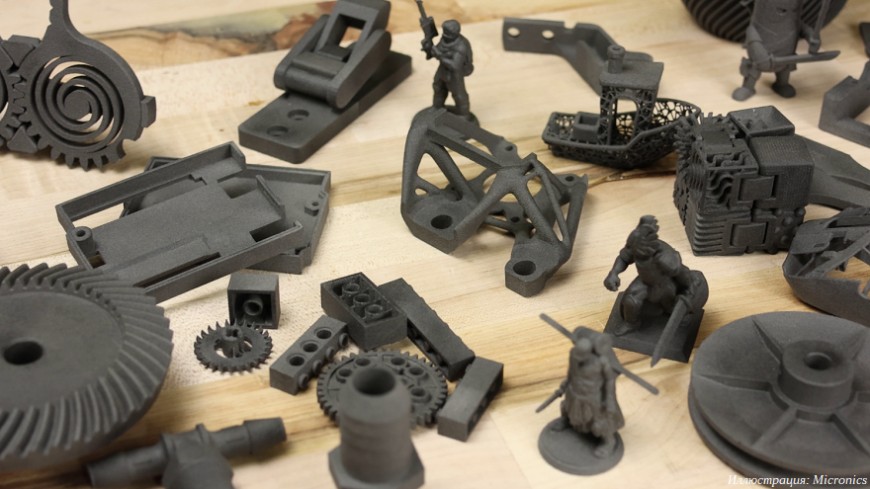
The selective laser sintering (SLS) 3D printing technology is the crown jewel of modern inventions and precision achievements in the urgent world of manufactured goods. It hints at an era where complex designs and intricate geometries are commonplace at the industry’s behest. From its birth project in the late 1980s, SLS remains an enduring protagonist in the saga of additive manufacturing, having every day redefined the limits of 3D printing innovation. But wait, what is it about this SLS that holds such a fascination and why is it so highly reputed today more than ever?

Because industries from automotive to healthcare increasingly turn to SLS for the simple reason of being able to produce strong, durable parts with intricate detailing, understanding current trends should not just come in handy-it becomes indispensable. The SLS 3D printing realm is in an uproar due to a surge of innovations spurred by new technologies, materials, and applications, reshaping the very landscape of manufacturing. This is a blog post that looks into these intriguing trends, illuminating what is most in vogue because of SLS today and what is back to come.
In the next sections, we’re going to pull aside the curtain and explore the workings of SLS technology, examine the advanced modern developments that shape the future, and explore the issues and opportunities that lay ahead. Whether you are an astute expert or an inquisitive novice in the area, read on through this fully-fledged guide that should give you the go-getting confidence to explore the enthralling world of SLS 3D printing tech. So buckle your seatbelt and join this journey into looking at what is surfacing to bring SLS 3D printing to a higher ladder and how it can transform our perspectives on manufacturing.
Explaining SLS 3D Printing: From the Step of the Process to Its Benefits.
SLS stands in a class by itself in the arena of additive manufacturing, bringing together accuracy with flexibility. This article is a pathway through the technical nitty-gritty of SLS printing, explaining why certain industries prefer this technique in extending the design and efficiency envelope.
Design for the remainder to follow. The following are the processes involved in SLS:

- CAD Model Preparation:
- Start with a digital 3D model, generally created in CAD software.
- The model is sliced into thin layers to prepare for printing.
- Material Preparation:
- Choose between various materials: nylon, polyamide, or metal.
- A layer of the selected material is dusted over the build platform.
- Layer-Sintering Process:
- A laser scans each layer according to the computer-generated model and sinters powder in the part of the cross-section.
- The platform then lowers and another layer of powder is added for the next build cycle.
- Post-Processing:
- After printing, it involves removing any loose powder.
- The additional process, like polishing or dyeing, can improve and enhance the part’s aesthetic appeal and utility.
Materials Used in SLS Printing
One of the standout features of SLS technology is its ability to work with a broad range of materials. This flexibility allows manufacturers to tailor material properties to specific applications. Common materials used in SLS include:
- Nylon (Polyamide): Known for its strength and flexibility, making it ideal for functional prototypes and end-use parts.
- TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): Offers elasticity and rubber-like properties for applications requiring flexibility.
- Aluminum and Steel: Utilized for producing lightweight yet strong metal parts.

| Material | Key Properties | Typical Applications |
| Nylon | Strong, flexible | Automotive, consumer goods |
| TPU | Elastic, durable | Footwear, medical devices |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, strong | Aerospace, automotive components |
Highlights of the Pros of the SLS 3D Printing Process
The technique of SLS offers quite a number of specific advantages that make it a favored choice by many industries:
- Design freedom: Capability to fabricate complex geometries and intricate details that cannot be feasible using traditional methods of manufacturing.
- Material efficiency: In most cases, the powder unused after the process can be recycled, and this is helpful in lessening wastage and in reducing costs.
- Strength and Durability: SLS parts are known for their serious toughness and are capable of withstanding rigorous functional testing.
- Absence of Support Structures: SLS does not require additional support structures, resulting in a saving of time and material as compared to other 3D printing techniques.
Applications Across Various Industries
The versatility of SLS technology enables its application across a wide range of industries. Here are some notable examples:
- Automotive: Used for producing functional prototypes and custom parts that meet high-performance standards.
- Healthcare: Facilitates the creation of patient-specific prosthetics and medical devices with precise dimensions.
- Consumer Goods: Allows for the production of customizable and durable products, enhancing consumer satisfaction and engagement.

Selective Laser Sintering is no more than just a manufacturing process; it opens doors to innovation. By knowing how SLS works and all its advantages, industries can use it to efficiently and creatively change production methods. As SLS technology continues to improve, its influence on manufacturing and design is expected to grow, ushering in the age of possibility governed by no bounds other than imagination.
The current trends in SLS 3D printing: Innovations forging the future

SLS-customized 3D printing continues to revolutionize the evolving manufacturing landscape with innovations in technology and materials that keep coming. As the technology continues getting adopted in the industry for unbeatable capability, it is crucial to take a peek at the latest trends in SLS landscape for staying ahead of the pack and in the great scheme of innovation. It’s this that this article seeks to delineate: the current trends defining the SLS landscape, emphasizing key innovations that will forge the future.
Material Innovation
The rapid development of new materials is one of the most exciting trends in SLS 3D printing. As industries demand higher performance and more specialized applications, material scientists are rising to the challenge.

- Polymer Advances: Recent breakthroughs have expanded the range of polymers available for SLS printing. Materials such as reinforced nylons and high-temperature polymers are gaining popularity for their enhanced strength and thermal resistance.
- Composite Materials: The integration of composite materials, such as carbon-fiber-reinforced polymers, offers improved mechanical properties and lightweight structures, ideal for aerospace and automotive applications.
- Metal SLS Printing: While traditionally dominated by polymers, SLS is making strides in metal printing. The introduction of aluminum and titanium powders is allowing for the creation of lightweight, yet strong, components crucial for high-performance sectors.
Emerging Materials in SLS Printing
| Material Type | Key Properties | Industry Applications |
| Reinforced Nylons | High strength, durability | Automotive, consumer goods |
| Carbon-Fiber Composites | Lightweight, high stiffness | Aerospace, sports equipment |
| High-Temperature Polymers | Thermal resistance, stability | Electronics, industrial applications |
| Metal Powders (Aluminum, Titanium) | Lightweight, strong | Aerospace, medical implants |
Technology Advancements
Technological advancements are accelerating SLS printing capabilities, enhancing both efficiency and precision.

- Improved Laser Systems: Modern laser systems offer increased power and precision, reducing build times while enhancing the quality of printed parts.
- Enhanced Software Solutions: Cutting-edge software is enabling more complex and precise designs. This includes AI-driven design tools that optimize geometry and material usage.
- Automation and Integration: The integration of automation technologies, such as robotic arms for powder handling and part removal, is streamlining the manufacturing process and reducing labor costs.
Cost-Efficiency Developments
As SLS technology becomes more accessible, cost-efficiency has become a focal point for both manufacturers and consumers.

- Affordable SLS Printers: The industry is witnessing a trend towards more affordable desktop SLS printers, making this technology accessible to small businesses and startups.
- Material Recycling: Advancements in material recycling are reducing waste and lowering costs. This includes the ability to recycle unused powder for future builds.
- Energy Efficiency: Newer SLS machines are designed with energy efficiency in mind, reducing operational costs and minimizing environmental impact.
The Impact on Various Industries
The convergence of these trends is having a significant impact across multiple industries, enhancing both product quality and innovation potential.
- Automotive: The automotive industry benefits from lightweight materials and cost-effective prototyping, allowing for faster design iterations and reduced time-to-market.
- Aerospace: SLS is enabling the production of complex, lightweight structures that meet stringent aerospace standards, optimizing performance and fuel efficiency.
- Healthcare: In healthcare, SLS allows for the creation of patient-specific medical devices and implants, improving treatment outcomes and patient satisfaction.
The trends in SLS 3D printing are not just about technological advancement—they represent a paradigm shift in manufacturing. As new materials and technologies emerge, they offer unprecedented opportunities for innovation across various sectors. Understanding and embracing these trends is essential for businesses aiming to lead in this evolving landscape. By staying informed and adaptable, companies can leverage SLS to not only meet current demands but also anticipate future needs, driving sustainable growth and competitive advantage.
Challenges and Opportunities in SLS 3D Printing
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing has emerged as a powerful tool across various industries, but like any technology, it comes with its own set of challenges and opportunities. Understanding these can help businesses leverage SLS effectively while navigating potential pitfalls. This article examines the key challenges facing SLS 3D printing today and the opportunities that lie ahead.
Key Challenges in SLS 3D Printing
- High Initial Investment:
- Cost of Equipment: SLS printers are generally more expensive than other 3D printing technologies, posing a barrier to entry for small businesses.
- Material Costs: The specialized powders used in SLS printing can be costly, especially for high-performance materials.
- Complexity in Post-Processing:
- Powder Removal: After printing, excess powder must be carefully removed, which can be labor-intensive and time-consuming.
- Surface Finish: Achieving a smooth surface finish often requires additional post-processing steps, such as polishing or coating.
- Material Limitations:
- Range of Materials: While the range of materials is expanding, it is still limited compared to other manufacturing methods.
- Material Properties: Ensuring consistent material properties across batches can be challenging, affecting part performance.
- Technical Expertise:
- Skill Requirements: Operating SLS equipment and optimizing designs for SLS printing require specialized skills and knowledge.
- Design Constraints: Designers must understand the unique constraints of SLS to fully exploit its advantages.
Opportunities in SLS 3D Printing
Despite these challenges, SLS offers numerous opportunities for innovation and growth:
- Customization and Personalization:
- Mass Customization: SLS enables the production of custom parts at scale, allowing companies to offer personalized products without significant cost increases.
- Tailored Solutions: Industries like healthcare can benefit from patient-specific devices, improving outcomes and satisfaction.
- Innovation in Materials:
- New Material Development: Continued research in materials science is expanding the range of usable materials, opening up new applications.
- Biodegradable and Sustainable Materials: The development of eco-friendly materials for SLS printing is gaining traction, aligning with sustainability goals.
- Advancements in Technology:
- Automation and AI: Integrating automation and AI into the SLS process can streamline production, reduce labor costs, and enhance part quality.
- Hybrid Manufacturing: Combining SLS with other manufacturing techniques can create hybrid systems that leverage the strengths of multiple technologies.
- Expansion into New Industries:
- Emerging Markets: As SLS technology becomes more accessible, its adoption is likely to grow in emerging markets, driving global industry expansion.
- New Applications: Industries such as fashion and architecture are beginning to explore SLS for innovative applications, from custom footwear to complex building components.
While SLS 3D printing faces certain challenges, these are outweighed by the immense opportunities it presents. By addressing the hurdles of cost, complexity, and expertise, businesses can unlock the full potential of SLS technology. As advancements in materials and technology continue, SLS is poised to play an increasingly vital role in manufacturing, enabling new levels of customization, efficiency, and innovation. For companies willing to invest in overcoming the initial challenges, the rewards can be significant, positioning them at the forefront of the next industrial revolution.
Future Prospects of SLS 3D Printing: What Lies Ahead?
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) 3D printing has already marked its territory as a transformative technology across various industries. As we look toward the future, the potential of SLS continues to expand, driven by technological advancements and an ever-growing range of applications. This article delves into the future prospects of SLS 3D printing, exploring the innovations and trends that could shape its evolution in the coming years.
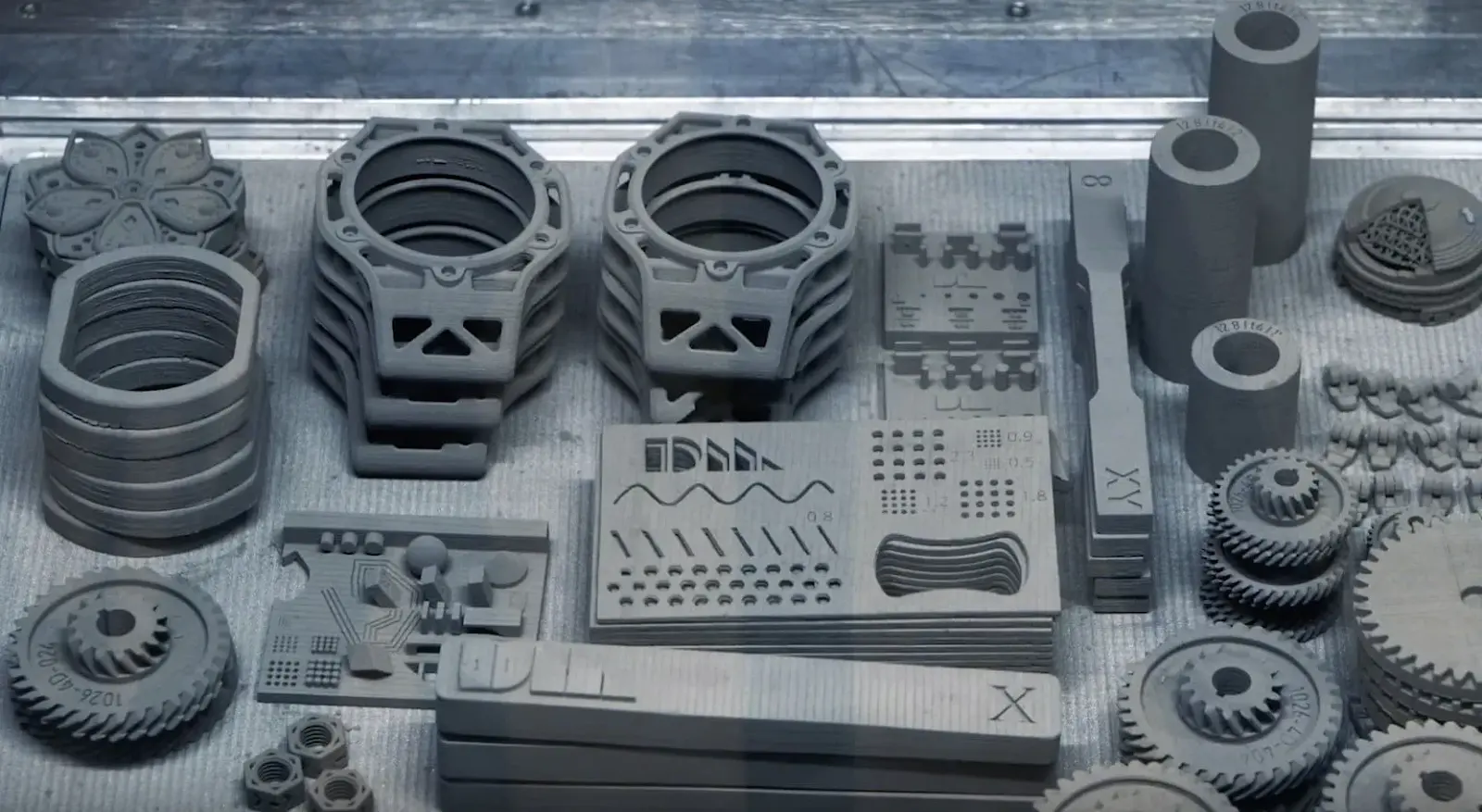
Technological Innovations on the Horizon
- Advanced Multi-Material Printing:
- Hybrid Material Capabilities: Future SLS systems might incorporate the ability to print with multiple materials in a single build, allowing for complex, multi-functional parts.
- Integration of Conductive Materials: The development of conductive powders could enable the printing of parts with integrated electronic circuits, opening up possibilities in electronics and IoT devices.
- Improved Speed and Efficiency:
- Faster Printing Speeds: Advances in laser technology and scanning systems are likely to reduce build times significantly, making SLS more competitive with traditional manufacturing methods.
- Batch Processing: Future systems could enhance batch processing capabilities, increasing throughput and efficiency for large-scale production.
- Enhanced Software and AI Integration:
- AI-Driven Design Optimization: Artificial intelligence could play a larger role in optimizing designs for SLS, improving material usage, and minimizing waste.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Adjustment: Advanced software solutions might offer real-time monitoring of the printing process, allowing for immediate adjustments and quality control.
Expanding Material Science
- Sustainable and Biodegradable Materials:
- Eco-Friendly Powders: There is a growing focus on developing sustainable materials that can be used in SLS, catering to industries that prioritize environmental responsibility.
- Recyclable Material Development: The future could see more materials that are easily recyclable, reducing waste and supporting circular economy models.
- High-Performance Alloys and Polymers:
- Next-Gen Alloys: The development of new metal alloys specifically for SLS could enhance the mechanical properties and applications of printed parts.
- Smart Materials: Materials that change properties in response to environmental stimuli (temperature, pressure) could be developed for SLS, useful in adaptive systems and smart technologies.
Broader Industry Adoption and Applications
- Healthcare and Biotechnology:
- Bioprinting and Medical Devices: SLS could advance into bioprinting applications, producing complex structures for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
- Personalized Medicine: The capacity for patient-specific solutions will likely grow, with SLS being used to create highly tailored medical devices and implants.
- Construction and Architecture:
- Large-Scale SLS Printers: The development of large-scale SLS systems could revolutionize construction, allowing for the printing of building components and even entire structures.
- Complex Architectural Designs: Architects could leverage SLS for more intricate designs, with the potential for creating more sustainable and efficient building materials.
- Consumer Products and Fashion:
- Mass Customization: As consumer demand for personalized products grows, SLS could become a standard in the production of custom goods, from footwear to fashion accessories.
- Innovative Textures and Finishes: The ability to produce unique textures and finishes could drive new trends in consumer products.
The future of SLS 3D printing is bright, with numerous technological and material advancements on the horizon. As industries continue to explore and adopt this technology, we can expect to see its impact grow even more profound. From sustainability and efficiency to customization and innovation, SLS is set to redefine manufacturing across sectors, pushing the boundaries of what is possible. By staying at the forefront of these trends, businesses can leverage SLS to not only meet current demands but also anticipate and shape the needs of the future.



