunting given the sheer number of options. However, the process can be simplified if you know the right factors to consider.
Material Options
Consider what materials a service provider can work with. If you require a specific type of nylon or a specialized material like alumide, ensure they can cater to that. A service provider with a wider material range offers more flexibility for your project.
Print Resolution
While SLS generally delivers good detail and accuracy, print resolutions can vary. High-resolution printing will result in more detailed and precise components, essential for industries such as healthcare or aerospace.
Post-Processing Capabilities
SLS 3D printed parts often require post-processing, such as bead blasting or color dyeing. If you require a specific finish, check if the service provider can offer that level of customization.
Speed and Scalability
The turnaround time for your 3D printed parts is crucial, especially in fast-paced industries. Discuss your timeline expectations with potential service providers. Also, if you anticipate needing larger production runs in the future, look for a service provider that can scale with your needs.
Price
Cost is a critical factor but remember that it’s not just about low prices. Consider value for money – a slightly more expensive service that offers high-resolution printing, an array of post-processing options, and faster turnaround times might be worth the additional investment.
Reputation and Experience
Investigate the service provider’s reputation. Look for reviews or case studies, and see if they’ve worked on projects similar to yours in the past. Experience in your sector can be extremely valuable.
The Future of SLS 3D Printing
When it comes to 3D printing, few techniques are as powerful as Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). It’s unique, it’s versatile, and it’s here to stay. As we look forward, several trends and advancements promise to make SLS even more impactful.
Miniaturization: Precision in Every Inch
One of the key trends in the world of SLS 3D printing is miniaturization. As industries like electronics and healthcare look for ever-smaller components, SLS’s ability to deliver high precision — down to the micron level — will be crucial.
Material Innovations: Choices Galore
While polymers remain the mainstay for SLS, the range of materials available is expanding. We’re looking at materials with enhanced thermal properties, superior tensile strength, and even metallized finish. As these innovations roll out, expect to see SLS expand into new territories.
Sustainability: Planet-Friendly Manufacturing
As we become more conscious of our environmental impact, sustainable manufacturing practices are also shaping the future of SLS. This includes the use of biodegradable materials, and more importantly, the efficiency in material usage that SLS provides. Less waste means a smaller footprint.
Cost-Efficiency: Expanding Accessibility
Overhead costs have long been a barrier to the widespread adoption of SLS. However, with advances in technology and increased competition, prices are coming down. As SLS becomes more cost-effective, it will make way for smaller businesses and individuals to avail of this powerful 3D printing technique.
As we navigate toward this exciting future, staying informed and understanding these trends will help us make the most of SLS 3D Printing.



