Imagine a world where complex prototypes materialize before your eyes, layer by layer, in a fraction of the time it takes traditional manufacturing methods. This isn’t science fiction—it’s the reality of top-down 3D printing, a revolutionary technology that’s reshaping the landscape of rapid prototyping and manufacturing.

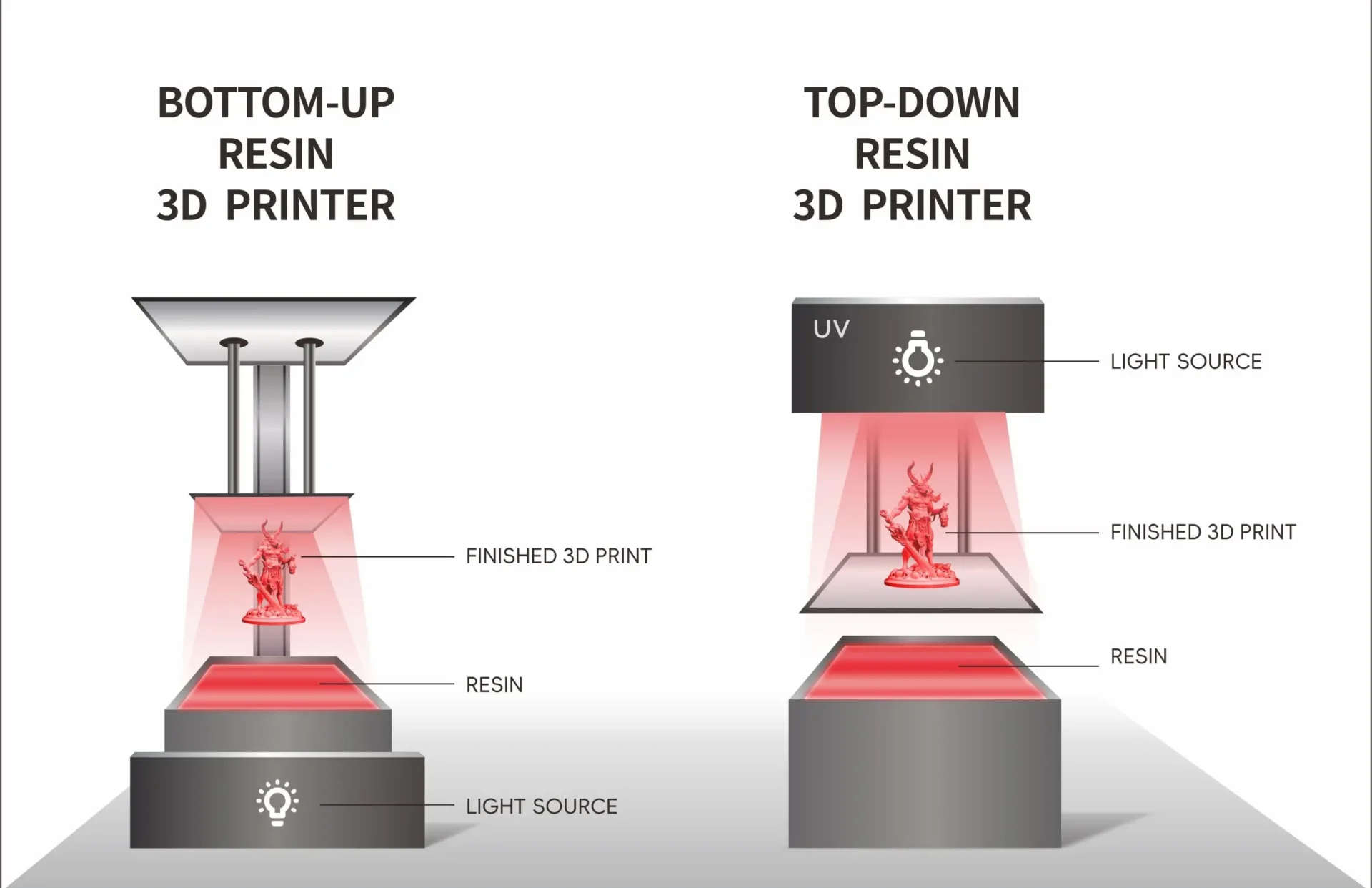
In an era where innovation is the lifeblood of industry, the ability to quickly iterate and refine designs can make or break a product’s success. Enter top-down 3D printing, a game-changing approach that’s turning the world of prototyping on its head—quite literally. Unlike its bottom-up counterparts, top-down 3D printing builds objects from the top down, offering unparalleled speed, precision, and surface finish.
But what exactly is top-down 3D printing, and why is it poised to revolutionize rapid prototyping? How does it differ from traditional 3D printing methods, and what industries stand to benefit the most from this technology? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of top-down 3D printing, exploring its inner workings, advantages, applications, and the challenges it faces. We’ll also peek into the future, examining emerging trends and developments that promise to push the boundaries of what’s possible in additive manufacturing.
Whether you’re a seasoned engineer, a curious entrepreneur, or simply a tech enthusiast, join us as we unravel the intricacies of top-down 3D printing and discover why it’s being hailed as the future of rapid prototyping. Get ready to rethink everything you thought you knew about 3D printing—the view from the top is about to change your perspective.
Understanding Top-Down 3D Printing: A Deep Dive into the Future of Additive Manufacturing
Have you ever watched a 3D printer in action and thought, “What if we could flip this process upside down?” Well, that’s exactly what top-down 3D printing does! This revolutionary approach to additive manufacturing is turning heads (and prints) in the industry. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of top-down 3D printing and explore why it’s making waves in rapid prototyping.
What’s the Buzz About Top-Down 3D Printing?
Top-down 3D printing is like the cool, rebellious cousin of traditional 3D printing. Instead of building objects from the bottom up, it creates them from the top down. Imagine a sculptor chiseling away at a block of marble, revealing the masterpiece hidden within. Now, replace the sculptor with a high-tech printer, and you’ve got the basic idea!
| Traditional 3D Printing | Top-Down 3D Printing |
| Builds from bottom up | Builds from top down |
| Layer-by-layer addition | Layer-by-layer solidification |
| Slower for some applications | Generally faster |
| Can have visible layer lines | Smoother surface finish |
The Magic Behind the Method
So, how does this upside-down wizardry work? Let’s break it down:
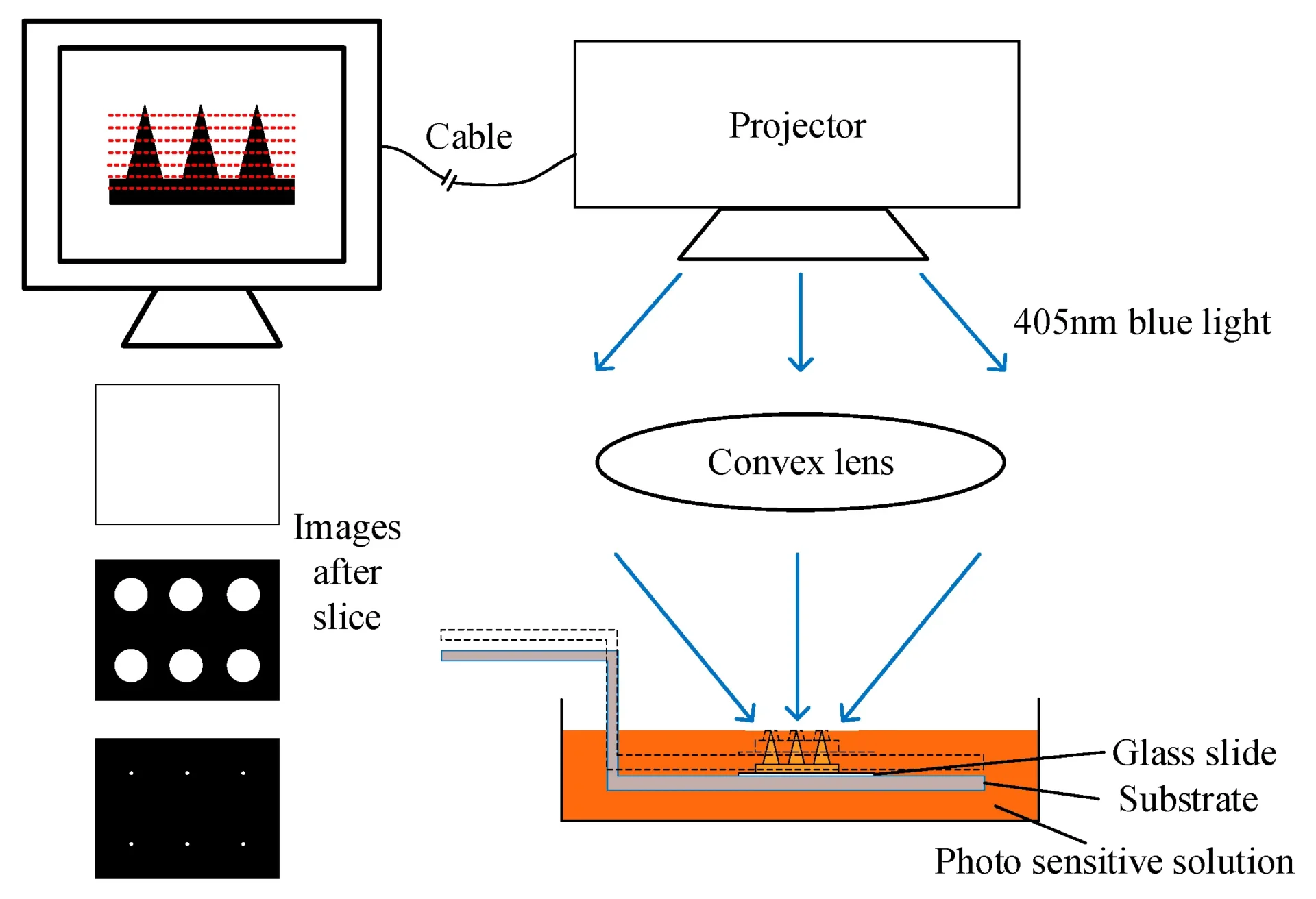
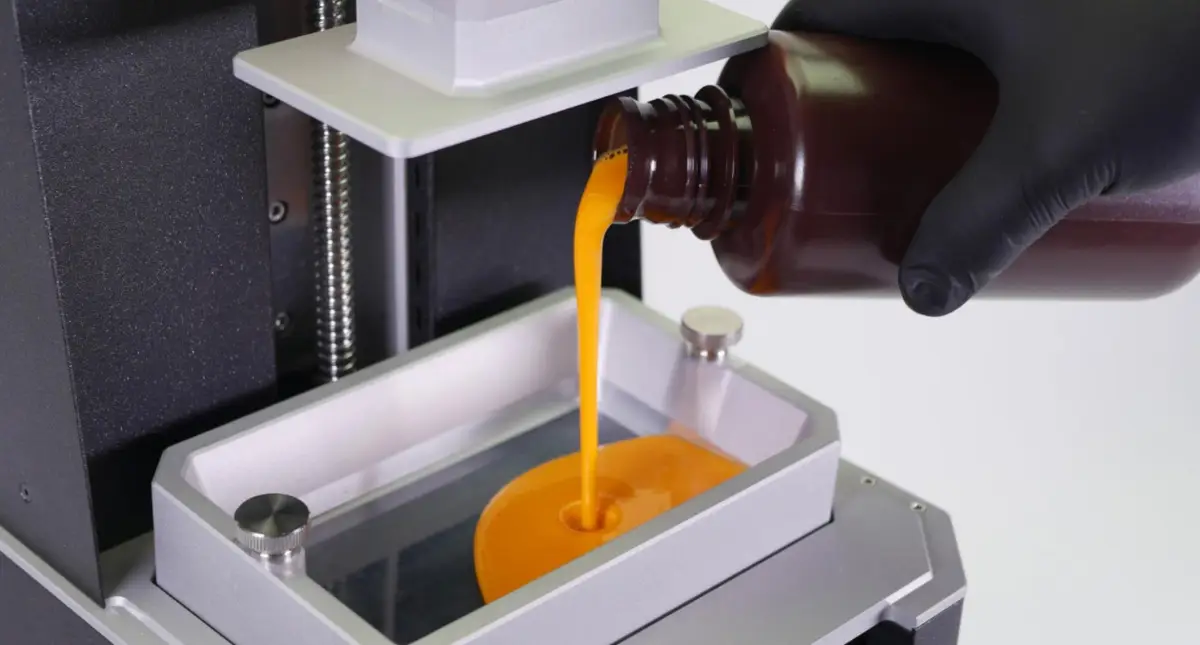
- The Vat: The process starts with a vat of liquid photopolymer resin. Think of it as a pool of potential just waiting to be shaped into something amazing.
- The Build Platform: Unlike traditional 3D printing, the build platform starts at the top of the vat and gradually moves downward.
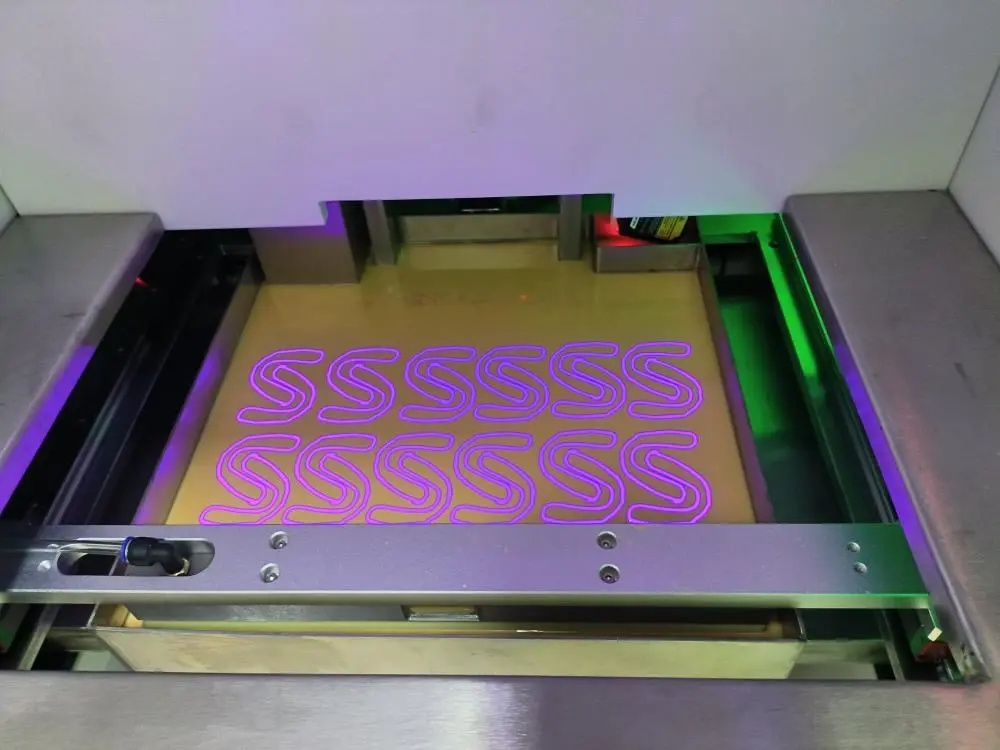
- Light Show: A high-resolution projector or laser beams light onto the surface of the resin, curing it in precise patterns.
- Layer by Layer: As each layer is cured, the platform lowers slightly, allowing fresh resin to flow over the top of the print.
- Rinse and Repeat: This process continues, layer by layer, until the entire object is formed, suspended upside down in the vat.

Types of Top-Down 3D Printing: Choose Your Flavor
Not all top-down 3D printing technologies are created equal. Here are the main players in the game:
- Stereolithography (SLA): The OG of top-down printing. Uses a laser to cure resin point by point.
- Pros: High precision, smooth surfaces
- Cons: Can be slower for large objects
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): Projects entire layers at once using a digital light projector.
- Pros: Faster than SLA, great for small, detailed objects
- Cons: Can have issues with larger prints

Why Should You Care?
Top-down 3D printing isn’t just a cool party trick. It’s revolutionizing rapid prototyping and manufacturing in several ways:
- Speed Demon: Many top-down methods are significantly faster than traditional 3D printing.
- Smooth Operator: The liquid resin approach often results in smoother surfaces and finer details.
- Material Matters: A growing range of resins allows for diverse material properties and applications.
- Size Matters (Less): Some top-down methods can produce larger objects more easily than bottom-up approaches.

The Bottom Line on Top-Down
Top-down 3D printing is more than just flipping the script on traditional additive manufacturing. It’s opening up new possibilities for rapid prototyping, custom manufacturing, and even mass production. As the technology continues to evolve, we’re likely to see even more innovative applications and improvements.

So, the next time you’re thinking about 3D printing, remember: sometimes, the best way forward is to start from the top!
Here’s a quick comparison to illustrate the point:
| Print Method | Time to Print a 10cm Model | Post-Processing Time |
| Traditional FDM | 8-10 hours | 1-2 hours |
| Top-Down SLA | 3-4 hours | 30 minutes |
| Top-Down DLP | 30 minutes – 1 hour | 15 minutes |
Surface Finish and Detail That’ll Make You Swoon
If traditional 3D prints were vinyl records, top-down prints would be high-definition digital audio. The difference in quality is that dramatic!
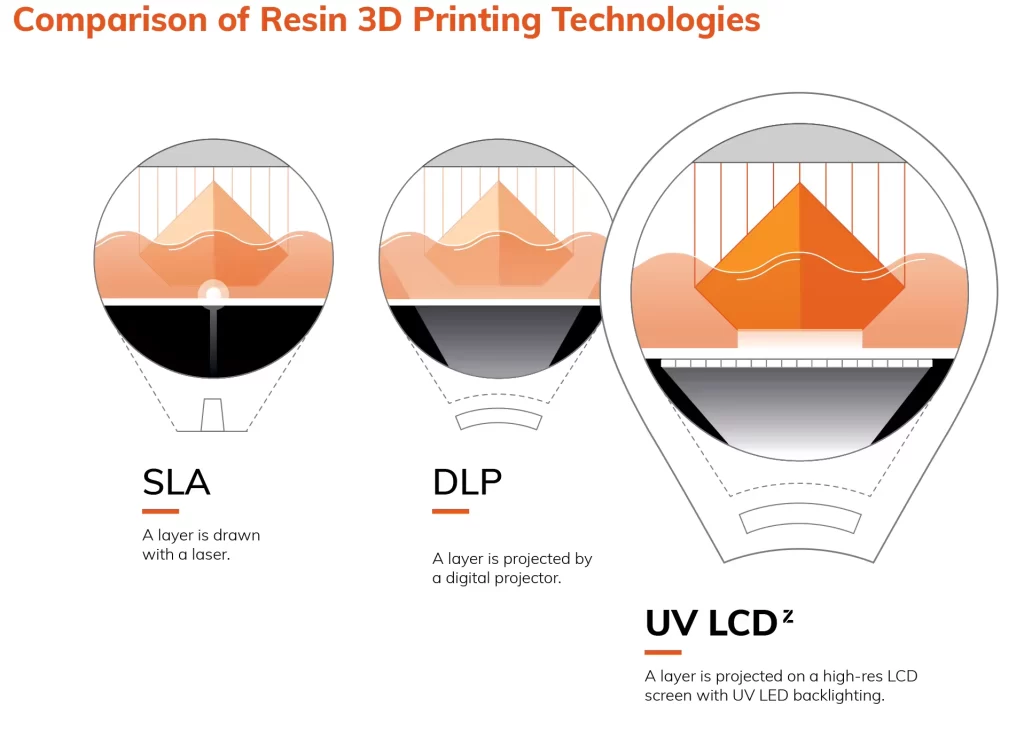
- Higher resolution: We’re talking micron-level precision here. It’s like going from 8-bit graphics to 4K Ultra HD.
- Smoother surfaces: Say goodbye to those pesky layer lines. Hello, silky smooth finishes!
- Finer details: Want to print a miniature Eiffel Tower complete with tiny rivets? Now you can!
Pro Tip: The smooth surface finish of top-down prints makes them ideal for creating molds for casting or injection molding. It’s like getting two manufacturing methods for the price of one!
Versatility That’ll Make Your Head Spin
Top-down 3D printing isn’t a one-trick pony. It’s more like a shape-shifting chameleon that can adapt to almost any situation.
- Wide range of materials: From flexible elastomers to rigid engineering plastics, the world is your oyster.
- Specialized resins: Need a heat-resistant part? A biocompatible implant? There’s probably a resin for that!
- Multi-material potential: Some advanced systems can even print with multiple materials in a single print. It’s like having a 3D color printer, but for physical properties!
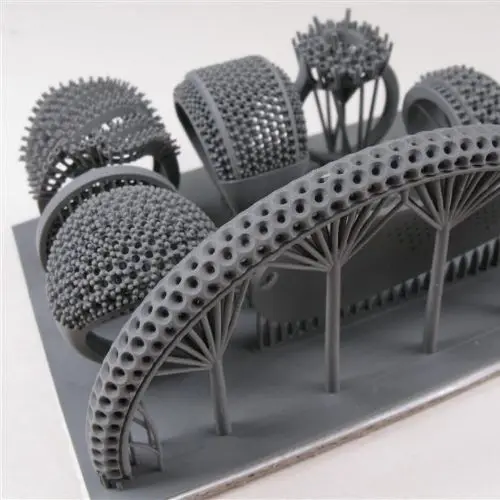
Standard Resins
- Fast Photocuring
- Optimized For 405nm DLP 3D Printers
- Low Viscosity For Fast Recoating
- Minimal Shrinkage And Warping
- Produces Parts With Smooth Surface Finish
- Available In Range Of Colors And Opacities
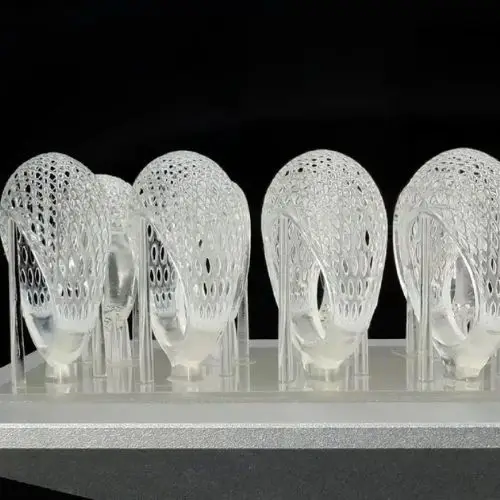
Transparent Resin
- Optimized For DLP/LCD 3D Printers
- Exceptional Optical Transparency
- High Precision And Resolution
- Resistant To Yellowing Over Time
- Low Viscosity For Reliable Printing


Tough Resins
- Exceptional Toughness & Resistant To Breakage
- Strong Elongation & High Flexibility
- High Precision, Minimal Shrinkage
and such as engineering Resins, Dental and Medical Resins, Jewelry and Casting Resins etc…
Top-Down 3D Printing: Revolutionizing Industries One Layer at a Time
Imagine a world where doctors can hold a perfect replica of a patient’s heart before surgery, where aerospace engineers can test intricate turbine designs in days instead of months, and where you can try on custom-fitted jewelry without leaving your house.This isn’t just a tech enthusiast’s daydream—it’s happening right now, and it’s changing the game across industries. Let’s dive into the exciting applications that are making waves!
Product Design and Development: From Concept to Reality at Light Speed
Gone are the days of waiting weeks for a prototype. Top-down 3D printing is turbocharging the product development cycle!
- Rapid iteration: Design in the morning, print in the afternoon, test by evening. Rinse and repeat until perfection!
- Functional prototypes: Create working models with moving parts and test real-world performance.
- Cost-effective customization: Personalize products without breaking the bank.
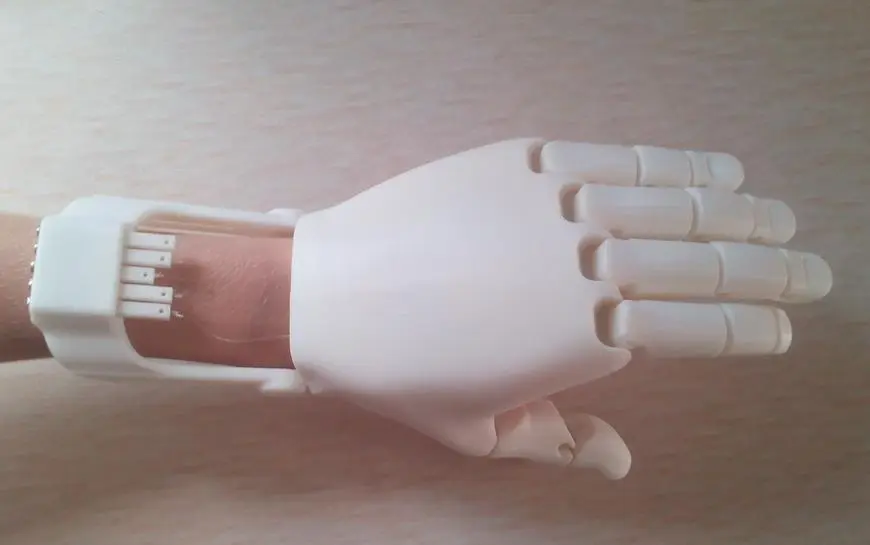
Medical Marvels: Saving Lives, One Print at a Time
Top-down 3D printing isn’t just changing industries—it’s changing lives in the medical field.
- Custom Prosthetics and Implants
- Perfectly fitted to each patient
- Faster production times
- More affordable options
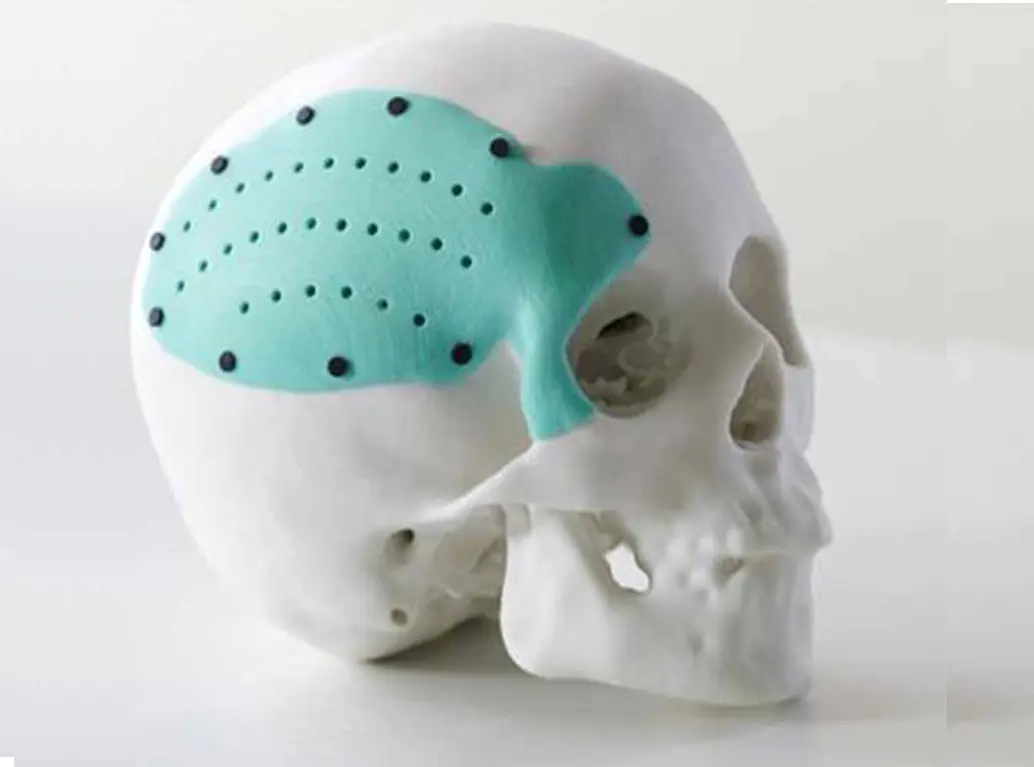
- Surgical Planning Models
- Accurate replicas of patient anatomy
- Allows surgeons to practice complex procedures
- Reduces surgery time and improves outcomes
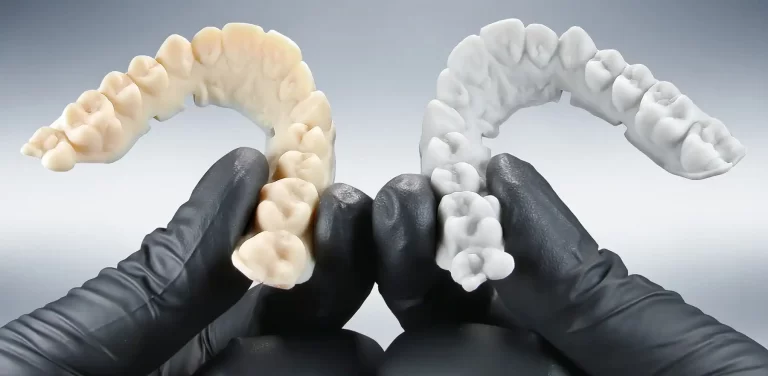
- Dental Applications
- Custom aligners and retainers
- Precise dental implants
- Faster turnaround for patients
The Cost Conundrum
Brace yourselves, because top-down 3D printing might make your wallet a bit lighter.
Initial Investment:
High-end top-down printers can cost anywhere from $3,000 to $500,000+
Specialized software and training add to the upfront costs
Material Costs:
Photopolymer resins are generally more expensive than filaments used in traditional 3D printing
Prices can range from $50 to $300 per liter, depending on the type of resin
Pro Tip: Consider the total cost of ownership, not just the initial price tag. Factor in maintenance, materials, and potential productivity gains.
New opportunities
This year, ZONGHENG3D has launched three top-down DLP 3D printers, specifically designed to address the pain points and stability issues of bottom-up DLP 3D printers. These new models aim to lower the barrier to entry for top-down DLP 3D printing technology, making it an optimal choice across various industry applications and bulk printing scenarios. Not only are these machines competitively priced, but they also offer compatibility with a wider range of resins. Coupled with customizable VAT systems, these printers can further drive down operational costs.
Peering into Tomorrow’s Tech
As material science advances, we will witness the emergence of more photosensitive resin materials suitable for Top Down DLP technology. These new materials will possess enhanced mechanical properties, heat resistance, and biocompatibility, thereby expanding the application scope of Top Down DLP 3D printers. For instance, in sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and biomedical, these high-performance materials will enable Top Down DLP 3D printers to produce more complex and durable components.
Secondly, print speed and efficiency will be crucial for the future development of Top Down DLP 3D printers. Although Top Down DLP technology has already achieved relatively fast print speeds, there is still room for improvement. By optimizing the light source system, refining the photopolymerization process, and developing new resins, the print speed of future Top Down DLP 3D printers is expected to be further enhanced. This will make Top Down DLP technology more competitive in both mass production and small-batch custom manufacturing.
Thirdly, intelligence and automation will be significant directions for the advancement of Top Down DLP 3D printers. With the continuous development of artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, future Top Down DLP 3D printers will reach a higher level of intelligence. For example, by integrating smart sensors and data processing systems, printers can achieve self-monitoring, fault diagnosis, and remote control functionalities. Moreover, automation technologies will streamline the operation of Top Down DLP 3D printers, making them more convenient and efficient, and reducing labor costs.
Finally, I believe that Top Down DLP 3D printing technology will make significant breakthroughs in the field of bioprinting. Bioprinting is a vital branch of 3D printing that involves the fabrication of cells, tissues, and organs. Leveraging its high resolution and superior print quality, Top Down DLP technology is poised to play a crucial role in bioprinting. In the future, we will see more bioprinters based on Top Down DLP technology coming to market, providing strong support for fields such as regenerative medicine, pharmaceutical development, and personalized healthcare.